Reappraisal involves changing the way you think about a situation to alter its emotional impact, while acceptance focuses on acknowledging emotions without judgment. Discover more about how these strategies affect relationship dynamics in this article.
Table of Comparison
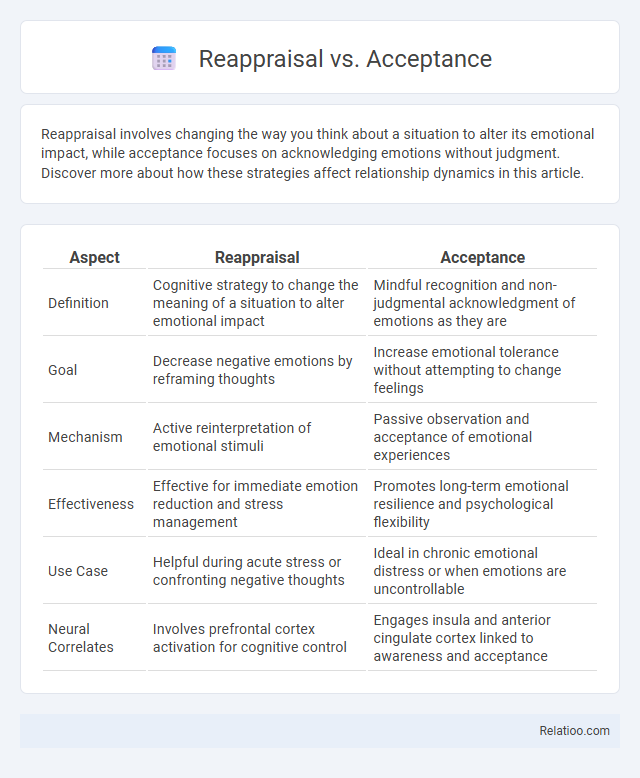
| Aspect | Reappraisal | Acceptance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Cognitive strategy to change the meaning of a situation to alter emotional impact | Mindful recognition and non-judgmental acknowledgment of emotions as they are |
| Goal | Decrease negative emotions by reframing thoughts | Increase emotional tolerance without attempting to change feelings |
| Mechanism | Active reinterpretation of emotional stimuli | Passive observation and acceptance of emotional experiences |
| Effectiveness | Effective for immediate emotion reduction and stress management | Promotes long-term emotional resilience and psychological flexibility |
| Use Case | Helpful during acute stress or confronting negative thoughts | Ideal in chronic emotional distress or when emotions are uncontrollable |
| Neural Correlates | Involves prefrontal cortex activation for cognitive control | Engages insula and anterior cingulate cortex linked to awareness and acceptance |
Understanding Reappraisal and Acceptance
Understanding reappraisal involves changing your interpretation of a situation to alter its emotional impact, which can reduce stress and enhance emotional regulation. Acceptance focuses on embracing your emotions without judgment, promoting psychological flexibility and reducing avoidance behaviors. Both reappraisal and acceptance serve unique roles in managing emotions effectively by either modifying emotional responses or fostering mindfulness and tolerance.
Core Principles: What is Reappraisal?
Reappraisal is a cognitive emotion regulation strategy that involves changing the way you interpret a situation to alter its emotional impact, effectively reducing negative feelings by reframing thoughts. Acceptance focuses on acknowledging and embracing your emotions without trying to change them, promoting psychological flexibility and reducing emotional avoidance. Understanding these core principles helps you choose whether to modify your emotional response through reappraisal or cultivate mindfulness and tolerance through acceptance.
Core Principles: What is Acceptance?
Acceptance involves embracing thoughts, emotions, and experiences without judgment or attempts to change them, fostering psychological flexibility and reducing resistance to distress. Core principles of acceptance include mindfulness, allowing present-moment awareness, and acknowledging reality as it is, which contrasts with reappraisal that actively changes the interpretation or meaning of an event. Unlike reappraisal that seeks cognitive reframing, acceptance promotes emotional openness and non-avoidance, supporting emotional regulation through experiential acknowledgment rather than cognitive alteration.
Psychological Foundations of Each Approach
Reappraisal involves cognitively reframing a situation to alter its emotional impact, relying on neural mechanisms in the prefrontal cortex to regulate emotional responses. Acceptance centers on embracing emotions without judgment, fostering mindfulness and reducing experiential avoidance, which engages brain regions linked to awareness such as the anterior cingulate cortex. Your understanding of these psychological foundations empowers you to choose strategies tailored to managing emotional experiences effectively.
Reappraisal: Benefits and Limitations
Reappraisal involves changing the way one interprets a situation to alter its emotional impact, leading to reduced stress and enhanced emotional regulation. Benefits of reappraisal include improved mental resilience and decreased negative affect, supported by neuroimaging studies indicating prefrontal cortex activation during its use. Limitations arise when reappraisal is applied excessively or inappropriately, potentially causing avoidance of genuine emotions and decreased emotional authenticity.
Acceptance: Benefits and Limitations
Acceptance promotes emotional resilience by encouraging individuals to experience emotions without judgment, reducing stress and enhancing psychological flexibility. Its benefits include improved mental health outcomes, such as decreased anxiety and depression, and fostering a more present-focused mindset. However, acceptance may limit proactive problem-solving in situations where direct intervention is necessary, potentially leading to passive coping or avoidance behaviors.
Comparing Emotional Outcomes
Reappraisal involves changing the interpretation of a situation to alter its emotional impact, often leading to reduced negative affect and increased positive emotions. Acceptance entails acknowledging emotions without attempting to change them, promoting emotional resilience and long-term well-being by reducing avoidance and distress. Comparing these, reappraisal tends to produce more immediate decreases in negative emotions, whereas acceptance supports sustained emotional balance and tolerance.
Practical Applications in Daily Life
Reappraisal involves changing your interpretation of a situation to alter its emotional impact, promoting emotional regulation and resilience in daily stressors. Acceptance encourages embracing your feelings without judgment, fostering mindfulness and reducing anxiety in challenging moments. Combining reappraisal and acceptance enhances your ability to manage emotions effectively, improving overall mental well-being in everyday life.
Choosing the Right Approach: Factors to Consider
Choosing between reappraisal and acceptance involves evaluating the context, emotional intensity, and personal goals. Reappraisal effectively reduces negative emotions by changing the interpretation of a situation, making it suitable for controllable or cognitive challenges. Acceptance promotes emotional resilience by embracing feelings without judgment, ideal for uncontrollable or persistent circumstances where changing the perception is difficult.
Integrating Reappraisal and Acceptance for Well-Being
Integrating reappraisal and acceptance strategies enhances emotional well-being by combining cognitive restructuring with mindful acknowledgment of emotions. Reappraisal reshapes negative interpretations, while acceptance fosters non-judgmental awareness, reducing emotional distress more effectively than either approach alone. Research indicates that this integration promotes resilience, emotional regulation, and lasting psychological health.
Infographic: Reappraisal vs Acceptance
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com