Self-concept defines how individuals perceive their own identity, while self-esteem measures the value they assign to that identity. Explore the distinctions and impacts of self-concept and self-esteem in relationships in this article.
Table of Comparison
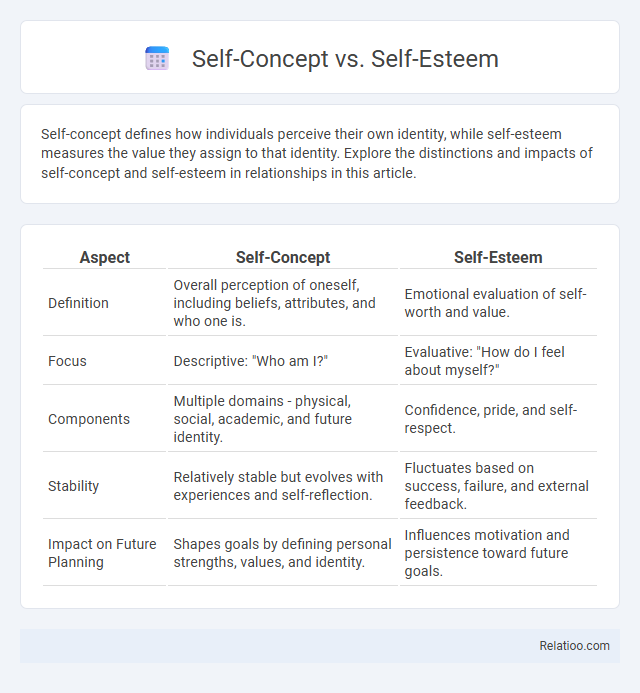
| Aspect | Self-Concept | Self-Esteem |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Overall perception of oneself, including beliefs, attributes, and who one is. | Emotional evaluation of self-worth and value. |
| Focus | Descriptive: "Who am I?" | Evaluative: "How do I feel about myself?" |
| Components | Multiple domains - physical, social, academic, and future identity. | Confidence, pride, and self-respect. |
| Stability | Relatively stable but evolves with experiences and self-reflection. | Fluctuates based on success, failure, and external feedback. |
| Impact on Future Planning | Shapes goals by defining personal strengths, values, and identity. | Influences motivation and persistence toward future goals. |
Understanding Self-Concept: Definition and Components
Self-concept refers to the comprehensive understanding you have about yourself, encompassing beliefs, attributes, and who you perceive yourself to be. It includes components such as self-image (how you see yourself), self-worth (the value you assign to yourself), and ideal self (who you aspire to become). Understanding these elements helps clarify how your self-concept shapes your behaviors, motivations, and emotional responses.
What is Self-Esteem? Key Characteristics
Self-esteem refers to an individual's overall subjective evaluation of their own worth, encompassing beliefs about oneself as well as emotional states such as triumph, despair, pride, and shame. Key characteristics of self-esteem include its dynamic nature, varying across time and contexts, its influence on motivation and behavior, and its foundation in both internal self-perceptions and external validation. Unlike self-concept, which is a cognitive understanding of oneself, and identity, which relates to one's role and social affiliations, self-esteem specifically addresses the emotional appraisal and valuation of the self.
Fundamental Differences Between Self-Concept and Self-Esteem
Self-concept refers to the comprehensive understanding and perception one holds about themselves, encompassing beliefs, attributes, and who they think they are. Self-esteem is the evaluative aspect of self-concept, reflecting the value and worth one assigns to their identity and characteristics. The fundamental difference lies in self-concept being descriptive and cognitive, while self-esteem is affective and evaluative, shaping confidence and emotional well-being.
How Self-Concept Shapes Personal Identity
Self-concept forms the foundation of personal identity by encompassing an individual's beliefs, values, and perceptions about themselves, which directly influence their sense of who they are. This cognitive schema integrates past experiences and social roles, helping to organize self-knowledge and guide behavior in various contexts. By continuously interacting with self-esteem, which reflects evaluative feelings about the self, self-concept dynamically shapes and reinforces the evolving structure of personal identity.
The Role of Self-Esteem in Emotional Well-being
Self-esteem plays a crucial role in emotional well-being by influencing how you perceive your worth and handle stress, setbacks, and interpersonal relationships. A positive self-esteem fosters resilience and confidence, reducing vulnerabilities to anxiety and depression, while low self-esteem often leads to emotional instability and negative self-judgments. Understanding the distinction between self-concept, identity, and self-esteem helps clarify how your overall self-image impacts your mental health.
Developmental Factors Influencing Self-Concept and Self-Esteem
Developmental factors such as early childhood experiences, social interactions, and family dynamics critically influence the formation of your self-concept and self-esteem. Positive reinforcement and supportive environments foster a healthy self-concept and high self-esteem, while negative experiences may lead to self-doubt and low self-worth. Identity evolves alongside these factors, integrating personal beliefs and social roles within your broader self-understanding.
Self-Concept vs Self-Esteem: Practical Examples
Your self-concept represents the comprehensive view you hold about yourself, including beliefs, attributes, and who you think you are, while self-esteem refers to the evaluative aspect, reflecting how much value or worth you assign to those self-perceptions. For example, a person with a strong self-concept as a skilled musician may have high self-esteem if they feel proud of their talent, whereas low self-esteem might occur if they doubt their abilities despite having the same self-concept. Understanding the distinction between these concepts helps you address issues like confidence or motivation by targeting either your self-beliefs or the value you place on them.
Psychological Theories on Self-Concept and Self-Esteem
Self-concept refers to the cognitive representation of oneself, encompassing beliefs, attributes, and who a person perceives themselves to be, as explained by Carl Rogers' Humanistic Theory which emphasizes self-concept as a crucial component of the self. Self-esteem, closely related yet distinct, involves the evaluative aspect of self, reflecting how much value individuals place on their self-concept, as highlighted in sociometer theory which posits self-esteem as a gauge of social acceptance or rejection. Identity integrates self-concept and self-esteem by forming an enduring sense of who one is, influenced by Erik Erikson's psychosocial development stages that underline identity formation as a central developmental task.
Improving Your Self-Concept and Boosting Self-Esteem
Improving your self-concept involves developing a clear and realistic understanding of your strengths, weaknesses, values, and beliefs, which forms the foundation of your identity. Boosting self-esteem requires nurturing positive self-values and practicing self-acceptance, enabling you to feel confident and worthy. Fostering a strong, coherent identity supports both self-concept and self-esteem by creating a consistent sense of who you are and guiding your personal growth.
The Impact of Self-Concept and Self-Esteem on Life Outcomes
Self-concept and self-esteem significantly influence your life outcomes by shaping how you perceive your abilities and worth in various situations. A positive self-concept fosters confidence and effective decision-making, while high self-esteem promotes resilience and emotional well-being. Understanding the distinction between self-concept, self-esteem, and identity allows for targeted personal development, enhancing career success, relationships, and overall mental health.
Infographic: Self-Concept vs Self-Esteem
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com