Stress tolerance measures how well an individual withstands stress without negative effects, while emotional resilience reflects the ability to recover and grow from emotional challenges. Explore this article to understand how balancing both traits enhances relationship health.
Table of Comparison
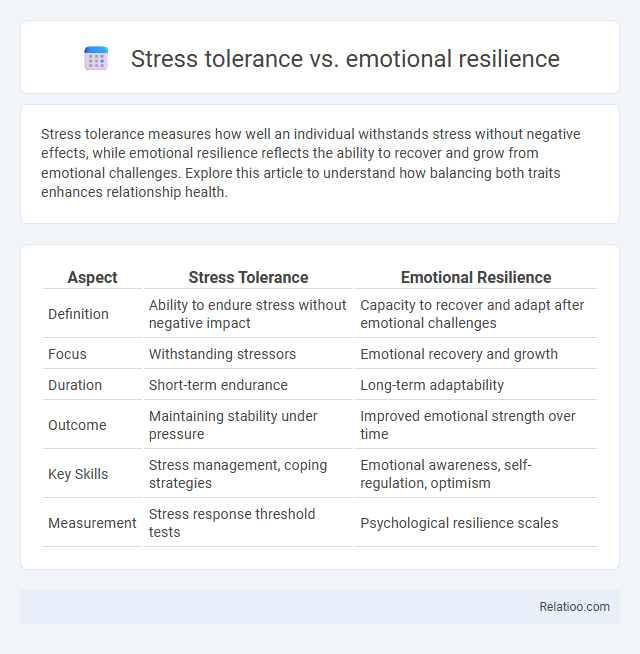
| Aspect | Stress Tolerance | Emotional Resilience |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Ability to endure stress without negative impact | Capacity to recover and adapt after emotional challenges |
| Focus | Withstanding stressors | Emotional recovery and growth |
| Duration | Short-term endurance | Long-term adaptability |
| Outcome | Maintaining stability under pressure | Improved emotional strength over time |
| Key Skills | Stress management, coping strategies | Emotional awareness, self-regulation, optimism |
| Measurement | Stress response threshold tests | Psychological resilience scales |
Understanding Stress Tolerance
Stress tolerance refers to the ability to endure stressful situations without significant negative effects on mental or physical health, emphasizing the capacity to manage external pressures effectively. Emotional resilience involves adapting to and recovering from emotional challenges, highlighting a dynamic process of bouncing back after stress. Understanding stress tolerance provides a foundation for developing strategies that enable individuals to maintain stability and functionality under prolonged or intense stress exposure.
Defining Emotional Resilience
Emotional resilience is the capacity to adapt and recover quickly from emotional stress, trauma, or adversity, enabling you to maintain psychological well-being despite challenges. While stress tolerance refers to the ability to endure stressful situations without adverse effects, emotional resilience involves actively managing emotions and bouncing back stronger. Developing emotional resilience enhances overall mental health by fostering positive coping strategies and reducing vulnerability to chronic stress.
Key Differences Between Stress Tolerance and Emotional Resilience
Stress tolerance refers to your ability to withstand stressful situations without feeling overwhelmed, while emotional resilience involves adapting positively to adversity and recovering from emotional setbacks. Key differences include stress tolerance being more about enduring pressure in the moment, whereas emotional resilience emphasizes long-term recovery and growth after challenges. Developing emotional resilience enhances your capacity to manage stress more effectively by transforming stressful experiences into opportunities for personal development.
Biological Foundations of Stress and Resilience
Stress tolerance and emotional resilience are distinct yet interconnected concepts rooted in the biological foundations of stress response systems. Stress tolerance primarily involves the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis regulating cortisol release to manage acute stress, while emotional resilience encompasses neuroplasticity, supported by the prefrontal cortex and amygdala interactions, enabling adaptive coping and recovery from chronic stress exposure. Genetic factors such as polymorphisms in the serotonin transporter gene and brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) play critical roles in modulating both stress tolerance and emotional resilience by influencing stress reactivity and neural adaptability.
Psychological Traits Influencing Each Quality
Stress tolerance is characterized by an individual's ability to withstand high-pressure situations without experiencing performance decline, often linked to physiological traits such as cortisol regulation and autonomic nervous system balance. Emotional resilience involves adaptive psychological traits including cognitive flexibility, optimism, and the capacity for emotional regulation that enable effective recovery from adversity. While stress tolerance emphasizes enduring stress, emotional resilience integrates coping mechanisms and positive reframing, highlighting the importance of traits like self-efficacy and social support in moderating stress responses.
Measuring Stress Tolerance and Emotional Resilience
Measuring stress tolerance involves assessing your physiological and psychological responses to pressure, often through biomarkers like cortisol levels and self-reported coping scales. Emotional resilience measurement focuses on your ability to bounce back from adversity, using tools such as resilience questionnaires and evaluations of emotional regulation skills. Both metrics provide valuable insights into how well you manage stress and recover from challenging situations, informing personalized strategies for mental well-being.
Impact on Mental and Physical Health
Stress tolerance refers to your ability to endure stressful situations without immediate breakdown, which affects physical health by influencing cortisol levels and cardiovascular function. Emotional resilience involves adapting effectively to adversity, promoting long-term mental well-being by enhancing mood regulation and reducing the risk of anxiety and depression. Both qualities are crucial for maintaining balanced mental and physical health, but emotional resilience provides a deeper protective impact through sustained psychological recovery and overall life satisfaction.
Strategies for Building Stress Tolerance
Stress tolerance involves your body's ability to endure physical or psychological stress without adverse effects, while emotional resilience refers to your capacity to adapt and recover from emotional challenges. Effective strategies for building stress tolerance include regular physical exercise to boost physiological resistance, mindfulness practices to regulate stress responses, and developing a structured routine to enhance predictability and control. Incorporating stress management techniques such as deep breathing, time management, and social support can strengthen your ability to withstand and thrive under pressure.
Techniques to Enhance Emotional Resilience
Emotional resilience involves adapting effectively to stress and adversity by managing your emotional responses, while stress tolerance primarily refers to your capacity to endure stressful situations without negative health effects. Techniques to enhance emotional resilience include practicing mindfulness meditation, developing strong social connections, and engaging in cognitive-behavioral strategies to reframe negative thoughts. Building these skills helps you maintain psychological well-being and bounce back more quickly from life's challenges.
Integrating Stress Tolerance and Resilience for Well-being
Integrating stress tolerance and emotional resilience enhances overall well-being by enabling individuals to effectively manage pressure and recover from adversity. Stress tolerance involves the capacity to endure challenging situations without immediate emotional disruption, while emotional resilience focuses on bouncing back and adapting after stress exposure. Combining these skills promotes sustained mental health, improved coping strategies, and greater psychological flexibility in diverse stressful environments.
Infographic: Stress tolerance vs Emotional resilience
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com