Stress tolerance enhances resilience by enabling individuals to withstand high-pressure situations without becoming overwhelmed. Emotional regulation improves decision-making and interpersonal interactions by managing emotional responses effectively; discover more about balancing these skills in this article.
Table of Comparison
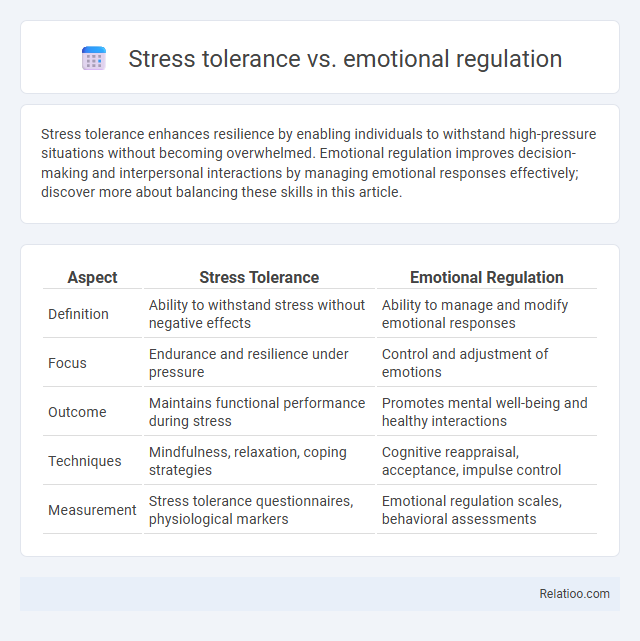
| Aspect | Stress Tolerance | Emotional Regulation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Ability to withstand stress without negative effects | Ability to manage and modify emotional responses |
| Focus | Endurance and resilience under pressure | Control and adjustment of emotions |
| Outcome | Maintains functional performance during stress | Promotes mental well-being and healthy interactions |
| Techniques | Mindfulness, relaxation, coping strategies | Cognitive reappraisal, acceptance, impulse control |
| Measurement | Stress tolerance questionnaires, physiological markers | Emotional regulation scales, behavioral assessments |
Understanding Stress Tolerance: Definition and Importance
Stress tolerance refers to your ability to withstand pressure and maintain performance during challenging situations, which is crucial for mental resilience and overall well-being. Emotional regulation involves managing and responding to emotional experiences effectively but is a component within the broader concept of stress tolerance. Understanding stress tolerance helps you develop strategies to cope better with adversity, preventing burnout and enhancing productivity.
Emotional Regulation: Key Concepts and Mechanisms
Emotional regulation involves managing and responding to your emotional experiences in a healthy and adaptive way, distinct from stress tolerance which primarily focuses on enduring stress without negative effects. Key concepts in emotional regulation include awareness of emotions, cognitive reappraisal, and impulse control, which help modulate emotional intensity and persistence. Mechanisms underlying effective emotional regulation involve neural processes in the prefrontal cortex and amygdala, supporting your ability to shift perspectives and maintain emotional balance during challenging situations.
Stress Tolerance vs Emotional Regulation: Core Differences
Stress tolerance refers to an individual's capacity to endure stressful situations without experiencing significant emotional or physical harm, while emotional regulation involves actively managing and modifying emotional responses to stressors. Stress tolerance is primarily about resilience and enduring pressure, whereas emotional regulation centers on controlling the intensity and expression of emotions during stressful experiences. Understanding these core differences helps in developing strategies that either enhance one's ability to withstand stress or improve emotional control for better mental health outcomes.
Biological Roots of Stress Response and Emotion Control
Stress tolerance and emotional regulation share biological roots in the brain's limbic system, particularly within the amygdala and prefrontal cortex, which coordinate the stress response and emotion control. The hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis plays a crucial role in stress tolerance by regulating cortisol release, impacting how individuals physiologically handle stress. Emotional regulation relies on neural circuits that modulate the intensity and duration of emotional reactions, balancing activation in the amygdala with top-down control from the prefrontal cortex to maintain psychological resilience.
Psychological Factors Influencing Stress Tolerance and Emotional Regulation
Psychological factors influencing stress tolerance and emotional regulation include individual differences in cognitive appraisal, coping mechanisms, and resilience. Effective emotional regulation enhances stress tolerance by enabling adaptive responses to stressors through skills like mindfulness and cognitive reappraisal. Neurobiological factors such as prefrontal cortex functioning also play a crucial role in modulating both stress tolerance and emotional regulation capabilities.
Techniques to Build Stress Tolerance
Techniques to build stress tolerance include gradual exposure to stressors, mindfulness meditation, and physical exercise, which enhance the body's resilience to pressure. Developing stress tolerance involves strengthening physiological and psychological responses to stress through controlled breathing, progressive muscle relaxation, and cognitive restructuring. Unlike emotional regulation, which focuses on managing emotional responses, stress tolerance emphasizes enduring and adapting to stress while maintaining functionality.
Strategies to Enhance Emotional Regulation Skills
Enhancing emotional regulation skills involves techniques such as mindfulness meditation, cognitive reappraisal, and deep breathing exercises, which reduce emotional reactivity and improve stress resilience. Developing awareness of emotional triggers and practicing adaptive coping strategies strengthen the ability to manage intense feelings effectively. Consistent use of these strategies supports better mental health and promotes balanced responses to stressors in daily life.
Impact on Mental Health: Stress Tolerance vs Emotional Regulation
Stress tolerance refers to the ability to endure and manage stress without significant psychological distress, while emotional regulation involves controlling and modifying emotional responses to stressors. Effective emotional regulation often leads to reduced symptoms of anxiety and depression by promoting adaptive coping mechanisms, whereas high stress tolerance alone may mask underlying emotional challenges. Research indicates that integrating emotional regulation strategies enhances mental health outcomes more significantly than relying solely on stress tolerance.
Real-Life Scenarios: Applying Stress Tolerance and Emotional Regulation
Stress tolerance enables you to withstand high-pressure situations without losing composure, such as managing multiple deadlines at work, while emotional regulation helps in recognizing and controlling the emotional responses triggered by stress. In real-life scenarios, combining stress tolerance with emotional regulation enhances decision-making under pressure and improves interpersonal interactions during conflicts. Practicing both skills allows your mind and body to respond adaptively, reducing the negative impact of stress on mental health and overall performance.
Integrating Both Skills for Resilience and Wellbeing
Integrating stress tolerance and emotional regulation enhances resilience by enabling individuals to withstand pressure while managing their emotional responses effectively. Stress tolerance builds the capacity to endure challenging situations without becoming overwhelmed, whereas emotional regulation helps maintain balanced reactions and prevent negative spirals. Combining these skills fosters psychological well-being, promotes adaptive coping strategies, and strengthens overall mental health during adversity.
Infographic: Stress tolerance vs Emotional regulation
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com