Personal identity shapes individual beliefs and values, while social identity defines group affiliations and societal roles. Explore how these identities interact and influence behavior in this article.
Table of Comparison
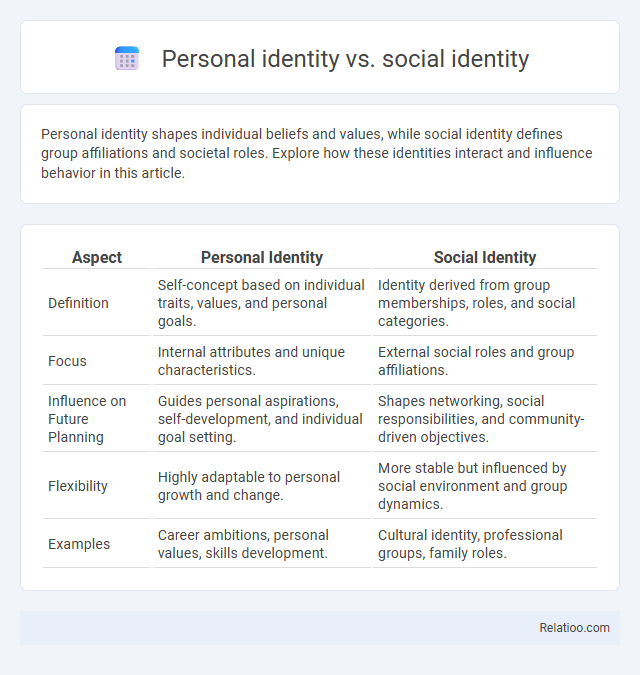
| Aspect | Personal Identity | Social Identity |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Self-concept based on individual traits, values, and personal goals. | Identity derived from group memberships, roles, and social categories. |
| Focus | Internal attributes and unique characteristics. | External social roles and group affiliations. |
| Influence on Future Planning | Guides personal aspirations, self-development, and individual goal setting. | Shapes networking, social responsibilities, and community-driven objectives. |
| Flexibility | Highly adaptable to personal growth and change. | More stable but influenced by social environment and group dynamics. |
| Examples | Career ambitions, personal values, skills development. | Cultural identity, professional groups, family roles. |
Understanding Personal Identity
Understanding personal identity involves recognizing the unique characteristics, values, and experiences that define who you are as an individual, distinct from social identity, which relates to group memberships and societal roles. Personal identity shapes your self-perception and influences decisions independent of external social labels. Your sense of identity is a complex interplay between personal introspection and the recognition of social contexts, but personal identity remains the core foundation of your self-awareness.
Defining Social Identity
Social identity refers to the aspects of an individual's self-concept derived from perceived membership in social groups, such as nationality, ethnicity, religion, or profession, shaping behavior through group norms and shared values. It differentiates from personal identity, which centers on unique traits and personal experiences that define an individual's sense of self independent of group affiliations. Understanding social identity is crucial for analyzing how group dynamics influence individual behavior, social interaction, and collective consciousness within societies.
Key Differences Between Personal and Social Identity
Personal identity centers on an individual's unique traits, beliefs, and experiences that define their self-concept, whereas social identity derives from group memberships and social categories such as nationality, ethnicity, or profession that influence one's sense of belonging. Key differences include the internal, subjective nature of personal identity versus the external, collective aspects of social identity, and the emphasis on individuality contrasted with social roles and group affiliations. Personal identity remains consistent across contexts, while social identity may shift depending on the social environment and interactions.
Influences on Personal Identity Development
Personal identity development is profoundly influenced by experiences, memories, and personal beliefs that shape individual self-awareness. Social identity, formed through group affiliations such as culture, ethnicity, and social roles, provides a collective framework impacting one's sense of belonging and self-concept. The dynamic interaction between personal identity and social identity continuously molds overall identity, with societal norms, peer interactions, and cultural expectations playing critical roles in personal growth.
The Role of Groups in Shaping Social Identity
Groups play a crucial role in shaping social identity by providing individuals with a sense of belonging and shared values, norms, and behaviors. Social identity emerges from membership in various groups such as family, ethnicity, nationality, or professional organizations, influencing self-concept and social interactions. This collective identity contrasts with personal identity, which is centered on individual traits and personal experiences.
Interplay Between Personal and Social Identity
Personal identity encompasses an individual's unique traits, beliefs, and experiences, while social identity derives from group memberships such as nationality, ethnicity, or profession. The interplay between personal and social identity shapes self-concept, influencing behavior and perception within varied social contexts. Understanding this dynamic interaction highlights how personal uniqueness coexists with collective belonging, impacting psychological well-being and social integration.
Identity Conflicts: When Personal and Social Identities Clash
Identity conflicts arise when personal identity--an individual's unique beliefs, values, and experiences--clashes with social identity, which is shaped by group affiliations such as ethnicity, gender, or occupation. This tension can lead to internal struggles, reduced self-esteem, and difficulties in social integration, particularly in multicultural or diverse environments. Resolving these conflicts often requires balancing authenticity with social acceptance, highlighting the complex interaction between individual identity and collective norms.
The Impact of Culture on Identity Formation
Culture profoundly shapes personal identity by influencing individual beliefs, values, and self-perception through shared traditions and social norms. Social identity emerges from group memberships, such as ethnicity, nationality, or religion, reinforcing a collective sense of belonging and cultural heritage. The dynamic interplay between personal and social identities within cultural contexts determines how individuals navigate their roles and create a coherent sense of self.
Personal and Social Identity in the Digital Age
Personal identity encompasses an individual's self-perception, values, and unique characteristics, while social identity refers to the groups and communities to which a person belongs, influencing their behavior and social roles. In the digital age, online platforms amplify the interplay between personal and social identities by allowing users to curate their self-presentation while engaging with diverse social networks that shape collective identity. Digital interactions create fluid and multifaceted identity experiences, blending personal narratives with social affiliations in virtual environments.
Fostering Healthy Identity Integration
Fostering healthy identity integration requires balancing your personal identity, which encompasses internal values and self-concept, with social identity derived from group memberships and social roles. Research highlights that harmonious identity integration promotes psychological well-being and resilience by reducing internal conflicts between individual desires and social expectations. Strategies such as reflective self-awareness and inclusive social interactions support this synthesis, enabling a stronger, cohesive sense of self.
Infographic: Personal Identity vs Social Identity
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com