Triggers are external events or situations that activate specific emotions, often rooted in past experiences. Understanding how triggers influence emotional responses is crucial for managing relationships effectively; learn more in this article.
Table of Comparison
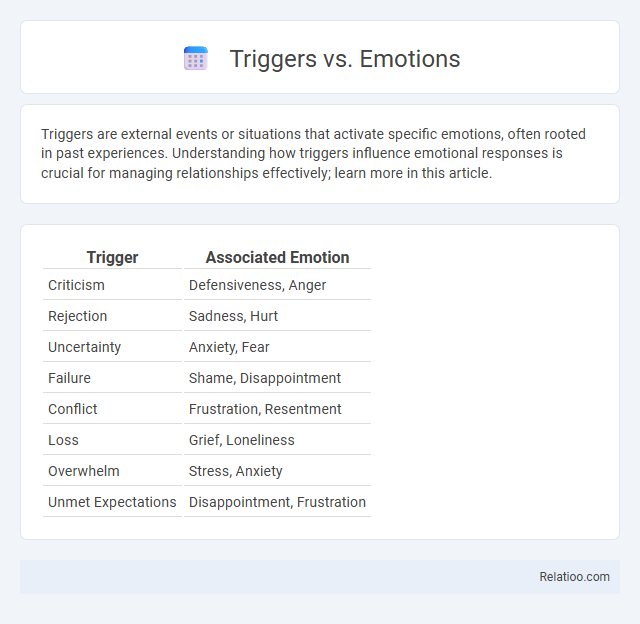
| Trigger | Associated Emotion |
|---|---|
| Criticism | Defensiveness, Anger |
| Rejection | Sadness, Hurt |
| Uncertainty | Anxiety, Fear |
| Failure | Shame, Disappointment |
| Conflict | Frustration, Resentment |
| Loss | Grief, Loneliness |
| Overwhelm | Stress, Anxiety |
| Unmet Expectations | Disappointment, Frustration |
Understanding Triggers: Definition and Examples
Triggers are specific stimuli or events that provoke intense emotional reactions, often rooted in past experiences or trauma. Emotions are the internal feelings such as anger, sadness, or anxiety that arise in response to these triggers, serving as signals for underlying psychological states. Understanding triggers involves identifying these external or internal cues and recognizing their connection to emotional responses to better manage reactions and promote emotional regulation.
What Are Emotions? A Brief Overview
Emotions are complex psychological and physiological responses that influence your thoughts, behaviors, and decision-making processes. They arise from the brain's interpretation of internal and external stimuli, distinguishing them from triggers, which are specific events or situations that activate emotional reactions. Understanding emotions helps you recognize how triggers can evoke different emotional experiences, enabling better emotional regulation and self-awareness.
Key Differences Between Triggers and Emotions
Triggers are external stimuli or events that provoke an immediate emotional response, while emotions are internal psychological states influenced by both triggers and personal experiences. Your emotional reactions are shaped by how you interpret triggers, meaning the same trigger can cause different emotions in different individuals. Understanding this distinction helps you manage emotional responses more effectively by identifying the source of your feelings and addressing them appropriately.
How Triggers Activate Emotional Responses
Triggers activate emotional responses by stimulating specific neural pathways associated with past experiences stored in your brain, often linked to trauma or strong memories. When a trigger occurs, it rapidly engages the amygdala, causing an immediate emotional reaction that can range from anxiety to anger or fear. Understanding how triggers interact with emotions is essential for managing your responses and achieving emotional regulation.
The Role of Personal History in Triggers and Emotions
Personal history shapes the intensity and type of emotional triggers individuals experience by linking specific past events to current reactions. Traumatic experiences or significant life moments create neural pathways that heighten sensitivity to certain stimuli, making emotional triggers highly personalized. Understanding this connection helps in developing targeted coping strategies that address the root cause embedded in one's unique personal history.
Common Types of Triggers and Their Effects
Common types of triggers include environmental cues, sensory stimuli, and specific memories that can provoke intense emotional responses such as anxiety, anger, or sadness. These triggers often activate your brain's fight-or-flight response, leading to physiological changes like increased heart rate and heightened alertness. Understanding your triggers helps manage emotions effectively and reduces the impact of automatic reactions on your mental well-being.
Emotional Reactions: From Mild to Intense
Emotional reactions to triggers range from mild irritation to intense distress, influenced by individual sensitivity and past experiences. Triggers activate emotional responses by recalling memories or associations, which can escalate feelings from subtle discomfort to overwhelming anxiety or anger. Understanding the spectrum of emotional intensity helps in managing reactions and developing coping mechanisms tailored to personal trigger thresholds.
Managing Triggers: Techniques for Self-Regulation
Managing triggers is essential for effective self-regulation, as triggers are external or internal events that evoke emotional responses. Techniques such as mindfulness meditation, deep breathing, and cognitive reframing help you recognize and control reactions before emotions escalate. Developing awareness of your specific triggers enables targeted strategies that reduce impulsivity and enhance emotional resilience.
Building Emotional Awareness and Intelligence
Triggers are external or internal stimuli that provoke emotional reactions, while emotions are the feelings experienced in response to these triggers, shaping behavior and decision-making. Building emotional awareness involves recognizing and understanding these emotions as they arise, enabling better regulation and response to triggers. Developing emotional intelligence enhances self-awareness, empathy, and adaptive coping strategies, ultimately improving interpersonal relationships and mental well-being.
Healing and Growth: Transforming Triggers into Strength
Triggers often ignite intense emotional reactions rooted in past experiences, serving as signals for unresolved trauma or pain. Healing involves recognizing and understanding these emotional triggers to cultivate self-awareness and resilience. Transforming triggers into strengths fosters personal growth by reframing responses, enabling empowerment and emotional regulation.
Infographic: Triggers vs emotions
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com