Reappraisal enhances emotional resilience by reframing negative experiences, while rumination intensifies distress through repetitive negative thinking. Discover effective strategies to strengthen your emotional well-being in this article.
Table of Comparison
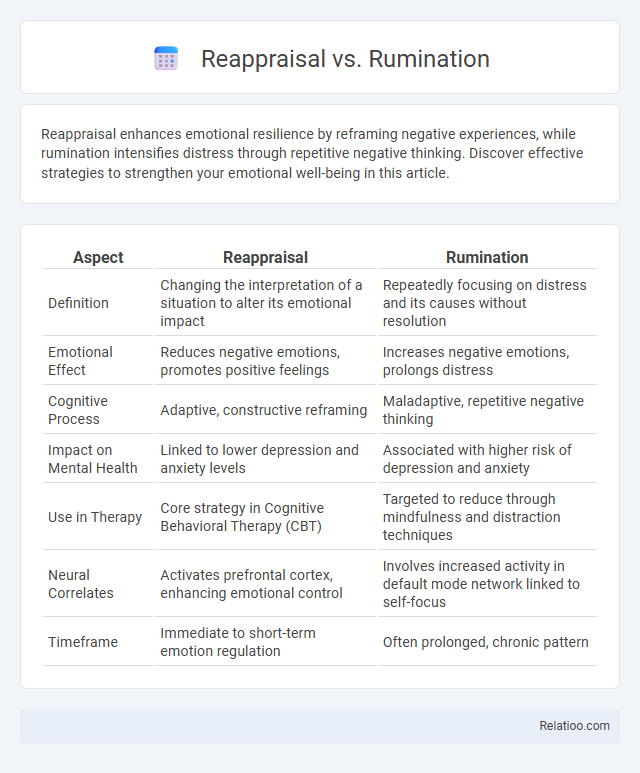
| Aspect | Reappraisal | Rumination |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Changing the interpretation of a situation to alter its emotional impact | Repeatedly focusing on distress and its causes without resolution |
| Emotional Effect | Reduces negative emotions, promotes positive feelings | Increases negative emotions, prolongs distress |
| Cognitive Process | Adaptive, constructive reframing | Maladaptive, repetitive negative thinking |
| Impact on Mental Health | Linked to lower depression and anxiety levels | Associated with higher risk of depression and anxiety |
| Use in Therapy | Core strategy in Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) | Targeted to reduce through mindfulness and distraction techniques |
| Neural Correlates | Activates prefrontal cortex, enhancing emotional control | Involves increased activity in default mode network linked to self-focus |
| Timeframe | Immediate to short-term emotion regulation | Often prolonged, chronic pattern |
Introduction to Reappraisal and Rumination
Reappraisal involves consciously changing the way you interpret a situation to alter its emotional impact, promoting healthier emotional regulation and resilience. Rumination, by contrast, entails repetitive and passive focus on negative feelings and their causes, often intensifying stress and prolonging emotional distress. Understanding the distinct mechanisms of reappraisal and rumination helps you develop effective strategies for managing emotions and improving mental well-being.
Defining Reappraisal: A Cognitive Strategy
Reappraisal is a cognitive strategy that involves changing the way one interprets a situation to alter its emotional impact, often leading to reduced negative emotions and enhanced psychological resilience. Unlike rumination, which involves repetitive and passive focus on distressing thoughts, reappraisal actively reframes the context to promote adaptive thinking. Effective use of reappraisal is linked to improved emotional regulation, mental health outcomes, and decreased risk of anxiety and depression.
Understanding Rumination: Patterns and Pitfalls
Rumination involves repetitive, passive focus on distress and its causes, often leading to heightened anxiety and depression, whereas reappraisal actively changes the interpretation of a situation to reduce emotional impact. Understanding rumination requires recognizing its patterns, such as dwelling on negative thoughts without problem-solving, which can trap Your mind in cycles of worry. Escaping these pitfalls involves adopting cognitive strategies like reappraisal to shift perspective and promote emotional resilience.
Psychological Impact: Reappraisal vs Rumination
Reappraisal, a cognitive strategy involving reframing negative situations, significantly reduces stress and enhances emotional regulation by promoting adaptive thinking patterns. Rumination, characterized by repetitive and passive focus on distress, exacerbates anxiety and depression through sustained negative mood and impaired problem-solving. Studies link reappraisal with lower physiological arousal and improved mental resilience, contrasting with rumination's association with increased cortisol levels and prolonged emotional distress.
Neural Mechanisms Behind Each Process
Reappraisal engages the prefrontal cortex to regulate emotional responses by reframing negative stimuli, promoting adaptive coping. Rumination activates the default mode network, particularly the medial prefrontal cortex, leading to persistent negative thought patterns and heightened emotional distress. Understanding these distinct neural mechanisms helps you develop strategies to shift from rumination to reappraisal, enhancing emotional resilience.
Effects on Mental Health and Well-being
Reappraisal, a cognitive emotion regulation strategy, involves reframing a situation to alter its emotional impact, typically reducing stress and enhancing well-being by promoting adaptive coping and resilience. Rumination, characterized by repetitive and passive focus on distress and its causes, correlates with increased symptoms of depression and anxiety, impairing mental health and hindering effective problem-solving. Compared to rumination, reappraisal fosters positive emotional outcomes and psychological flexibility, making it a more beneficial approach for maintaining long-term mental health and overall well-being.
Practical Techniques for Reappraisal
Effective practical techniques for reappraisal involve consciously reframing negative thoughts by identifying alternative, positive interpretations of stressful events. Mindfulness practices and cognitive-behavioral strategies help individuals recognize and challenge unhelpful thought patterns, fostering adaptive emotional regulation. Regular use of these techniques reduces rumination, promotes psychological resilience, and enhances overall mental well-being.
Risks Associated with Persistent Rumination
Persistent rumination is linked to increased risks of depression, anxiety, and impaired cognitive functioning due to repetitive focus on negative thoughts. In contrast, reappraisal involves reframing thoughts to reduce emotional distress and promote psychological resilience. While reappraisal fosters adaptive coping mechanisms, ongoing rumination perpetuates negative mood states and exacerbates mental health vulnerabilities.
Choosing the Right Strategy for Emotional Regulation
Reappraisal involves reframing a situation to alter its emotional impact, promoting adaptive emotional regulation and reducing stress. Rumination, characterized by repetitive and passive focus on distress, often exacerbates negative emotions and prolongs psychological distress. Choosing the right strategy depends on context and individual traits, with cognitive reappraisal typically yielding better mental health outcomes compared to rumination, which can increase vulnerability to anxiety and depression.
Summary: Key Differences and Takeaways
Reappraisal involves actively changing one's interpretation of a situation to alter its emotional impact, promoting adaptive coping and emotional regulation. Rumination entails repetitive, passive focus on negative feelings and events, often intensifying distress and contributing to anxiety or depression. The key difference lies in cognitive engagement: reappraisal fosters constructive reframing, whereas rumination reinforces negative thought patterns without resolution.
Infographic: Reappraisal vs Rumination
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com