Emotional contagion occurs when individuals unconsciously mimic and catch others' emotions, while empathy involves consciously understanding and sharing another person's emotional experience. Explore this article to learn how distinguishing between these mechanisms enhances relationship quality and emotional connection.
Table of Comparison
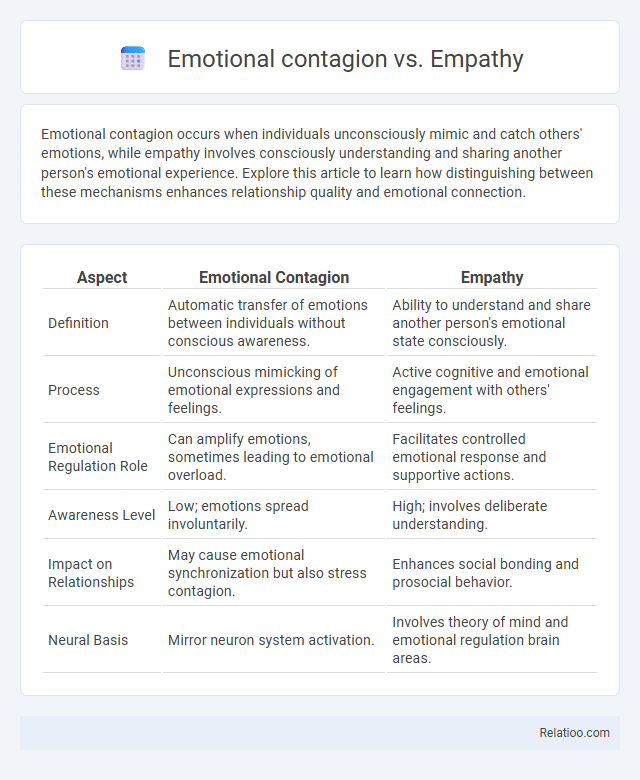
| Aspect | Emotional Contagion | Empathy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Automatic transfer of emotions between individuals without conscious awareness. | Ability to understand and share another person's emotional state consciously. |
| Process | Unconscious mimicking of emotional expressions and feelings. | Active cognitive and emotional engagement with others' feelings. |
| Emotional Regulation Role | Can amplify emotions, sometimes leading to emotional overload. | Facilitates controlled emotional response and supportive actions. |
| Awareness Level | Low; emotions spread involuntarily. | High; involves deliberate understanding. |
| Impact on Relationships | May cause emotional synchronization but also stress contagion. | Enhances social bonding and prosocial behavior. |
| Neural Basis | Mirror neuron system activation. | Involves theory of mind and emotional regulation brain areas. |
Understanding Emotional Contagion
Emotional contagion is the automatic, unconscious process of catching and mirroring others' emotions, influencing mood and behavior without deliberate effort. Unlike empathy, which involves a conscious understanding and sharing of another's emotional experience, emotional contagion occurs through subtle social cues such as facial expressions, tone of voice, and body language. Recognizing emotional contagion is crucial for managing interpersonal dynamics and emotional regulation in social and professional environments.
Defining Empathy
Empathy is the ability to understand and share the feelings of another person by mentally putting oneself in their emotional experience. Unlike emotional contagion, which involves the automatic, unconscious spread of emotions between individuals, empathy requires cognitive processing and perspective-taking to genuinely comprehend another's emotional state. This distinction highlights empathy as a complex, active process essential for effective emotional communication and social bonding.
Key Differences Between Emotional Contagion and Empathy
Emotional contagion involves automatically mirroring others' emotions, often unconsciously absorbing feelings like stress or joy, whereas empathy requires consciously understanding and sharing another person's emotional experience. Key differences include the passive nature of emotional contagion versus the active, cognitive process of empathy, which involves perspective-taking and emotional regulation. Your ability to distinguish these mechanisms enhances emotional intelligence and improves interpersonal communication.
The Science Behind Emotional Contagion
Emotional contagion involves the automatic synchronization of emotions between individuals through neural mechanisms like mirror neurons, enabling rapid, unconscious sharing of feelings. Empathy, in contrast, requires cognitive processing to understand and resonate with another's emotional state, engaging brain regions such as the anterior insula and anterior cingulate cortex. The science behind emotional contagion reveals that it facilitates social bonding and group cohesion by allowing emotions to spread quickly within a population, often influencing behavior without deliberate awareness.
How Empathy is Developed
Empathy develops through a combination of emotional contagion and cognitive processing, allowing individuals to not only share but also understand others' feelings. Neuroscientific studies highlight the role of mirror neurons in emotional contagion, which provides the foundational experience necessary for empathy to emerge. Social interactions and reflection further enhance empathy by fostering perspective-taking and emotional regulation skills.
Emotional Contagion in Social Settings
Emotional contagion in social settings occurs when individuals unconsciously mimic and synchronize their emotions with others, leading to shared emotional experiences that influence group dynamics. Unlike empathy, which involves understanding and sharing another's emotional state consciously, emotional contagion operates automatically and shapes collective moods and behaviors. Your awareness of emotional contagion can help you navigate social interactions more effectively by recognizing how moods spread within groups and adjusting your responses to foster positive environments.
Empathy’s Role in Relationships
Empathy plays a crucial role in relationships by allowing you to deeply understand and share the feelings of others, fostering emotional connections and trust. Unlike emotional contagion, which involves automatically mirroring others' emotions, empathy requires conscious awareness and perspective-taking. Strong empathetic skills enhance communication, reduce conflicts, and promote emotional support in close relationships.
Negative Effects of Emotional Contagion
Emotional contagion, unlike empathy, involves the automatic and unconscious transfer of emotions, often leading to the spread of negative feelings such as stress, anxiety, and anger within groups. Negative effects of emotional contagion include decreased morale, impaired decision-making, and increased workplace conflicts due to the rapid and unconscious absorption of others' negative emotions. In contrast, empathy requires conscious perspective-taking and emotional regulation, which can mitigate the adverse impact of negative emotions while fostering understanding and supportive interactions.
Cultivating Healthy Empathy
Cultivating healthy empathy involves recognizing and managing emotional contagion, which is the automatic mimicry and synchronization of emotions with others. Unlike emotional contagion, empathy requires conscious awareness and the ability to understand and share another person's emotional state without becoming overwhelmed. Developing boundaries and emotional regulation skills helps foster genuine empathy while preventing the negative effects of emotional contagion.
Emotional Contagion and Empathy in the Digital Age
Emotional contagion refers to the automatic transfer of emotions from one person to another through nonverbal cues, while empathy involves the conscious ability to understand and share the feelings of others. In the digital age, emotional contagion spreads rapidly through social media platforms via emojis, memes, and viral content, influencing your mood and social interactions on a large scale. Your capacity for empathy, however, plays a crucial role in interpreting these digital signals accurately and fostering genuine connections amidst the fast-paced, emotion-driven online environment.
Infographic: Emotional contagion vs Empathy
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com