Emotional regulation involves managing one's own emotions independently, while emotional co-regulation requires mutual support between partners to navigate feelings together. Discover how mastering both can strengthen your relationship in this article.
Table of Comparison
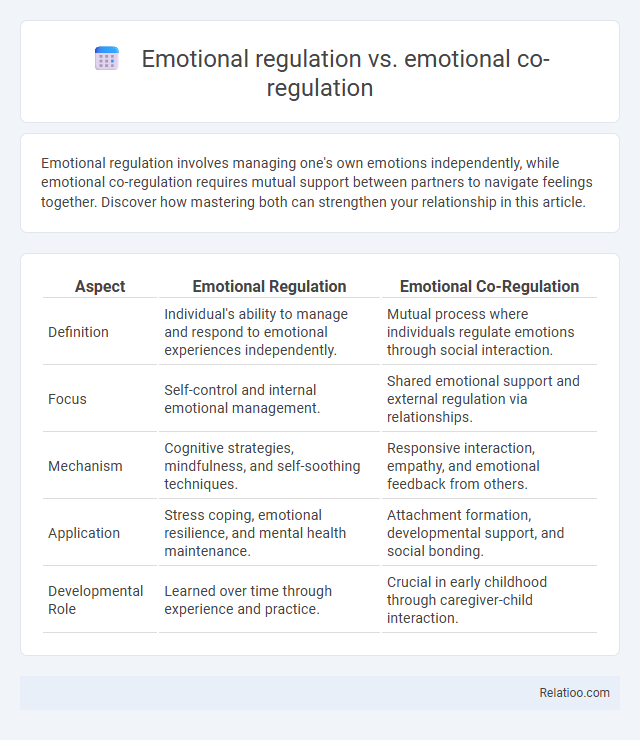
| Aspect | Emotional Regulation | Emotional Co-Regulation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Individual's ability to manage and respond to emotional experiences independently. | Mutual process where individuals regulate emotions through social interaction. |
| Focus | Self-control and internal emotional management. | Shared emotional support and external regulation via relationships. |
| Mechanism | Cognitive strategies, mindfulness, and self-soothing techniques. | Responsive interaction, empathy, and emotional feedback from others. |
| Application | Stress coping, emotional resilience, and mental health maintenance. | Attachment formation, developmental support, and social bonding. |
| Developmental Role | Learned over time through experience and practice. | Crucial in early childhood through caregiver-child interaction. |
Understanding Emotional Regulation: Definition and Importance
Emotional regulation involves your ability to manage and respond to emotional experiences effectively, ensuring mental well-being and social adaptability. Emotional co-regulation refers to the interactive process where individuals, such as a caregiver and child, mutually influence each other's emotional states to achieve stability. Understanding the distinctions between self-regulation and co-regulation is crucial for fostering healthy emotional development and relationships.
What is Emotional Co-Regulation? Core Concepts
Emotional co-regulation refers to the process where two or more individuals mutually influence and support each other's emotional states, fostering shared understanding and balance. Core concepts include responsiveness, where one person attunes to and helps modulate another's emotions, and synchronization, which creates a calming and adaptive emotional connection. You benefit from emotional co-regulation as it enhances emotional resilience and strengthens interpersonal relationships through collaborative emotional management.
Key Differences Between Emotional Regulation and Co-Regulation
Emotional regulation involves managing your own emotions independently by recognizing, understanding, and modulating feelings internally. Emotional co-regulation, however, emphasizes the dynamic process where two individuals actively support and influence each other's emotional states through interpersonal interaction. Key differences lie in autonomy and social context: emotional regulation is self-driven, while co-regulation depends on relational support to stabilize and navigate emotions effectively.
The Science Behind Self-Regulation of Emotions
Emotional regulation involves individual efforts to manage and modify emotional responses through cognitive and behavioral strategies. Emotional co-regulation refers to the interactive process where individuals, such as caregivers and children, mutually influence each other's emotional states to maintain equilibrium. Neuroscientific studies highlight the role of prefrontal cortex activity and limbic system interactions in self-regulation, while social contexts modulate co-regulation dynamics via mirror neuron systems and attachment-related neural pathways.
How Co-Regulation Works in Relationships
Emotional regulation involves an individual managing their own feelings, while emotional co-regulation refers to the interactive process where two or more people help each other modulate emotions. In relationships, co-regulation works through responsive communication, where partners recognize and respond to each other's emotional cues, creating a safe environment that fosters emotional stability and mutual support. This dynamic helps maintain emotional balance and strengthens interpersonal bonds by fostering empathy and shared understanding.
Emotional Regulation in Child Development
Emotional regulation in child development involves a child's ability to manage and respond to their emotional experiences effectively, fostering resilience and social competence. Emotional co-regulation occurs when caregivers and children work together to navigate emotions, providing external support that gradually leads to independent emotional control. Your role in supporting emotional regulation helps children build lifelong skills for managing feelings, improving mental health, and forming healthy relationships.
The Role of Caregivers in Emotional Co-Regulation
Emotional co-regulation involves caregivers actively supporting and guiding children's emotional experiences, helping them manage distress and develop self-regulation skills through responsive interactions. Unlike emotional regulation, which refers to an individual's ability to manage their feelings independently, emotional co-regulation is a relational process where caregivers provide external regulatory support to facilitate emotional stability. The role of caregivers in emotional co-regulation is crucial, as consistent and sensitive responses promote secure attachments and enhance children's long-term emotional competence.
Practical Strategies for Enhancing Emotional Regulation
Emotional regulation involves an individual's ability to monitor, evaluate, and modify emotional reactions to achieve goals or maintain well-being, while emotional co-regulation refers to mutual regulation occurring between two or more individuals, typically seen in caregiver-child interactions or close relationships. Practical strategies for enhancing emotional regulation include mindfulness practices, cognitive reappraisal techniques, and self-soothing activities such as deep breathing or progressive muscle relaxation. For emotional co-regulation, fostering secure attachment, active listening, and empathetic communication help partners or caregivers model and support adaptive emotional responses.
Benefits of Emotional Co-Regulation for Mental Health
Emotional co-regulation involves mutual support and shared emotional management between individuals, enhancing resilience and reducing stress more effectively than individual emotional regulation. Your mental health benefits from emotional co-regulation through improved emotional understanding, decreased feelings of isolation, and strengthened social connections that promote psychological well-being. This collaborative process fosters adaptive coping strategies, leading to greater emotional stability and reduced risk of mental health disorders.
Integrating Emotional Regulation and Co-Regulation Skills
Emotional regulation involves individual strategies to manage and respond to emotional experiences effectively, while emotional co-regulation emphasizes the dynamic support between individuals, often between caregivers and children, to modulate emotions collaboratively. Integrating emotional regulation and co-regulation skills fosters resilience by combining personal coping mechanisms with interpersonal emotional support systems, enhancing overall emotional well-being. This integration leverages neurobiological processes and social interactions to create adaptive emotional responses across varying contexts.
Infographic: Emotional regulation vs Emotional co-regulation
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com