Effective anger management techniques specifically target controlling outbursts and reducing aggressive behaviors in relationships. Emotional regulation encompasses a broader skill set, including recognizing, understanding, and managing a wide range of emotions for healthier interpersonal connections; explore these differences in detail in this article.
Table of Comparison
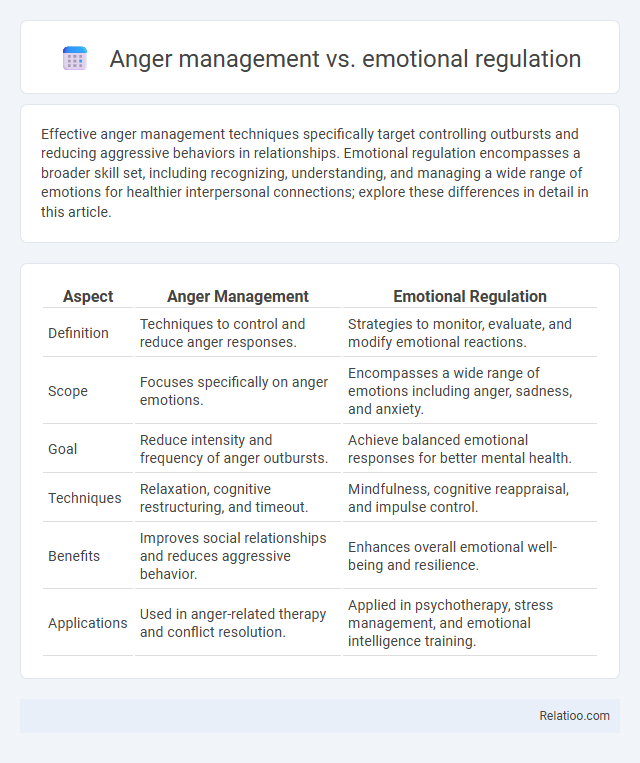
| Aspect | Anger Management | Emotional Regulation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Techniques to control and reduce anger responses. | Strategies to monitor, evaluate, and modify emotional reactions. |
| Scope | Focuses specifically on anger emotions. | Encompasses a wide range of emotions including anger, sadness, and anxiety. |
| Goal | Reduce intensity and frequency of anger outbursts. | Achieve balanced emotional responses for better mental health. |
| Techniques | Relaxation, cognitive restructuring, and timeout. | Mindfulness, cognitive reappraisal, and impulse control. |
| Benefits | Improves social relationships and reduces aggressive behavior. | Enhances overall emotional well-being and resilience. |
| Applications | Used in anger-related therapy and conflict resolution. | Applied in psychotherapy, stress management, and emotional intelligence training. |
Introduction to Anger Management and Emotional Regulation
Anger management involves techniques and strategies to control and reduce the intensity of anger responses, focusing on behavioral changes and coping mechanisms. Emotional regulation encompasses a broader range of skills targeting the ability to monitor, evaluate, and modify emotional reactions, including but not limited to anger. Understanding differences is essential for applying appropriate interventions in clinical psychology and personal development.
Defining Anger Management
Anger management involves techniques and strategies designed to help individuals recognize, control, and express anger in healthy ways, preventing destructive outcomes. Emotional regulation encompasses a broader skill set for managing a wide range of emotions, including anger, sadness, and anxiety, by adjusting emotional responses to fit situations appropriately. You can benefit from mastering anger management specifically to reduce impulsive outbursts and improve interpersonal relationships.
What is Emotional Regulation?
Emotional regulation refers to the ability to monitor, evaluate, and modify emotional reactions in adaptive ways, encompassing strategies to manage not only anger but a wide range of emotions such as anxiety, sadness, and frustration. Unlike anger management, which specifically targets controlling and reducing anger responses, emotional regulation involves a broader skill set that includes recognizing emotional triggers, employing cognitive reappraisal, and maintaining emotional balance. Effective emotional regulation enhances mental health, improves interpersonal relationships, and supports resilience against emotional dysregulation disorders.
Key Differences Between Anger Management and Emotional Regulation
Anger management focuses specifically on identifying triggers and implementing strategies to control or reduce anger responses, while emotional regulation encompasses a broader range of skills to manage all emotions, including frustration, sadness, and anxiety. Emotional regulation helps Your brain process emotions in a balanced way before they escalate, whereas anger management often deals with reactive techniques after anger has already surfaced. Understanding these key differences allows for more effective personal development and emotional well-being.
Common Triggers: Anger vs Other Emotions
Common triggers for anger often include perceived threats, frustration, or injustice, whereas emotional regulation addresses a broader spectrum of emotions such as sadness, anxiety, and joy. Anger management specifically targets recognizing and controlling anger responses to prevent aggressive behavior and promote constructive expression. Emotional regulation encompasses strategies that help individuals modulate intensity and duration of various emotions, improving overall emotional resilience and mental well-being.
Techniques for Effective Anger Management
Effective anger management techniques include cognitive restructuring, which helps individuals identify and change negative thought patterns driving anger, and relaxation strategies like deep breathing and progressive muscle relaxation to reduce physiological arousal. Emotional regulation complements anger management by enhancing awareness and control over emotional responses, employing mindfulness and acceptance practices to modulate intense feelings. Combining these methods leads to comprehensive improvement in controlling anger and regulating emotional reactions in stressful situations.
Strategies for Emotional Regulation
Effective strategies for emotional regulation include mindfulness practices, cognitive reappraisal, and deep-breathing exercises that help individuals manage their emotional responses proactively. Unlike traditional anger management, which targets controlling anger episodes specifically, emotional regulation encompasses a broader spectrum of emotions and builds resilience by improving self-awareness and adaptive coping skills. These techniques foster long-term emotional well-being by promoting balanced reactions to stressors and reducing impulsivity.
The Role of Mindfulness in Managing Emotions
Mindfulness plays a crucial role in managing emotions by enhancing emotional regulation, which involves recognizing and modulating your emotional responses effectively. While anger management specifically targets reducing and coping with anger, emotional regulation encompasses a broader spectrum of emotions, with mindfulness fostering awareness and non-reactivity. By practicing mindfulness, you can develop greater control over emotional triggers, leading to healthier responses and improved emotional balance.
Long-Term Benefits of Emotional Regulation Skills
Emotional regulation skills provide long-term benefits by fostering resilience, reducing chronic stress, and enhancing interpersonal relationships through improved self-awareness and adaptive coping strategies. Unlike anger management, which primarily targets controlling anger episodes, emotional regulation encompasses managing a wide range of emotions, leading to sustained mental health and emotional stability. Developing these skills contributes to lasting behavioral change, greater emotional intelligence, and overall psychological well-being.
Choosing the Right Approach: Anger Management or Emotional Regulation
Choosing between anger management and emotional regulation depends on your specific needs and emotional patterns. Anger management focuses on controlling and reducing aggressive behavior, often employing strategies like relaxation techniques and cognitive restructuring. Emotional regulation provides a broader approach by helping you understand and manage a range of emotions, leading to healthier responses and long-term emotional balance.
Infographic: Anger management vs Emotional regulation
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com