Renting offers flexibility and lower upfront costs while homeownership builds equity and long-term financial stability. Discover the detailed advantages and drawbacks of each option in this article.
Table of Comparison
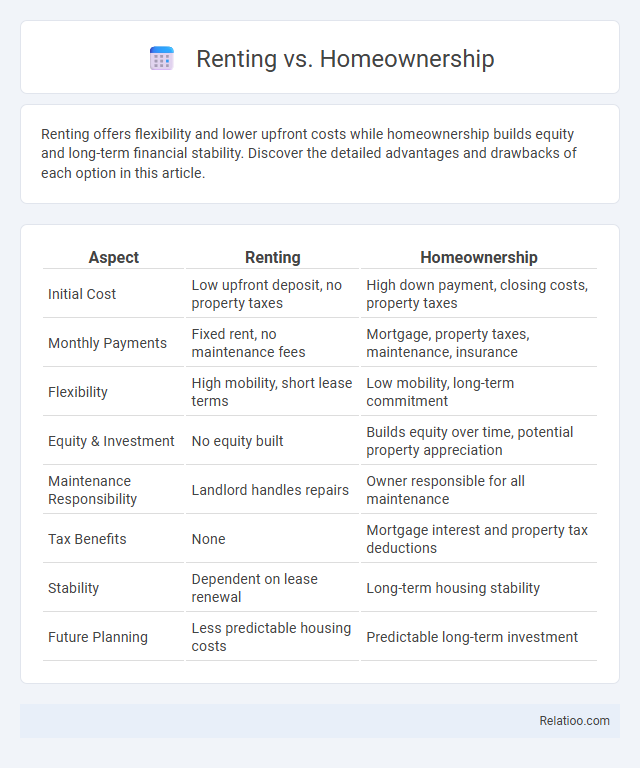
| Aspect | Renting | Homeownership |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Cost | Low upfront deposit, no property taxes | High down payment, closing costs, property taxes |
| Monthly Payments | Fixed rent, no maintenance fees | Mortgage, property taxes, maintenance, insurance |
| Flexibility | High mobility, short lease terms | Low mobility, long-term commitment |
| Equity & Investment | No equity built | Builds equity over time, potential property appreciation |
| Maintenance Responsibility | Landlord handles repairs | Owner responsible for all maintenance |
| Tax Benefits | None | Mortgage interest and property tax deductions |
| Stability | Dependent on lease renewal | Long-term housing stability |
| Future Planning | Less predictable housing costs | Predictable long-term investment |
Understanding Renting and Homeownership
Renting provides flexibility and lower upfront costs, ideal for those prioritizing mobility and minimal maintenance responsibilities. Homeownership offers long-term financial benefits through equity building and property appreciation, but requires commitment to mortgage payments, property taxes, and upkeep. Understanding these factors helps you make informed decisions aligned with your financial goals and lifestyle preferences.
Financial Considerations: Upfront and Ongoing Costs
Renting often requires lower upfront costs, such as a security deposit and first month's rent, while homeownership demands a substantial down payment, closing costs, and ongoing expenses like property taxes, insurance, and maintenance. Lifestyle changes, such as relocating for work or downsizing, can significantly impact your financial stability by altering monthly costs and savings potential. Understanding the balance between initial investment and recurring fees is essential to making informed decisions about Your housing and financial future.
Flexibility and Mobility Comparison
Renting offers superior flexibility and mobility, allowing individuals to relocate quickly without the constraints of selling property, which is essential for transient lifestyles or job-related moves. Homeownership provides stability and long-term investment benefits but significantly reduces mobility due to the complexities and costs involved in buying or selling a home. Lifestyle changes such as remote work increase the value of flexibility, making renting more attractive for those who prioritize spontaneous relocation and minimal commitment.
Building Equity vs Paying Rent
Building equity through homeownership allows you to convert your monthly payments into an investment, increasing your net worth over time. Renting may offer flexibility but results in payments that accumulate no financial return or asset value. Prioritizing lifestyle change involves balancing housing costs with long-term financial goals, where owning supports wealth building and renting supports mobility.
Maintenance Responsibilities and Costs
Renting typically limits your maintenance responsibilities to minor repairs, with landlords covering major costs, allowing you to budget more predictably. Homeownership requires you to manage and finance all maintenance and repairs, which can be costly and unpredictable, impacting your overall expenses significantly. Your decision between renting, buying, or embracing a lifestyle change should factor in how much time, effort, and money you are willing to invest in property upkeep.
Tax Benefits and Incentives
Renting offers flexibility but lacks tax benefits such as mortgage interest deductions and property tax credits available to homeowners. Homeownership provides significant tax incentives, including deductions on mortgage interest and property taxes, which can reduce your taxable income substantially. Lifestyle changes, like downsizing or relocating to areas with favorable tax programs, can also enhance your financial benefits by minimizing property-related expenses and maximizing available local incentives.
Lifestyle Preferences and Long-Term Goals
Lifestyle preferences significantly influence the choice between renting, homeownership, and making a lifestyle change, as renters often prioritize flexibility and lower maintenance responsibilities, while homeowners value stability, equity building, and customization of living space. Long-term goals such as financial security, investment growth, and community ties typically incline individuals toward homeownership, whereas those seeking career mobility or experiential living may prefer renting or alternative lifestyles like tiny homes or co-living arrangements. Evaluating personal priorities alongside market conditions enables informed decisions that align living arrangements with future aspirations and quality of life.
Market Trends and Regional Variations
Renting remains attractive in urban areas with high housing prices and transient populations, while homeownership is favored in suburban and rural regions due to affordability and long-term investment benefits. Market trends show rising rent prices outpacing wage growth in major cities, pushing many toward homeownership or lifestyle changes like relocating to more affordable markets. Regional variations significantly impact these decisions, with tech hubs experiencing intense competition and coastal areas facing supply constraints that drive prices up, prompting shifts toward remote work and flexible living arrangements.
Risk Factors and Economic Uncertainty
Renting offers flexibility with lower upfront costs but exposes tenants to rent hikes and limited asset building, increasing vulnerability during economic downturns. Homeownership involves significant financial commitment and risks such as fluctuating property values and maintenance expenses, yet can provide long-term equity growth and stability. Lifestyle changes, including downsizing or relocating, carry risks of market timing losses and adjustment costs but may enhance financial resilience by aligning housing choices with economic conditions and personal priorities.
Choosing the Right Option for Your Situation
Evaluating renting, homeownership, and lifestyle changes requires analyzing financial stability, long-term goals, and personal preferences to determine the best housing solution. Homeownership offers equity buildup and tax benefits but demands upfront costs and maintenance responsibilities, while renting provides flexibility and lower initial expenses. Lifestyle changes, such as relocating for work or downsizing, influence housing decisions by shaping priorities around convenience, affordability, and future plans.
Infographic: Renting vs Homeownership
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com