Sarcasm is a sharp, often humorous expression intended to mock or convey contempt, while cynicism reflects a deep distrust in others' motives, often leading to pessimism about relationships. Explore how understanding these attitudes can impact your connections and communication in this article.
Table of Comparison
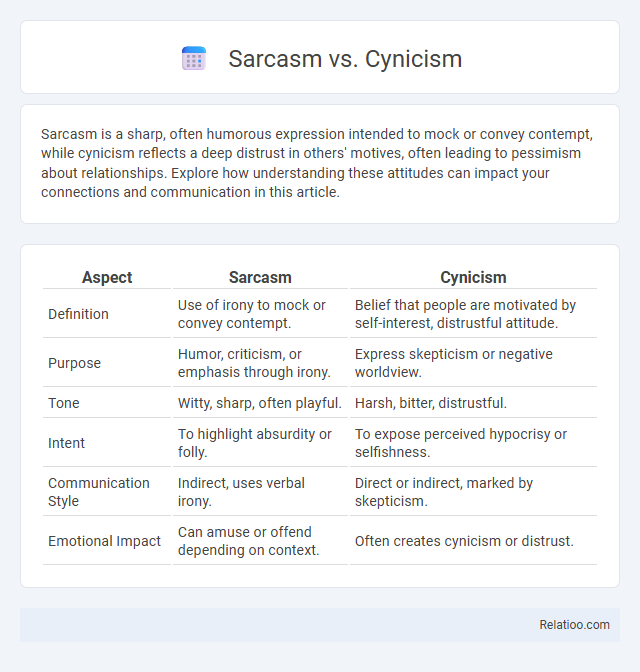
| Aspect | Sarcasm | Cynicism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Use of irony to mock or convey contempt. | Belief that people are motivated by self-interest, distrustful attitude. |
| Purpose | Humor, criticism, or emphasis through irony. | Express skepticism or negative worldview. |
| Tone | Witty, sharp, often playful. | Harsh, bitter, distrustful. |
| Intent | To highlight absurdity or folly. | To expose perceived hypocrisy or selfishness. |
| Communication Style | Indirect, uses verbal irony. | Direct or indirect, marked by skepticism. |
| Emotional Impact | Can amuse or offend depending on context. | Often creates cynicism or distrust. |
Defining Sarcasm: Meaning and Origins
Sarcasm is a form of verbal irony where speakers say the opposite of what they mean to mock or convey contempt, often relying on tone and context for interpretation. Its origins trace back to the Greek word "sarkasmos," meaning "to tear flesh," emphasizing its biting and cutting nature. Understanding sarcasm involves recognizing its intent to amuse or criticize, distinguishing it from cynicism, which reflects a distrustful or pessimistic worldview.
Cynicism Explained: History and Implications
Cynicism originated in ancient Greece with Diogenes, who rejected societal norms and materialism to pursue virtue through simplicity. Unlike sarcasm, which is a sharp, often humorous verbal irony, and skepticism, which questions the validity of claims, cynicism involves a deep distrust of human motives and a belief in inherent selfishness. Your understanding of cynicism reveals its lasting impact on philosophy, challenging assumptions about human nature and ethical behavior.
Key Differences Between Sarcasm and Cynicism
Sarcasm involves using sharp, often humorous remarks to mock or convey contempt, typically aimed at a specific situation or person. Cynicism reflects a general distrust or skepticism toward others' motives, often characterized by a pessimistic worldview that questions sincerity. Understanding these differences helps you recognize sarcasm as a linguistic tool for humor or criticism, while cynicism represents an underlying attitude of doubt and negativity.
Psychological Roots of Sarcasm
Sarcasm originates from complex psychological roots involving social cognition, emotional regulation, and humor as a defensive mechanism, distinguishing it from cynicism's general distrust and skepticism. Unlike cynicism, which reflects a consistent negative worldview, sarcasm often serves as a nuanced form of communication used to convey wit, irony, or criticism, sometimes masking genuine feelings. Understanding the psychological underpinnings of sarcasm can help you decode its intent, recognizing it as a layered expression influenced by both individual personality traits and social context.
The Philosophical Basis of Cynicism
The philosophical basis of Cynicism lies in the ancient Greek school founded by Antisthenes, emphasizing virtue, self-sufficiency, and living in accordance with nature while rejecting societal conventions and materialism. Sarcasm and irony, though often confused with cynicism, primarily function as linguistic tools for mockery or humor rather than as comprehensive life philosophies. Unlike sarcasm's sharp verbal wit and cynicism's broader worldview of skepticism toward human motives, philosophical cynicism advocates for a radical authenticity and ethical rigor rooted in Stoic principles.
Social Functions: How Sarcasm and Cynicism Shape Conversations
Sarcasm often functions as a social tool to convey humor, criticism, or irony, shaping conversations by revealing underlying attitudes and prompting reflection or laughter. Cynicism influences dialogues by expressing skepticism or distrust toward motives, impacting social dynamics through a critical or disillusioned lens that can challenge prevailing narratives. Both sarcasm and cynicism affect social interactions by either softening critique with wit or fostering doubt and critique, thus modulating the tone and direction of conversations.
Sarcasm vs Cynicism in Popular Culture
Sarcasm and cynicism often appear intertwined in popular culture but serve different purposes; sarcasm uses sharp, witty remarks to mock or convey contempt, while cynicism embodies a deeper skepticism about human motives and societal values. In movies, TV shows, and social media, sarcastic characters provide humor and social critique through clever dialogue, whereas cynical figures express distrust and pessimism about the world. Understanding the subtle differences enriches your appreciation of character dynamics and cultural commentary across various media.
Effects on Relationships and Communication
Sarcasm often creates confusion and misinterpretation in communication, leading to misunderstandings that can strain relationships due to its indirect and ironic nature. Cynicism fosters a negative outlook that erodes trust and openness, resulting in emotional distance and decreased empathy between individuals. While sarcasm can sometimes be playful or humorous, persistent cynicism tends to damage relational dynamics by promoting skepticism and disengagement.
How to Recognize Sarcasm and Cynicism
Sarcasm is recognized through tone of voice, exaggerated statements, and context where the literal meaning contradicts the speaker's intent, often used humorously or mockingly. Cynicism is identified by a general distrust or negative outlook on human motives, reflected in statements that express skepticism or disbelief in sincerity or goodness. Observing vocal inflections, facial expressions, and situational cues helps distinguish sarcasm's playful or biting humor from cynicism's deeper, more pervasive pessimism.
Navigating Sarcasm and Cynicism in Everyday Life
Navigating sarcasm and cynicism in everyday life requires understanding their distinct nuances: sarcasm often uses humor or irony to mock or convey contempt, while cynicism reflects a distrustful or pessimistic outlook towards people's motives. Recognizing when sarcasm serves as playful banter versus when cynicism signals deeper skepticism helps you respond appropriately and maintain positive communication. Balancing awareness of these tones can improve interactions and reduce misunderstandings in both personal and professional settings.
Infographic: Sarcasm vs Cynicism
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com