Stress tolerance refers to the ability to manage everyday pressures without becoming overwhelmed, while distress tolerance involves enduring and coping with intense emotional pain during crises. Explore this article to understand how these skills impact relationship stability and emotional resilience.
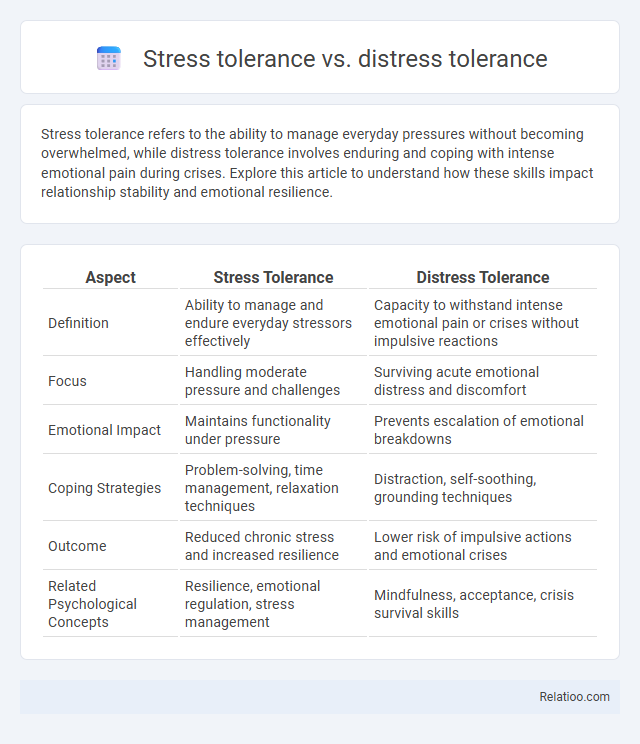
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Stress Tolerance | Distress Tolerance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Ability to manage and endure everyday stressors effectively | Capacity to withstand intense emotional pain or crises without impulsive reactions |
| Focus | Handling moderate pressure and challenges | Surviving acute emotional distress and discomfort |
| Emotional Impact | Maintains functionality under pressure | Prevents escalation of emotional breakdowns |
| Coping Strategies | Problem-solving, time management, relaxation techniques | Distraction, self-soothing, grounding techniques |
| Outcome | Reduced chronic stress and increased resilience | Lower risk of impulsive actions and emotional crises |
| Related Psychological Concepts | Resilience, emotional regulation, stress management | Mindfulness, acceptance, crisis survival skills |
Understanding Stress Tolerance vs Distress Tolerance
Understanding stress tolerance involves recognizing your ability to manage and cope with everyday pressures and challenges without becoming overwhelmed. Distress tolerance, a subset of stress management skills, specifically refers to how well you can survive and endure acute emotional pain or crisis situations without resorting to harmful behaviors. Developing both stress tolerance and distress tolerance enhances your overall emotional resilience, enabling you to navigate life's stresses effectively.
Defining Stress Tolerance: Key Concepts
Stress tolerance refers to Your ability to withstand and effectively manage stress without significant negative impact on mental or physical health. It involves adaptive coping mechanisms, resilience, and maintaining performance under pressure. Distress tolerance, in contrast, specifically addresses how well You can endure emotional pain or discomfort, often without resorting to maladaptive behaviors.
What is Distress Tolerance?
Distress tolerance refers to your ability to endure and manage intense emotional pain or discomfort without resorting to harmful behaviors. Unlike general stress tolerance, which involves coping with daily pressures and challenges, distress tolerance specifically targets acute emotional crises and the capacity to stay grounded during overwhelming situations. Developing strong distress tolerance skills helps you maintain control and make rational decisions even when faced with severe psychological distress.
Differences Between Stress and Distress Tolerance
Stress tolerance refers to the ability to manage and function effectively under stressful conditions, while distress tolerance specifically involves enduring and coping with emotional pain and negative feelings without resorting to harmful behaviors. The key difference lies in stress tolerance encompassing both physical and psychological stress management, whereas distress tolerance centers on emotional regulation during intense negative experiences. Understanding these distinctions helps in developing targeted coping strategies for overall mental resilience and emotional health.
Psychological Mechanisms of Stress Tolerance
Stress tolerance involves an individual's capacity to manage and adapt to stressors through psychological mechanisms such as cognitive appraisal, emotional regulation, and resilience building, enabling effective coping without significant mental health decline. Distress tolerance specifically refers to the ability to endure negative emotional states, emphasizing acceptance and mindfulness strategies to reduce maladaptive responses like avoidance or substance use. These psychological mechanisms underpin stress tolerance by facilitating adaptive responses, enhancing emotional flexibility, and promoting sustained well-being amid challenging circumstances.
Core Skills in Distress Tolerance
Core skills in distress tolerance emphasize mindfulness, self-soothing, and crisis survival strategies to manage emotional pain without making situations worse. These skills help regulate intense feelings and maintain psychological resilience during distressing moments. Stress tolerance broadly refers to enduring pressure, while distress tolerance specifically addresses managing emotional suffering using targeted coping techniques.
Causes of Low Stress and Distress Tolerance
Low stress tolerance often results from chronic exposure to high-pressure environments or inadequate coping mechanisms, leading to heightened physiological and psychological responses. Distress tolerance deficits typically stem from unresolved trauma, negative thought patterns, or insufficient emotional regulation skills, impairing an individual's ability to withstand painful emotions. Both low stress and distress tolerance increase vulnerability to anxiety disorders, depression, and impaired decision-making under pressure.
Strategies to Improve Stress Tolerance
Stress tolerance involves your ability to endure and manage pressure without becoming overwhelmed, while distress tolerance refers to coping with intense emotional pain in crisis situations. Strategies to improve stress tolerance include practicing mindfulness meditation, engaging in regular physical activity, and developing problem-solving skills to increase resilience. Building a strong social support network and maintaining a healthy lifestyle with balanced nutrition and adequate sleep also enhance your capacity to handle stress effectively.
Effective Techniques for Distress Tolerance
Effective techniques for distress tolerance emphasize managing intense emotional pain without worsening the situation, often using grounding exercises, deep breathing, and mindfulness to remain present and calm. Unlike general stress tolerance, which involves coping with everyday pressures, distress tolerance specifically targets acute emotional crises by promoting acceptance and self-soothing strategies. By incorporating these methods, your ability to navigate overwhelming feelings improves, preventing harmful reactions and maintaining emotional balance.
Building Resilience: Integrating Both Tolerances
Building resilience involves integrating stress tolerance and distress tolerance to effectively manage adversity. Stress tolerance helps you cope with everyday pressures by maintaining calm and focus under challenging conditions, while distress tolerance equips you to endure and survive intense emotional pain without impulsive reactions. Developing both tolerances enhances your capacity to navigate stress and emotional upheaval, fostering long-term psychological strength and adaptability.
Infographic: Stress tolerance vs Distress tolerance
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com