Cash budget tracks actual cash inflows and outflows to ensure liquidity, while profit budget projects net income by estimating revenues and expenses. Discover how these budgets interact and complement each other to improve financial planning in this article.
Table of Comparison
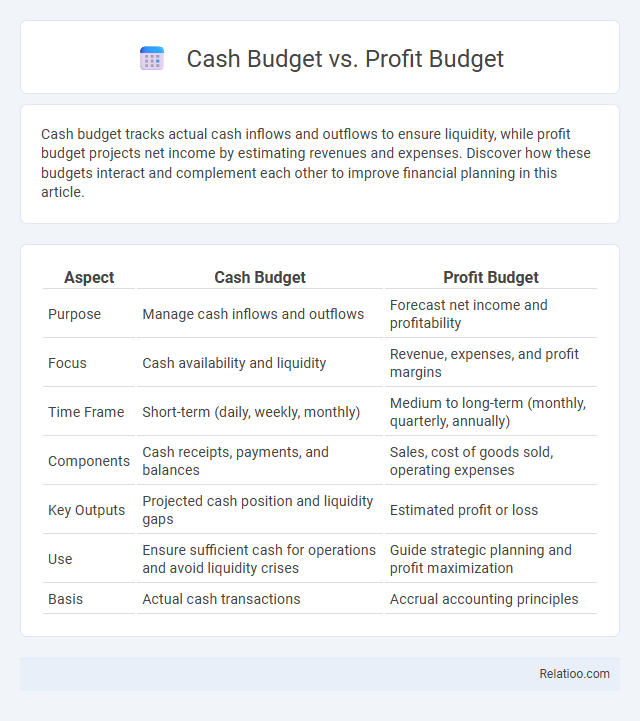
| Aspect | Cash Budget | Profit Budget |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Manage cash inflows and outflows | Forecast net income and profitability |
| Focus | Cash availability and liquidity | Revenue, expenses, and profit margins |
| Time Frame | Short-term (daily, weekly, monthly) | Medium to long-term (monthly, quarterly, annually) |
| Components | Cash receipts, payments, and balances | Sales, cost of goods sold, operating expenses |
| Key Outputs | Projected cash position and liquidity gaps | Estimated profit or loss |
| Use | Ensure sufficient cash for operations and avoid liquidity crises | Guide strategic planning and profit maximization |
| Basis | Actual cash transactions | Accrual accounting principles |
Introduction to Cash Budget vs Profit Budget
Cash budget tracks the actual inflow and outflow of cash within a specific period, ensuring Your business maintains sufficient liquidity for daily operations. Profit budget estimates expected revenues and expenses to forecast net income, helping measure financial performance over time. Understanding the distinction between cash budget and profit budget is crucial for effective financial planning and decision-making.
Definition of Cash Budget
A Cash Budget is a financial plan that estimates cash inflows and outflows over a specific period, ensuring sufficient liquidity to meet obligations and avoid shortfalls. Unlike a Profit Budget, which projects revenues and expenses to determine net income, the Cash Budget focuses strictly on actual cash movements, making it crucial for managing daily operations and short-term financial planning. The broader Budget encompasses various financial plans, including both cash and profit budgets, to guide overall financial strategy and resource allocation.
Definition of Profit Budget
A Profit Budget is a detailed financial plan that estimates the expected net profit for a specific period by projecting revenues and deducting all anticipated expenses. Unlike a Cash Budget, which focuses on cash inflows and outflows to ensure liquidity, and a general Budget that encompasses overall financial planning, the Profit Budget specifically targets profitability analysis. You can use the Profit Budget to evaluate your business's ability to generate earnings and guide strategic decisions.
Key Differences Between Cash Budget and Profit Budget
Cash budget focuses on the inflows and outflows of actual cash, tracking liquidity to ensure your business can meet short-term obligations. Profit budget estimates revenues and expenses to project net income, emphasizing profitability rather than immediate cash availability. Key differences include timing and scope: cash budget monitors real-time cash position, while profit budget accounts for non-cash items like depreciation to assess overall financial performance.
Components of a Cash Budget
A cash budget focuses on projecting cash inflows and outflows, including components such as cash receipts from sales, cash payments for expenses, and financing activities like loans or equity. Unlike a profit budget, which estimates revenues and expenses to determine net profit, the cash budget emphasizes liquidity and ensuring Your business can meet short-term obligations. Understanding these components helps manage cash effectively while distinguishing it from broader budget types that cover overall financial planning.
Components of a Profit Budget
A Profit Budget primarily includes components such as projected sales revenue, cost of goods sold (COGS), operating expenses, and anticipated gross and net profit margins. Unlike a Cash Budget, which tracks cash inflows and outflows, the Profit Budget focuses on profitability by estimating revenues and deducting all relevant costs to assess financial performance. Understanding these components helps You make informed decisions to optimize business profitability and align financial planning with strategic goals.
Importance of Cash Budget in Financial Planning
A cash budget is crucial in financial planning because it tracks your actual cash inflows and outflows, ensuring sufficient liquidity to meet short-term obligations, unlike a profit budget that focuses primarily on projected revenues and expenses for profitability assessment. While overall budgets provide comprehensive financial plans, cash budgets specifically prevent cash shortages and help manage day-to-day financial health, making them indispensable for maintaining business solvency. Your ability to monitor and control cash flow directly influences operational stability and investment decisions, highlighting the cash budget's vital role.
Role of Profit Budget in Business Management
Profit Budget plays a crucial role in business management by projecting expected net income, helping You evaluate profitability and make informed financial decisions. Unlike Cash Budgets, which track actual cash inflows and outflows to ensure liquidity, the Profit Budget focuses on revenues and expenses over a period to guide strategic planning. Integrating Profit Budget data with overall Budget frameworks allows management to align operational goals with financial performance targets effectively.
Common Mistakes in Preparing Budgets
Common mistakes in preparing cash budgets include underestimating timing differences between receipts and disbursements, leading to inaccurate cash flow projections. Profit budgets often err by relying on overly optimistic sales forecasts without adjusting for variable costs, which skews profit expectations. General budget errors typically arise from inadequate contingency planning and failure to align budget assumptions with actual market conditions, resulting in unrealistic financial targets.
Conclusion: Choosing Between Cash Budget and Profit Budget
Choosing between a cash budget and a profit budget depends largely on your business priorities and financial goals. A cash budget emphasizes short-term liquidity by tracking actual cash inflows and outflows, crucial for maintaining solvency and managing day-to-day expenses. Meanwhile, a profit budget focuses on forecasting revenues and expenses to gauge profitability, helping you plan for growth and long-term financial stability.
Infographic: Cash Budget vs Profit Budget
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com