Physical barriers in relationships include distance and lack of time, while psychological barriers involve trust issues and emotional vulnerabilities. Explore this article to understand how overcoming both barriers can strengthen your connection.
Table of Comparison
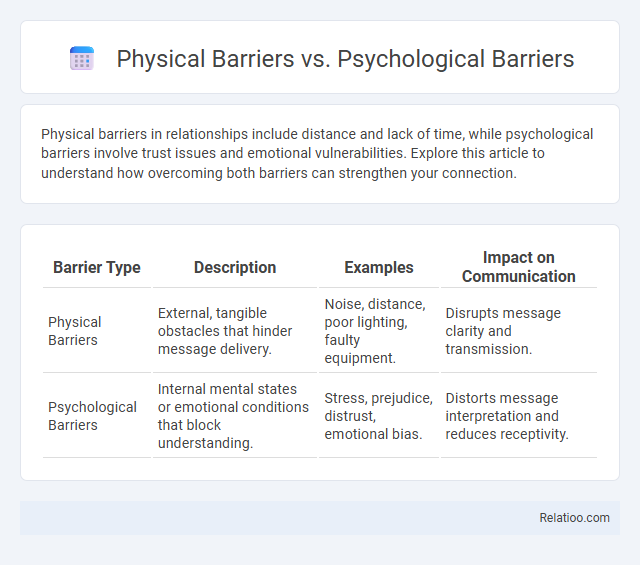
| Barrier Type | Description | Examples | Impact on Communication |
|---|---|---|---|
| Physical Barriers | External, tangible obstacles that hinder message delivery. | Noise, distance, poor lighting, faulty equipment. | Disrupts message clarity and transmission. |
| Psychological Barriers | Internal mental states or emotional conditions that block understanding. | Stress, prejudice, distrust, emotional bias. | Distorts message interpretation and reduces receptivity. |
Introduction to Communication Barriers
Physical barriers in communication include tangible obstacles like noise, distance, and environmental factors that hinder message transmission. Psychological barriers involve mental states such as stress, mistrust, or preconceived notions that distort perception and interpretation of messages. Listening barriers arise from inattentiveness, selective hearing, or preconceived judgments, leading to ineffective communication despite message reception.
Defining Physical Barriers
Physical barriers refer to tangible obstacles that impede communication, such as walls, noise, distance, or environmental conditions that block or distort messages. Unlike psychological barriers, which stem from emotional or mental states, or listening barriers caused by inattentiveness or selective hearing, physical barriers directly affect the transmission of information. Understanding these obstacles allows you to identify and mitigate factors limiting effective communication in your environment.
Defining Psychological Barriers
Psychological barriers refer to internal mental obstacles that affect how you process and interpret information, such as stress, prejudice, or emotional state, which can hinder effective communication. Unlike physical barriers that involve tangible obstructions like noise or distance, and listening barriers that include inattentiveness or selective hearing, psychological barriers are rooted in the mind's filtering mechanisms. Understanding and addressing these mental blocks is crucial for improving your ability to engage and respond accurately in conversations.
Key Differences between Physical and Psychological Barriers
Physical barriers are tangible obstacles such as noise, distance, or environmental factors that hinder effective communication, while psychological barriers arise from mental or emotional states like stress, prejudice, or mistrust that affect perception and understanding. Unlike physical barriers, psychological barriers are internal and subjective, often influenced by an individual's mindset or attitudes. Listening barriers overlap with psychological factors, including distractions or selective hearing, which impede absorption and processing of information.
Common Examples of Physical Barriers
Common examples of physical barriers in communication include environmental noise, such as construction sounds or loud machinery, which disrupt message clarity. Structural obstacles like walls, closed doors, and distance between communicators also hinder effective information exchange. These tangible impediments directly affect the transmission of verbal and nonverbal messages, contrasting with psychological barriers like stress or bias, and listening barriers such as selective hearing or distractions.
Common Examples of Psychological Barriers
Common examples of psychological barriers include stress, anxiety, and preconceived notions that distort communication and hinder understanding. These barriers can cause your mind to filter or misinterpret messages, leading to ineffective listening and response. Unlike physical barriers such as noise or distance, psychological obstacles arise internally, affecting cognitive and emotional processing during interactions.
Impact of Physical Barriers on Communication
Physical barriers such as noise, distance, and environmental distractions significantly disrupt communication by hindering the clear transmission and reception of messages. These barriers cause misunderstandings, reduce message clarity, and lead to decreased engagement between communicators. Overcoming physical barriers is essential to ensure effective information flow and maintain productive interpersonal or organizational communication.
Impact of Psychological Barriers on Communication
Psychological barriers, such as anxiety, mistrust, and emotional distress, significantly impact communication by distorting message interpretation and reducing openness between participants. Unlike physical barriers, which impede communication through environmental factors, psychological barriers influence the mindset and attitude, leading to misunderstandings and reluctance to express thoughts clearly. Listening barriers, including selective listening and cognitive biases, often stem from psychological factors, further hindering effective information exchange and collaborative understanding.
Strategies to Overcome Physical Barriers
Physical barriers, such as noise, distance, and environmental distractions, can severely disrupt communication by blocking clear message transmission. To overcome these barriers, you can employ strategies like optimizing the communication environment, using technology such as microphones or video conferencing tools, and ensuring proper seating arrangements to facilitate better interaction. Enhancing your awareness of physical obstacles and proactively adjusting your surroundings significantly improves the clarity and effectiveness of your communication.
Strategies to Overcome Psychological Barriers
Psychological barriers such as anxiety, mistrust, and preconceived notions can heavily impede effective communication, requiring targeted strategies for resolution. You can overcome these barriers by fostering an open-minded environment, encouraging active listening, and employing empathy to understand emotional states and cognitive biases. Building trust through consistent, transparent interactions and providing supportive feedback also diminishes resistance stemming from personal insecurities and mental blocks.
Infographic: Physical Barriers vs Psychological Barriers
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com