Perseveration involves repetitive, uncontrollable focus on a specific thought or behavior within relationships, while intrusive thoughts are unwanted, often distressing ideas that disrupt emotional connection. Explore this article to understand how these cognitive patterns impact relationship dynamics and strategies to manage them.
Table of Comparison
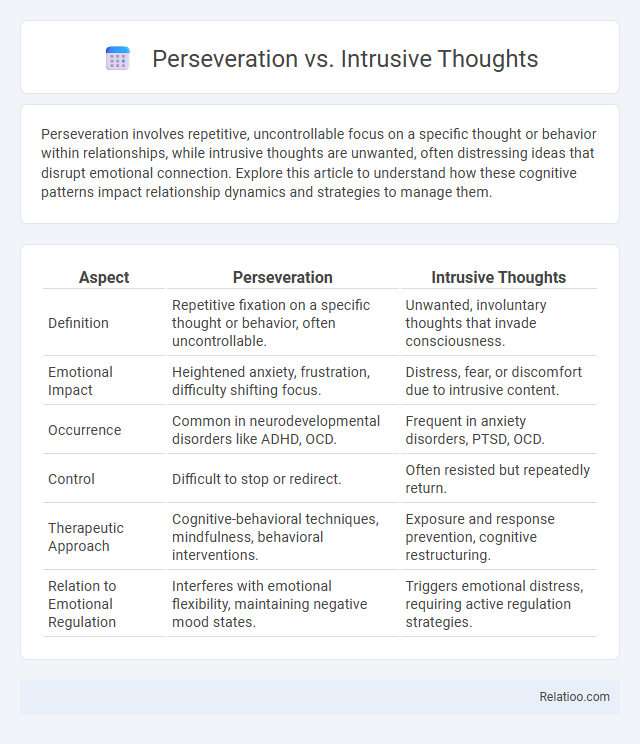
| Aspect | Perseveration | Intrusive Thoughts |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Repetitive fixation on a specific thought or behavior, often uncontrollable. | Unwanted, involuntary thoughts that invade consciousness. |
| Emotional Impact | Heightened anxiety, frustration, difficulty shifting focus. | Distress, fear, or discomfort due to intrusive content. |
| Occurrence | Common in neurodevelopmental disorders like ADHD, OCD. | Frequent in anxiety disorders, PTSD, OCD. |
| Control | Difficult to stop or redirect. | Often resisted but repeatedly return. |
| Therapeutic Approach | Cognitive-behavioral techniques, mindfulness, behavioral interventions. | Exposure and response prevention, cognitive restructuring. |
| Relation to Emotional Regulation | Interferes with emotional flexibility, maintaining negative mood states. | Triggers emotional distress, requiring active regulation strategies. |
Defining Perseveration and Intrusive Thoughts
Perseveration is the uncontrollable repetition of a response, such as a word, phrase, or gesture, often linked to brain injury or neurological disorders. Intrusive thoughts are unwanted, involuntary thoughts or images that repeatedly invade Your mind, commonly associated with anxiety or obsessive-compulsive disorder. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment in neuropsychological and psychiatric contexts.
Key Differences Between Perseveration and Intrusive Thoughts
Perseveration involves the uncontrollable repetition of a particular response or behavior despite the absence of a stimulus, commonly observed in neurological disorders such as autism spectrum disorder or frontal lobe damage. Intrusive thoughts are unwanted, distressing ideas or images that involuntarily enter the mind, often linked to anxiety disorders and obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD). The key difference lies in perseveration being a behavioral or verbal repetition reflecting cognitive inflexibility, while intrusive thoughts are involuntary mental intrusions causing emotional distress without repetitive physical action.
Psychological Roots of Perseveration
Perseveration, characterized by the repetitive fixation on a particular thought or behavior, often stems from disruptions in cognitive flexibility linked to frontal lobe dysfunction or neurodevelopmental disorders such as autism and ADHD. Unlike intrusive thoughts, which are unwanted and distressing mental intrusions associated with anxiety and obsessive-compulsive disorder, perseveration involves a difficulty in shifting attention away from a stimulus or response pattern. The psychological roots of perseveration highlight deficits in executive functioning, emotional regulation, and inhibitory control that impair adaptive cognitive processing.
Causes and Triggers of Intrusive Thoughts
Intrusive thoughts are often triggered by stress, anxiety, or traumatic experiences, causing unwanted, distressing mental images or ideas that repeatedly enter your mind. Unlike perseveration, which involves the repetitive focus on a particular response or behavior due to brain injury or developmental disorders, intrusive thoughts typically stem from underlying emotional conflicts or unresolved fears. Understanding the causes and triggers of intrusive thoughts can help differentiate them from perseveration and guide effective coping strategies.
Perseveration in Neurological Disorders
Perseveration in neurological disorders is characterized by the uncontrollable repetition of words, phrases, or behaviors, often due to frontal lobe damage or conditions like Alzheimer's disease and traumatic brain injury. Intrusive thoughts, by contrast, are unwanted, distressing ideas that spontaneously enter your mind without repetitive behavior, commonly seen in anxiety or OCD. Differentiating these symptoms is crucial for accurate diagnosis and tailored intervention in cognitive and neuropsychological treatment.
Intrusive Thoughts in Anxiety and OCD
Intrusive thoughts in anxiety and OCD are unwanted, distressing mental images or ideas that repeatedly invade Your mind, causing significant distress and disruption. Unlike perseveration, which involves the repetitive focus on a specific thought or behavior, intrusive thoughts are typically ego-dystonic and resisted because they conflict with Your values or desires. Understanding the nuances between intrusive thoughts and perseveration is crucial for effective cognitive-behavioral strategies to reduce anxiety and OCD symptoms.
Recognizing Symptoms and Manifestations
Perseveration involves the uncontrollable repetition of a word, phrase, or gesture, often linked to neurological disorders like autism or brain injury, whereas intrusive thoughts are unwanted, distressing ideas or images that repeatedly enter your mind, commonly associated with anxiety or OCD. Recognizing symptoms of perseveration includes difficulty shifting attention or responses despite changes in context, while intrusive thoughts manifest as persistent, unwanted mental intrusions causing significant distress. Identifying these manifestations accurately helps tailor effective cognitive-behavioral interventions to manage your mental health challenges.
Impact on Daily Functioning and Mental Health
Perseveration involves the repetitive focus on a particular thought or behavior, often disrupting Your ability to complete tasks and maintain social interactions, leading to increased stress and anxiety. Intrusive thoughts are unwanted, involuntary thoughts that can cause significant emotional distress and impair concentration, negatively affecting mental health and daily functioning. Both conditions can reduce productivity, exacerbate mood disorders, and require targeted therapeutic strategies to manage their impact effectively.
Effective Coping Strategies and Treatments
Effective coping strategies for perseveration emphasize mindfulness techniques, cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), and structured routines to reduce repetitive thoughts and behaviors. Intrusive thoughts often respond well to exposure and response prevention (ERP), acceptance and commitment therapy (ACT), and medication such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) to ease distressing mental intrusions. You can improve mental resilience by combining therapy, medication, and personalized stress management plans tailored to address the unique features of each condition.
When to Seek Professional Help
Persistent perseveration or intrusive thoughts that disrupt daily functioning, cause significant distress, or impair decision-making signal the need for professional help. If your repetitive thoughts become uncontrollable, interfere with relationships, or lead to compulsive behaviors, consulting a mental health specialist is crucial. Seeking early intervention can provide tailored strategies to manage symptoms and improve overall well-being effectively.
Infographic: Perseveration vs Intrusive Thoughts
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com