Emotional resilience enables individuals to recover quickly from stress, while psychological flexibility allows adaptive responses to changing thoughts and emotions, enhancing overall mental health. Discover how mastering both skills can strengthen your relationships in this article.
Table of Comparison
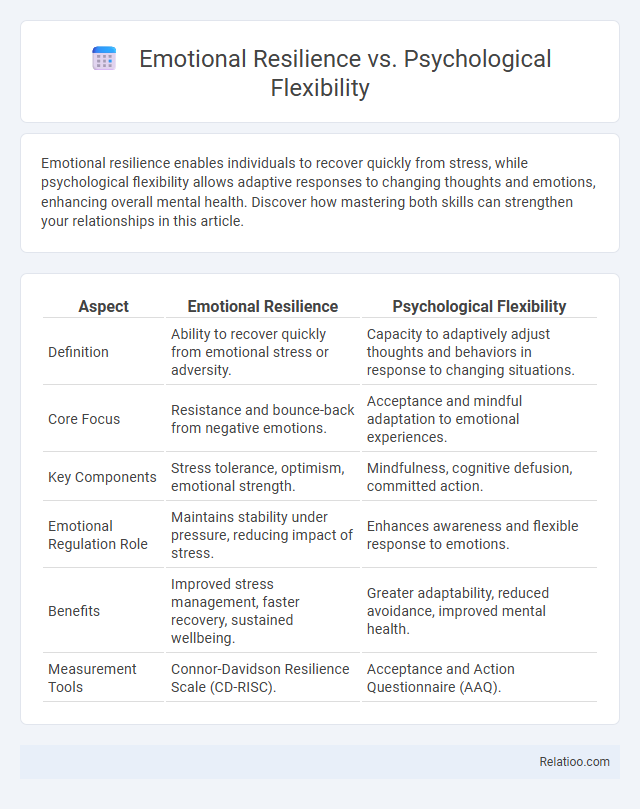
| Aspect | Emotional Resilience | Psychological Flexibility |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Ability to recover quickly from emotional stress or adversity. | Capacity to adaptively adjust thoughts and behaviors in response to changing situations. |
| Core Focus | Resistance and bounce-back from negative emotions. | Acceptance and mindful adaptation to emotional experiences. |
| Key Components | Stress tolerance, optimism, emotional strength. | Mindfulness, cognitive defusion, committed action. |
| Emotional Regulation Role | Maintains stability under pressure, reducing impact of stress. | Enhances awareness and flexible response to emotions. |
| Benefits | Improved stress management, faster recovery, sustained wellbeing. | Greater adaptability, reduced avoidance, improved mental health. |
| Measurement Tools | Connor-Davidson Resilience Scale (CD-RISC). | Acceptance and Action Questionnaire (AAQ). |
Defining Emotional Resilience
Emotional resilience refers to your ability to adapt to stressful situations, recover from adversity, and maintain mental well-being despite challenges. Psychological flexibility involves adjusting your thoughts and behaviors to align with your values, even in the face of difficult emotions, which supports emotional resilience by promoting adaptive coping strategies. Developing emotional resilience strengthens your capacity to bounce back from setbacks and sustain emotional equilibrium under pressure.
What is Psychological Flexibility?
Psychological flexibility refers to the ability to adapt to changing situational demands by shifting mental states or perspectives while maintaining balance among competing desires, needs, and life domains. This concept involves openness to experience, mindful awareness, and committed action aligned with personal values, which differentiates it from emotional resilience that primarily focuses on bouncing back from stress. Unlike emotional resilience, psychological flexibility emphasizes acceptance and cognitive defusion, enabling individuals to navigate complex emotional landscapes with greater ease and creativity.
Key Differences Between Emotional Resilience and Psychological Flexibility
Emotional resilience refers to the capacity to recover quickly from emotional setbacks by maintaining stability under stress, whereas psychological flexibility involves adapting thoughts and behaviors proactively in response to changing situational demands. Key differences lie in emotional resilience emphasizing bounce-back ability and stress tolerance, while psychological flexibility centers on cognitive adaptability and openness to experience. Both constructs contribute to mental well-being but operate through distinct mechanisms: resilience stabilizes emotional equilibrium, flexibility enhances problem-solving and acceptance strategies.
Core Components of Emotional Resilience
Core components of emotional resilience include self-awareness, emotional regulation, and adaptive coping strategies that enable you to bounce back from adversity. Unlike psychological flexibility, which emphasizes openness to experience and value-driven behavior, emotional resilience centers on maintaining stability and strength during stress. Developing these core components strengthens your ability to manage emotional challenges and sustain mental well-being.
Essential Elements of Psychological Flexibility
Psychological flexibility involves adapting your thoughts and emotions to changing situations, incorporating acceptance, mindfulness, and committed action as essential elements. Emotional resilience refers to the ability to recover from stress and adversity, while emotional resilience emphasizes managing emotions effectively during challenges. Understanding psychological flexibility helps you respond dynamically to life's difficulties by embracing experiences without avoidance or judgment.
Benefits of Developing Emotional Resilience
Developing emotional resilience enhances your ability to recover quickly from stress, promoting mental well-being and reducing the impact of anxiety and depression. Psychological flexibility complements this by allowing you to adapt thoughts and behaviors to changing circumstances, increasing overall emotional health. Together, these skills foster greater coping capacity, improved decision-making under pressure, and a more balanced emotional life.
Advantages of Cultivating Psychological Flexibility
Cultivating psychological flexibility enhances the ability to adapt to changing circumstances and manage stress effectively, leading to improved mental health and well-being. Unlike emotional resilience, which focuses primarily on bouncing back from adversity, psychological flexibility promotes acceptance and mindful engagement with one's thoughts and feelings, fostering long-term emotional balance. This adaptability supports better decision-making, reduces anxiety, and strengthens relationships by allowing individuals to respond to challenges with openness rather than avoidance.
Emotional Resilience in Real-Life Scenarios
Emotional resilience refers to the ability to adapt and recover quickly from stress, adversity, or trauma, essential for maintaining mental well-being in real-life scenarios such as workplace challenges or personal loss. Psychological flexibility, a complementary concept, involves adapting one's thinking and behavior to changing situations and demands, enhancing emotional resilience by promoting adaptive coping strategies. Developing emotional resilience through mindfulness, cognitive reframing, and social support improves outcomes in high-pressure environments and contributes to sustained psychological health.
Psychological Flexibility in Coping with Change
Psychological flexibility is the ability to adapt to changing circumstances by effectively managing thoughts and emotions, enhancing mental well-being during transitions. Unlike emotional resilience, which emphasizes bouncing back from adversity, psychological flexibility involves accepting experiences and committed action aligned with personal values. This adaptive capacity supports coping with change by fostering openness, mindfulness, and value-driven behavior, making it crucial in dynamic environments.
Integrating Both for Optimal Mental Health
Emotional resilience and psychological flexibility are crucial components for maintaining optimal mental health, where emotional resilience refers to the ability to bounce back from stress, and psychological flexibility allows you to adapt your thoughts and behaviors in response to changing circumstances. Integrating both enhances your capacity to manage difficult emotions and challenging situations effectively, promoting long-term psychological well-being. Strengthening these traits through mindfulness, cognitive-behavioral strategies, and stress management techniques optimizes your overall mental health resilience.
Infographic: Emotional Resilience vs Psychological Flexibility
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com