Public healthcare provides universal access to essential medical services funded by the government, ensuring equitable treatment for all citizens. Private healthcare offers faster service and advanced treatments through patient-funded or insurance-based models; learn more about their differences in this article.
Table of Comparison
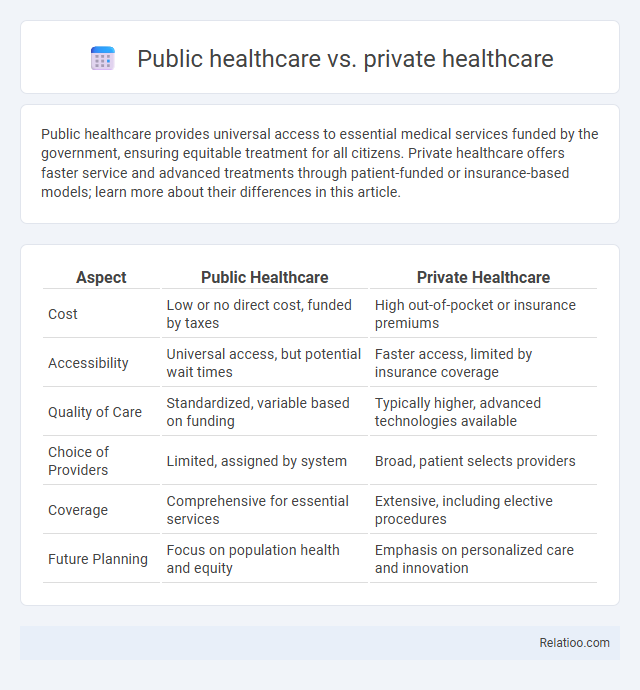
| Aspect | Public Healthcare | Private Healthcare |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | Low or no direct cost, funded by taxes | High out-of-pocket or insurance premiums |
| Accessibility | Universal access, but potential wait times | Faster access, limited by insurance coverage |
| Quality of Care | Standardized, variable based on funding | Typically higher, advanced technologies available |
| Choice of Providers | Limited, assigned by system | Broad, patient selects providers |
| Coverage | Comprehensive for essential services | Extensive, including elective procedures |
| Future Planning | Focus on population health and equity | Emphasis on personalized care and innovation |
Introduction to Public and Private Healthcare
Public healthcare systems are government-funded and provide medical services to all citizens, ensuring equitable access regardless of income. Private healthcare relies on individual payments or insurance, offering faster service and more personalized care but often at higher costs. Understanding these differences helps you navigate options during a health crisis by balancing affordability, quality, and urgency of care.
Funding Models: Public vs. Private Systems
Public healthcare systems primarily rely on government funding through taxation, ensuring broad access and reducing individual costs, while private healthcare depends on insurance premiums and out-of-pocket payments, often leading to varied affordability and service quality. Your choice between these models influences overall accessibility and financial burden during health crises, where public systems may offer more coordinated emergency response and private systems may provide faster but costly care. Understanding these funding distinctions helps navigate healthcare options and prepare effectively for potential health emergencies.
Accessibility and Coverage Comparison
Public healthcare systems offer widespread accessibility and generally cover essential medical services for entire populations, funded primarily through taxation. Private healthcare provides faster access and a broader range of specialized treatments but often entails higher costs and limited coverage based on individual insurance plans. During health crises, public healthcare's universal coverage ensures more equitable resource distribution, while private healthcare capacity may be constrained by insurance limitations and service affordability.
Quality of Care in Public and Private Facilities
Public healthcare facilities provide essential services with a focus on accessibility and affordability, often facing challenges such as resource limitations and longer wait times that can affect the quality of care. Private healthcare centers typically offer more personalized and immediate attention, advanced technology, and specialized treatments, resulting in higher patient satisfaction and better clinical outcomes. Your choice between public and private healthcare greatly influences the level of care quality, availability of services, and overall patient experience during a health crisis.
Wait Times and Service Efficiency
Public healthcare systems often experience longer wait times due to high demand and limited resources, impacting timely access to treatments. Private healthcare offers faster service and shorter wait times, improving efficiency but usually at a higher cost to patients. Your choice between public and private healthcare should balance the urgency of care needed against affordability and the importance of quick service delivery during a health crisis.
Cost to Patients: Out-of-Pocket Expenses
Public healthcare systems often minimize out-of-pocket expenses by subsidizing treatment costs through government funding, making it more affordable for patients. Private healthcare typically involves higher out-of-pocket expenses due to premium fees, specialized services, and limited insurance coverage. Your financial burden during a health crisis can significantly increase in private settings, whereas public healthcare aims to provide more accessible, cost-effective care options.
Innovation and Technology Adoption
Public healthcare systems prioritize widespread access and cost-effective solutions, often integrating government-funded innovation programs for technologies like telemedicine and electronic health records. Private healthcare providers focus on cutting-edge technology adoption such as AI diagnostics and personalized medicine to deliver faster, customized patient care. During health crises, rapid deployment of digital health tools, real-time data analytics, and AI-driven predictive models enhance response capabilities across both public and private sectors.
Equity and Healthcare Disparities
Public healthcare systems aim to provide equitable access to essential medical services, reducing healthcare disparities by prioritizing underserved populations and emphasizing universal coverage. Private healthcare often offers advanced treatments and shorter wait times but can exacerbate inequities due to high costs and limited accessibility for low-income groups. Health crises expose and intensify existing disparities by disproportionately affecting vulnerable communities, highlighting the urgent need for integrated strategies that ensure equitable resource allocation and care accessibility.
Patient Satisfaction and Experience
Public healthcare systems often provide accessible and affordable services, but patient satisfaction can be hindered by longer wait times and limited resources during health crises. Private healthcare typically offers faster services and personalized care, leading to higher patient satisfaction and better experience, though it may be cost-prohibitive for many. During health crises, both systems face challenges, but private healthcare's resource availability often results in more timely and effective patient outcomes.
Future Trends in Public and Private Healthcare
Future trends in public and private healthcare emphasize the integration of advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence, telemedicine, and personalized medicine to improve patient outcomes and accessibility. Public healthcare systems are increasingly adopting data-driven approaches to enhance preventive care and manage population health during health crises, while private healthcare focuses on innovative treatments and patient-centric services for competitive advantage. The convergence of digital health platforms and collaborative partnerships between public and private sectors is expected to transform healthcare delivery amidst growing global health challenges.
Infographic: Public healthcare vs Private healthcare
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com