Saving builds a secure financial foundation by preserving capital in low-risk accounts, while investing seeks higher returns through market exposure, balancing potential growth against risk. Discover more about effectively managing your money through saving and investing strategies in this article.
Table of Comparison
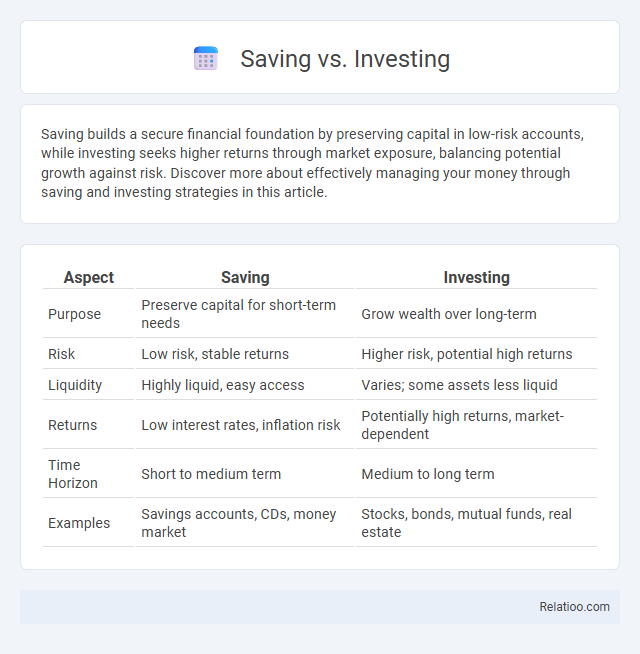
| Aspect | Saving | Investing |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Preserve capital for short-term needs | Grow wealth over long-term |
| Risk | Low risk, stable returns | Higher risk, potential high returns |
| Liquidity | Highly liquid, easy access | Varies; some assets less liquid |
| Returns | Low interest rates, inflation risk | Potentially high returns, market-dependent |
| Time Horizon | Short to medium term | Medium to long term |
| Examples | Savings accounts, CDs, money market | Stocks, bonds, mutual funds, real estate |
Introduction to Saving and Investing
Saving involves setting aside a portion of income in secure, low-risk accounts to build an emergency fund or achieve short-term goals, emphasizing capital preservation and liquidity. Investing, in contrast, allocates money into assets such as stocks, bonds, or real estate, aiming for higher returns over the long term while accepting greater risk and market volatility. Effective financial management integrates saving and investing strategies to optimize wealth growth, balance risk, and ensure financial stability.
Key Differences Between Saving and Investing
Saving involves setting aside a portion of Your income in low-risk, easily accessible accounts to preserve capital and maintain liquidity, while investing allocates funds into assets like stocks, bonds, or real estate with the goal of generating higher returns over time but with increased risk. Financial management encompasses both saving and investing strategies, emphasizing budgeting, risk assessment, and portfolio diversification to optimize Your overall financial health. Understanding the key differences between saving and investing helps You balance short-term security with long-term wealth growth.
Benefits of Saving
Saving builds a financial safety net that provides liquidity for emergencies and short-term goals, ensuring peace of mind and reducing reliance on credit. It fosters disciplined money habits that pave the way for long-term wealth creation through investing. Effective saving strategies complement financial management by improving cash flow control and supporting budget stability.
Advantages of Investing
Investing offers the advantage of potential wealth growth through compound interest, outperforming traditional saving accounts with higher returns over time. Your investments diversify risk across various asset classes, providing financial security and inflation protection. Effective financial management ensures your investments align with goals, optimizing long-term financial success and stability.
Risks Involved in Saving and Investing
Saving typically involves low-risk options like savings accounts or certificates of deposit, which offer stability but lower returns; the risk primarily lies in inflation eroding purchasing power over time. Investing carries higher risks, including market volatility, potential loss of principal, and economic downturns, yet it offers the opportunity for greater long-term growth through assets like stocks, bonds, or real estate. Effective financial management balances saving and investing strategies to manage risk exposure while optimizing wealth accumulation and liquidity needs.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Goals
Choosing the right approach between saving, investing, and financial management depends on your specific financial goals, risk tolerance, and time horizon. Saving offers low-risk, liquid options ideal for short-term needs and emergency funds, while investing provides growth potential suited for long-term wealth accumulation through stocks, bonds, or mutual funds. Effective financial management integrates both strategies by budgeting, monitoring cash flow, and aligning assets with objectives to maximize returns and ensure financial stability.
Time Horizon: Short-term vs Long-term
Saving typically suits a short-term time horizon, providing liquidity and low-risk growth for immediate or upcoming expenses. Investing targets long-term goals, leveraging market growth and compounding returns to build substantial wealth over years or decades. Your financial management strategy should balance these approaches, aligning with your time horizon to optimize risk tolerance and achieve both short-term security and long-term prosperity.
Tools and Accounts for Saving and Investing
Savings accounts, certificates of deposit (CDs), and money market accounts are essential tools for securely storing your emergency funds while earning modest interest. Investing tools include brokerage accounts, individual retirement accounts (IRAs), and robo-advisors, which offer opportunities for portfolio growth through stocks, bonds, and mutual funds. Effective financial management involves selecting the right mix of saving and investing accounts tailored to your risk tolerance and long-term goals.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Many individuals confuse saving with investing, failing to recognize that saving typically offers lower returns and prioritizes liquidity, while investing aims for growth but comes with higher risks. A common mistake is neglecting a balanced financial management plan that integrates both saving for emergencies and investing for long-term goals, which can jeopardize your financial stability. Avoid errors such as not diversifying investments, withdrawing savings prematurely, or overlooking budgeting, as these can hinder wealth accumulation and financial security.
Building a Balanced Financial Strategy
Building a balanced financial strategy involves integrating saving, investing, and financial management to optimize wealth growth and risk control. Saving provides liquidity and security for short-term needs, while investing targets higher returns through diversified assets such as stocks, bonds, and mutual funds. Effective financial management includes budgeting, debt control, and periodic portfolio review to align financial goals with market conditions and personal risk tolerance.
Infographic: Saving vs Investing
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com