Arguments often involve emotional reactions and a desire to win, while disagreements center on differing opinions without personal conflict. Explore this article to understand how healthy communication transforms disagreements into constructive discussions.
Table of Comparison
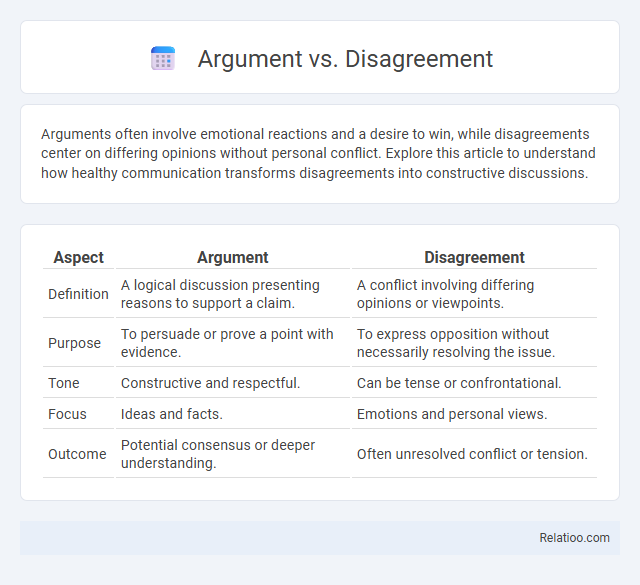
| Aspect | Argument | Disagreement |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A logical discussion presenting reasons to support a claim. | A conflict involving differing opinions or viewpoints. |
| Purpose | To persuade or prove a point with evidence. | To express opposition without necessarily resolving the issue. |
| Tone | Constructive and respectful. | Can be tense or confrontational. |
| Focus | Ideas and facts. | Emotions and personal views. |
| Outcome | Potential consensus or deeper understanding. | Often unresolved conflict or tension. |
Understanding Argument and Disagreement: Key Definitions
An argument involves a reasoned exchange of ideas where participants present evidence and logical reasoning to support their positions, aiming for clarity or resolution. A disagreement occurs when two or more parties hold opposing views or beliefs but may not necessarily engage in structured reasoning or debate. Understanding the distinction between argument and disagreement is crucial for effective communication, as arguments promote constructive dialogue while disagreements may simply reflect conflicting opinions without resolution efforts.
The Core Differences Between Argument and Disagreement
An argument involves a structured exchange where individuals present evidence and reasoning to support opposing viewpoints, often aiming to reach a resolution or deeper understanding. A disagreement, in contrast, simply reflects a difference in opinion or perspective without necessarily engaging in constructive dialogue or evidence-based discussion. The core difference lies in the presence of logical reasoning and intent to resolve in arguments, whereas disagreements may remain unresolved and lack structured debate.
Purpose and Context: Why Arguments Occur
Arguments occur as structured exchanges aiming to resolve differences through evidence and reasoning, typically in academic, legal, or formal settings. Disagreements represent simple differences in opinion or perspective without necessarily seeking resolution, often found in everyday conversations or informal contexts. Conflicts arise from deeper emotional or value-based clashes, where the purpose extends beyond logic to involve personal stakes, identity, or power dynamics.
When Disagreements Arise: Common Triggers
Disagreements often arise from misunderstandings, differences in values, or conflicting goals between individuals or groups. Emotional stress, communication breakdowns, and varying interpretations of facts frequently trigger these disputes. Recognizing these common triggers can help manage conflicts before they escalate into heated arguments.
Argumentation Styles: Constructive vs. Destructive
An argument involves reasoned exchange of ideas aiming to reach understanding, while a disagreement reflects a difference in opinions without necessarily involving conflict. Constructive argumentation styles promote active listening, empathy, and problem-solving, fostering collaboration and growth. Your ability to recognize and adopt constructive approaches can transform disagreements into opportunities for meaningful dialogue and resolution.
Emotional Impact: Arguments vs. Disagreements
Arguments often evoke intense emotional responses such as anger or frustration due to personal attacks or heightened tension, while disagreements tend to involve calmer, more rational exchanges focused on differing viewpoints without escalating emotions. Your ability to manage emotional impact during arguments can prevent conflicts from escalating and preserve relationships. Understanding the emotional dynamics helps in distinguishing between constructive disagreements and harmful arguments, promoting healthier communication.
Communication Techniques for Healthy Debate
Effective communication techniques distinguish argument, disagreement, and debate by fostering constructive dialogue rather than conflict escalation. Active listening, empathetic responses, and clear articulation of viewpoints help transform disagreements into opportunities for understanding, while structured debates rely on evidence-based reasoning and respectful rebuttals to maintain civility. Employing nonverbal cues, avoiding personal attacks, and summarizing key points enhance clarity and promote healthy exchanges in any form of dispute.
Resolving Disagreements: Effective Strategies
Resolving disagreements effectively requires active listening, empathy, and clear communication to ensure that all parties feel heard and understood. You can de-escalate conflicts by identifying the root causes and focusing on common goals rather than personal differences. Implementing structured problem-solving techniques and seeking compromise fosters constructive dialogue and long-term resolution.
The Role of Critical Thinking in Arguments
Critical thinking plays a pivotal role in distinguishing arguments from mere disagreements by enabling you to analyze evidence, identify logical fallacies, and construct coherent reasoning. In arguments, critical thinking fosters productive dialogue by focusing on rational evaluation rather than emotional conflict, unlike disagreements that often rely on subjective opinions. Applying critical thinking enhances your ability to resolve disputes effectively, turning disagreements into constructive arguments grounded in clarity and understanding.
Building Stronger Relationships Through Respectful Discourse
Respectful discourse transforms arguments and disagreements into opportunities for growth by fostering understanding and empathy. You can build stronger relationships by actively listening, valuing differing perspectives, and maintaining calm while expressing your views. Emphasizing mutual respect during discussions helps prevent conflict escalation and promotes collaborative problem-solving.
Infographic: Argument vs Disagreement
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com