Stress tolerance significantly enhances relationship stability by allowing partners to manage pressure without conflict. Explore deeper insights into balancing stress tolerance and self-control for healthier connections in this article.
Table of Comparison
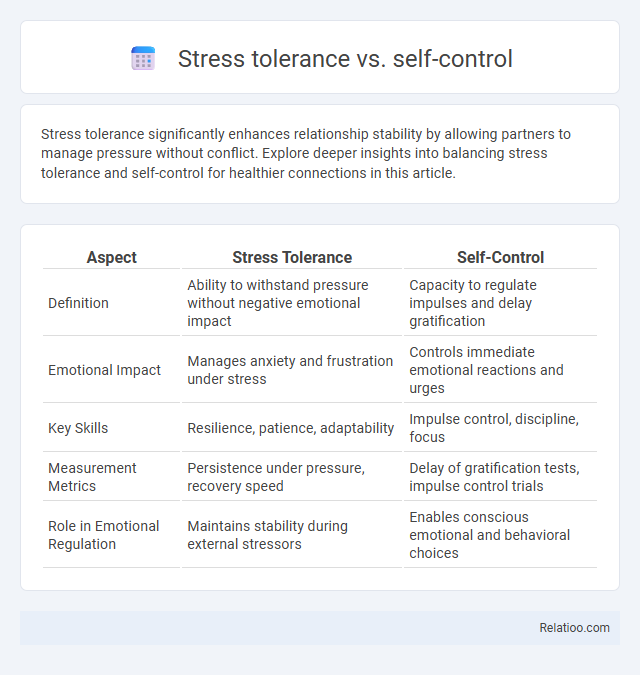
| Aspect | Stress Tolerance | Self-Control |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Ability to withstand pressure without negative emotional impact | Capacity to regulate impulses and delay gratification |
| Emotional Impact | Manages anxiety and frustration under stress | Controls immediate emotional reactions and urges |
| Key Skills | Resilience, patience, adaptability | Impulse control, discipline, focus |
| Measurement Metrics | Persistence under pressure, recovery speed | Delay of gratification tests, impulse control trials |
| Role in Emotional Regulation | Maintains stability during external stressors | Enables conscious emotional and behavioral choices |
Understanding Stress Tolerance and Self-Control
Stress tolerance refers to an individual's ability to endure and manage stress without becoming overwhelmed, while self-control involves regulating emotions, thoughts, and behaviors to achieve long-term goals despite immediate stressors. Understanding stress tolerance helps identify how much pressure a person can withstand before performance deteriorates, whereas self-control empowers individuals to maintain focus and make rational decisions under stress. Enhancing both stress tolerance and self-control contributes to improved mental resilience and effective stress management strategies.
Defining Stress Tolerance
Stress tolerance is the ability to endure and manage pressure or adverse conditions without experiencing negative emotional or physical effects. Unlike self-control, which primarily involves regulating impulses and behaviors, stress tolerance emphasizes resilience and adaptability during challenging situations. Your capacity for stress tolerance directly influences mental well-being and performance under pressure.
Defining Self-Control
Self-control is the ability to regulate one's emotions, thoughts, and behaviors in the face of temptations and impulses, enabling goal-oriented actions despite stress or adversity. Stress tolerance refers to an individual's capacity to withstand or manage stress without negative effects, while self-control actively modulates responses to stressors through conscious regulation. Effective self-control enhances stress tolerance by fostering resilience and adaptive coping mechanisms.
Key Differences Between Stress Tolerance and Self-Control
Stress tolerance refers to your ability to endure and adapt to stressful situations without becoming overwhelmed, while self-control involves regulating impulses, emotions, and behaviors to maintain focus and discipline. Stress tolerance primarily manages the external pressure and emotional resilience, whereas self-control governs internal commands and decision-making processes. Understanding these distinctions helps improve coping strategies by targeting either endurance in adversity or conscious behavioral regulation.
Biological Foundations of Stress Tolerance
Stress tolerance is fundamentally linked to the biological regulation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis, which modulates cortisol secretion in response to stressors, thereby influencing an individual's capacity to withstand stress. Self-control, while related to cognitive processes like executive function and prefrontal cortex activity, primarily governs impulse regulation rather than physiological stress reactivity. Understanding the neuroendocrine mechanisms underlying stress tolerance provides insights into resilience by highlighting how the autonomic nervous system and genetic factors contribute to an organism's ability to adapt to environmental challenges.
Psychological Mechanisms of Self-Control
Stress tolerance reflects your ability to endure high-pressure situations without significant emotional disturbance, while self-control involves actively regulating impulses and emotions to achieve long-term goals. Psychological mechanisms of self-control engage the prefrontal cortex, enhancing cognitive processes like attention regulation, inhibitory control, and decision-making. This neural activity supports stress tolerance by helping you manage emotional reactions and maintain focus under stress.
Real-Life Examples: Stress Tolerance vs Self-Control
Stress tolerance allows you to remain calm and effective during pressure, such as managing multiple deadlines at work without losing focus, while self-control involves regulating impulsive reactions, like resisting the urge to respond angrily in a heated meeting. For instance, a nurse demonstrating stress tolerance maintains composure during emergencies, whereas self-control helps them avoid burnout by managing emotional responses. Both skills complement each other in real-life scenarios where balancing emotional resilience and disciplined behavior is crucial for success and well-being.
How to Cultivate Stress Tolerance
Cultivating stress tolerance involves practicing mindfulness techniques that enhance emotional regulation and resilience during high-pressure situations. Developing consistent habits like regular physical exercise, adequate sleep, and balanced nutrition strengthens the body's response to stress. Incorporating cognitive-behavioral strategies, such as reframing negative thoughts, promotes sustained mental endurance and reduces susceptibility to stress-related disorders.
Strategies to Improve Self-Control
Stress tolerance involves enduring pressure without negative effects, while self-control is the ability to regulate impulses and maintain focus on long-term goals. Strategies to improve self-control include practicing mindfulness, setting clear goals, and employing techniques like delayed gratification and self-monitoring. Your ability to strengthen self-control enhances resilience against stress and improves decision-making under pressure.
Integrating Both Traits for Personal Growth
Balancing stress tolerance and self-control enhances your ability to manage challenges and maintain emotional stability under pressure. Developing stress tolerance enables resilience against external pressures, while self-control fosters disciplined responses to internal impulses and distractions. Integrating both traits cultivates a holistic approach to personal growth by improving adaptability and decision-making in high-stress situations.
Infographic: Stress tolerance vs Self-control
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com