Emotional numbing involves a reduced ability to experience feelings, often leading to detachment in relationships, while emotional suppression is the conscious effort to hide or control emotions to manage interpersonal dynamics. Explore the differences and impacts of these emotional responses on relationships in this article.
Table of Comparison
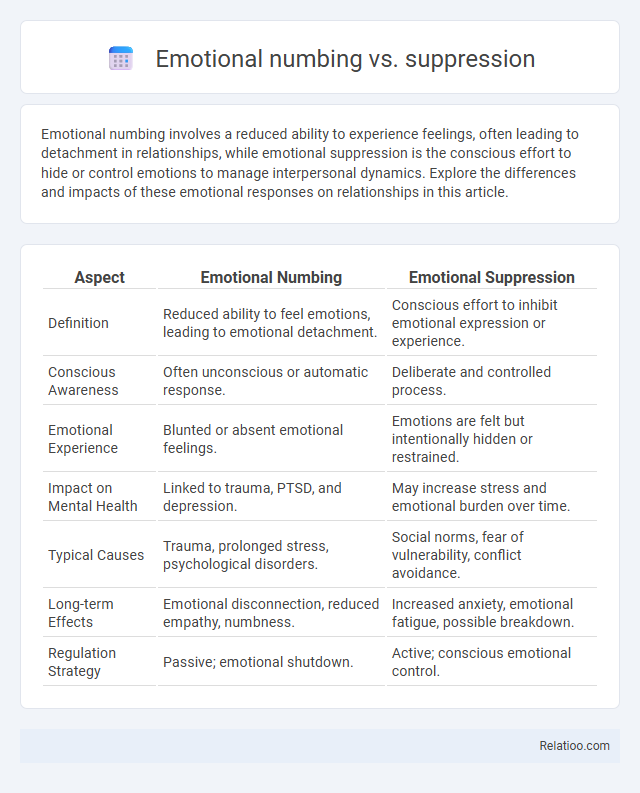
| Aspect | Emotional Numbing | Emotional Suppression |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Reduced ability to feel emotions, leading to emotional detachment. | Conscious effort to inhibit emotional expression or experience. |
| Conscious Awareness | Often unconscious or automatic response. | Deliberate and controlled process. |
| Emotional Experience | Blunted or absent emotional feelings. | Emotions are felt but intentionally hidden or restrained. |
| Impact on Mental Health | Linked to trauma, PTSD, and depression. | May increase stress and emotional burden over time. |
| Typical Causes | Trauma, prolonged stress, psychological disorders. | Social norms, fear of vulnerability, conflict avoidance. |
| Long-term Effects | Emotional disconnection, reduced empathy, numbness. | Increased anxiety, emotional fatigue, possible breakdown. |
| Regulation Strategy | Passive; emotional shutdown. | Active; conscious emotional control. |
Understanding Emotional Numbing
Emotional numbing involves a reduced ability to experience feelings, often linked to trauma or stress, distinguishing it from suppression, which is the conscious effort to avoid or control emotions. Understanding emotional numbing requires recognizing its impact on mental health, including decreased emotional responsiveness and difficulty connecting with others. Unlike suppression, emotional numbing is an involuntary condition that can hinder emotional healing and requires specific therapeutic interventions.
Defining Emotional Suppression
Emotional suppression involves consciously pushing down or avoiding feelings to manage emotional responses, differing from emotional numbing, which is an unconscious blunting of emotions often linked to trauma or stress. Emotional numbing reduces your capacity to experience a full range of feelings, whereas emotional suppression requires active effort to hide or control emotions. Understanding these distinctions helps you recognize whether emotional avoidance is a deliberate strategy or an automatic defense mechanism.
Key Differences Between Numbing and Suppression
Emotional numbing involves a diminished ability to feel emotions, often linked to trauma or depression, leading to a general emotional blunting. Emotional suppression is a conscious effort to push away or hide specific feelings in response to stress or discomfort. The key difference lies in numbing being an involuntary, persistent state reducing emotional responsiveness, whereas suppression is a deliberate, temporary strategy to manage emotional expression.
Psychological Causes of Emotional Numbing
Emotional numbing involves a reduced ability to feel emotions, often linked to trauma, PTSD, or depression, which your brain uses as a defense mechanism to protect you from overwhelming pain. Emotional suppression is a conscious effort to push away emotions, while emotional numbing is more automatic and unconscious, arising from psychological causes such as chronic stress, anxiety, or early-life adversity. Understanding these distinctions helps in addressing underlying psychological factors contributing to emotional numbing and promotes more effective therapeutic interventions.
Common Triggers for Emotional Suppression
Emotional suppression often occurs as a response to stressors such as trauma, chronic anxiety, or overwhelming social situations. Common triggers include experiences of rejection, fear of vulnerability, or exposure to conflict, which lead your mind to deliberately block or hide feelings to maintain control. Emotional numbing, unlike suppression, is an unconscious process where your sensitivity to emotions diminishes, often resulting from prolonged trauma or emotional exhaustion.
Signs and Symptoms: Numbing vs Suppression
Emotional numbing manifests as a reduced ability to feel emotions, often showing signs like emotional detachment, lack of responsiveness, and diminished pleasure in activities. Emotional suppression involves consciously pushing down feelings, leading to symptoms such as increased stress, muscle tension, and difficulty expressing emotions. Your awareness of these signs can help differentiate between involuntary numbing and deliberate suppression, guiding appropriate emotional support or therapy.
Emotional Impact on Mental Health
Emotional numbing, suppression, and repression differ significantly in how they affect mental health: emotional numbing leads to a pervasive inability to feel positive or negative emotions, often resulting in feelings of detachment and increased risk of depression or anxiety disorders. Suppression involves consciously pushing emotions aside, which can create stress and emotional exhaustion over time by preventing healthy emotional processing. Understanding these differences is crucial for your mental well-being, as unresolved emotional numbing or suppression may escalate into chronic psychological issues requiring professional intervention.
Long-Term Consequences of Avoiding Emotions
Emotional numbing, suppression, and avoidance each disrupt healthy emotional processing, leading to significant long-term consequences such as increased risk of anxiety, depression, and impaired interpersonal relationships. Chronic emotional numbing blunts the ability to experience pleasure and connection, while suppression often results in heightened physiological stress and reduced emotional resilience. Prolonged avoidance of emotions compromises mental health by preventing effective coping mechanisms, ultimately exacerbating emotional distress and diminishing overall well-being.
Strategies to Overcome Emotional Numbing and Suppression
Emotional numbing and suppression both involve diminishing the experience of emotions, with numbing often resulting from trauma and suppression being a conscious effort to avoid feelings. Effective strategies to overcome emotional numbing include mindfulness practices, trauma-focused therapy such as EMDR, and reconnecting with emotional triggers in safe environments. For emotional suppression, cognitive-behavioral techniques, journaling, and expressive therapies help individuals acknowledge and process repressed emotions to restore emotional balance.
Professional Approaches for Emotional Healing
Professional approaches for emotional healing distinguish between emotional numbing, suppression, and emotional avoidance to tailor effective interventions. Therapists utilize techniques such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) to address emotional suppression by helping clients recognize and express feelings appropriately, while trauma-focused therapies like EMDR target emotional numbing by processing unresolved traumatic memories. Mindfulness-based interventions support emotional awareness, reducing avoidance patterns and fostering healthy emotional regulation critical for sustained psychological well-being.
Infographic: Emotional numbing vs suppression
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com