Urban relationships often face challenges like fast-paced lifestyles and limited social support, while rural relationships benefit from close-knit communities and stronger family ties. Discover how these dynamics shape emotional connections and communication styles in this article.
Table of Comparison
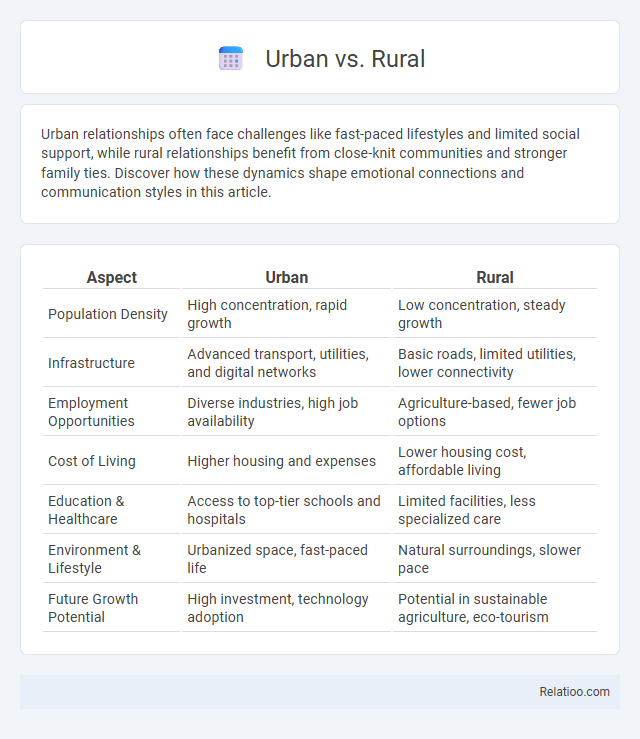
| Aspect | Urban | Rural |
|---|---|---|
| Population Density | High concentration, rapid growth | Low concentration, steady growth |
| Infrastructure | Advanced transport, utilities, and digital networks | Basic roads, limited utilities, lower connectivity |
| Employment Opportunities | Diverse industries, high job availability | Agriculture-based, fewer job options |
| Cost of Living | Higher housing and expenses | Lower housing cost, affordable living |
| Education & Healthcare | Access to top-tier schools and hospitals | Limited facilities, less specialized care |
| Environment & Lifestyle | Urbanized space, fast-paced life | Natural surroundings, slower pace |
| Future Growth Potential | High investment, technology adoption | Potential in sustainable agriculture, eco-tourism |
Understanding Urban and Rural Environments
Urban environments feature dense populations, extensive infrastructure, and diverse economic opportunities, shaping a fast-paced lifestyle. Rural areas offer open spaces, agricultural activities, and a close-knit community atmosphere, promoting a slower, nature-oriented way of living. Understanding these differences helps Your decision-making when considering relocation, ensuring alignment with lifestyle preferences and long-term goals.
Key Differences Between Urban and Rural Areas
Urban areas feature dense populations, advanced infrastructure, and diverse economic opportunities, while rural regions offer lower population density, expansive natural landscapes, and more agricultural-based livelihoods. Access to healthcare, education, and entertainment tends to be more comprehensive in cities, whereas rural areas provide a quieter environment with closer community ties. When considering relocation, evaluating your priorities for lifestyle, job availability, and social amenities helps determine the best fit between urban and rural living.
Population Density and Demographics
Urban areas exhibit high population density with diverse demographics characterized by younger, multicultural residents and varied socioeconomic backgrounds. Rural regions feature low population density, often dominated by older populations and homogeneous cultural groups, with economies centered on agriculture or resource-based industries. Relocation trends show increasing movement from rural to urban zones driven by job opportunities, education access, and lifestyle amenities, significantly impacting demographic compositions and population distributions.
Infrastructure and Accessibility
Urban areas feature advanced infrastructure with extensive public transportation, high-speed internet, and numerous healthcare facilities, ensuring superior accessibility for residents. Rural regions often have limited infrastructure, leading to challenges in transportation, internet connectivity, and access to essential services. When considering relocation, you should evaluate the infrastructure and accessibility differences to match your lifestyle needs and ensure convenient access to resources.
Employment Opportunities and Economic Activities
Urban areas offer diverse employment opportunities with thriving sectors such as technology, finance, and service industries, boosting economic activities and career growth. Rural regions predominantly rely on agriculture, small-scale manufacturing, and local businesses, which may limit job variety but support community-based economies. Your decision to relocate can significantly impact access to job markets, income potential, and professional development depending on whether you choose urban vibrancy or rural stability.
Lifestyle and Quality of Life
Urban living offers diverse cultural experiences, extensive job opportunities, and advanced healthcare, enhancing overall quality of life despite higher living costs and noise pollution. Rural areas provide a quieter lifestyle with closer access to nature, lower housing costs, and stronger community ties, though they may lack some conveniences and specialized services. Relocating often aims to balance lifestyle preferences and quality of life factors such as employment prospects, education quality, and environmental conditions.
Education and Healthcare Services
Urban areas generally offer more accessible and advanced education and healthcare services, including specialized schools, universities, hospitals, and clinics with cutting-edge technology. Rural regions often face challenges such as limited educational resources, fewer healthcare facilities, and longer travel distances to access essential services. Relocation decisions frequently consider the quality and availability of schools and medical care, as families prioritize environments that support academic success and comprehensive health services.
Social Dynamics and Community Engagement
Urban areas typically offer diverse social dynamics with numerous opportunities for community engagement through cultural events, networking, and public spaces, fostering vibrant interactions. Rural communities often emphasize close-knit relationships and strong social cohesion, where Your involvement can directly impact local traditions and collective well-being. Relocation challenges include adapting to new social norms and community structures, requiring proactive engagement to build meaningful connections and integrate smoothly.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Urban areas typically have higher carbon emissions due to dense population and transportation demands, while rural regions contribute less but face challenges like deforestation and agricultural runoff. Relocation to urban centers can increase environmental strain through energy consumption and waste generation, but sustainable city planning and green infrastructure can mitigate these effects. Balancing urban development with rural conservation is essential for minimizing environmental impact and promoting long-term sustainability.
Future Trends and Urbanization Challenges
Rapid urbanization is driving significant demographic shifts, with future trends indicating increased migration from rural to urban areas due to better employment, education, and healthcare opportunities. Emerging smart city technologies and sustainable urban planning are critical to addressing challenges like overcrowding, infrastructure strain, and environmental degradation. Effective relocation strategies and policies must prioritize equitable resource distribution and resilient infrastructure to balance growth and quality of life between urban and rural regions.
Infographic: Urban vs Rural
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com