Escalation often intensifies conflicts by raising tensions, while negotiation seeks collaborative solutions to resolve disputes peacefully. Explore effective strategies for managing relationship challenges through escalation and negotiation in this article.
Table of Comparison
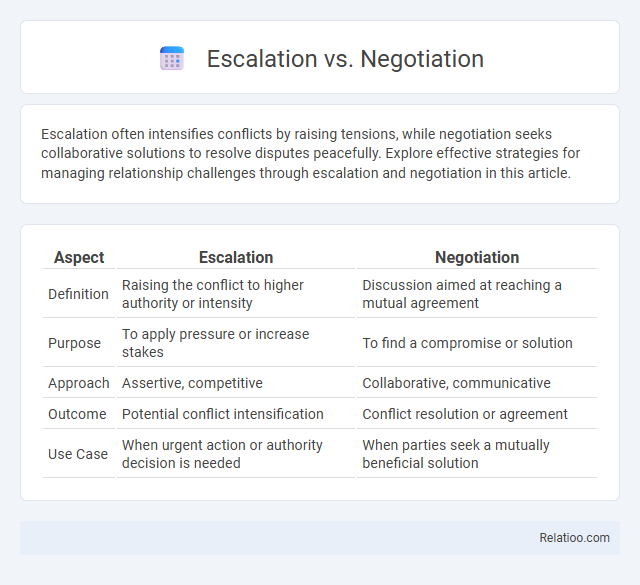
| Aspect | Escalation | Negotiation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Raising the conflict to higher authority or intensity | Discussion aimed at reaching a mutual agreement |
| Purpose | To apply pressure or increase stakes | To find a compromise or solution |
| Approach | Assertive, competitive | Collaborative, communicative |
| Outcome | Potential conflict intensification | Conflict resolution or agreement |
| Use Case | When urgent action or authority decision is needed | When parties seek a mutually beneficial solution |
Understanding Escalation and Negotiation
Understanding escalation involves recognizing the process of intensifying a conflict or issue to higher levels of authority for resolution, often when initial attempts at handling it have failed. Negotiation focuses on dialogue between parties to reach a mutually beneficial agreement without external intervention, emphasizing communication, compromise, and problem-solving skills. Effective conflict management requires distinguishing when escalation is necessary and when negotiation can resolve disputes amicably.
Key Differences Between Escalation and Negotiation
Escalation involves intensifying a conflict or issue, often by involving higher authority or increasing pressure, whereas negotiation focuses on dialogue and compromise to resolve disputes amicably. Key differences include escalation's tendency to heighten tensions and prompt authoritative intervention, while negotiation aims to find mutually acceptable solutions through communication and bargaining. Understanding when to escalate versus negotiate is crucial for effective conflict management and decision-making.
When to Escalate vs When to Negotiate
Knowing when to escalate involves recognizing situations where issues cannot be resolved at your level and require higher authority intervention, such as critical customer complaints or complex technical problems. Negotiation is optimal when both parties have shared interests and the goal is to reach a mutually beneficial agreement without external involvement. Your ability to discern when to escalate versus negotiate improves conflict resolution efficiency and enhances overall organizational workflow.
Risks and Benefits of Escalation
Escalation carries significant risks such as increased conflict intensity, strained relationships, and potential resource depletion, which can hinder resolution efforts and escalate costs. However, its benefits include signaling urgency, gaining managerial attention, and securing additional resources or authority needed to address complex problems. Properly managed escalation can accelerate problem-solving and prevent prolonged stagnation, but it requires careful assessment to avoid unnecessary escalation that might worsen situations.
Advantages of Choosing Negotiation
Negotiation offers the advantage of fostering collaborative problem-solving, allowing you to reach mutually beneficial agreements without the need for conflict escalation or formal intervention. This method preserves relationships by addressing issues directly and openly, which can prevent costly delays and reduce stress associated with escalation processes. Choosing negotiation empowers you to maintain control over outcomes, ensuring that solutions align closely with your interests and those of other parties involved.
Common Triggers for Escalation
Common triggers for escalation include unresolved conflicts, communication breakdowns, and unmet expectations that intensify emotions and complicate dispute resolution. Negotiation aims to address these underlying issues through dialogue and compromise, preventing the situation from escalating further. Your ability to recognize these triggers early can facilitate effective negotiation and avoid unnecessary escalation.
Effective Negotiation Strategies
Effective negotiation strategies emphasize clear communication, understanding underlying interests, and finding mutually beneficial solutions to prevent conflicts from escalating. Escalation often results from unresolved issues or poor negotiation tactics, increasing tension and complexity. Applying proven negotiation techniques such as active listening, empathy, and collaborative problem-solving reduces the likelihood of escalation and promotes sustainable agreements.
Impact of Escalation on Relationships
Escalation often intensifies conflicts, risking damage to trust and collaboration between parties. Negotiation aims to resolve disputes through dialogue, preserving and even strengthening relationships by fostering mutual understanding. Repeated escalation without resolution can create long-term animosity, making future negotiations more difficult and less effective.
Conflict Resolution: Escalation vs Negotiation
Conflict resolution often hinges on the strategic choice between escalation and negotiation, where escalation intensifies disputes by raising stakes and pressures, while negotiation seeks to lower tensions through dialogue and compromise. Your ability to recognize early warning signs and adopt negotiation techniques like active listening and empathy can prevent conflicts from escalating into unmanageable disputes. Understanding when to escalate--which involves formal interventions or third-party mediation--and when to negotiate effectively determines the success of resolving disagreements constructively.
Choosing the Right Approach for Long-Term Success
Choosing the right approach between escalation, negotiation, and mediation depends on the nature and urgency of the conflict. Escalation often intensifies disputes, risking long-term relationships, while negotiation fosters mutual understanding and collaborative solutions, essential for sustainable success. You must assess the situation carefully to ensure your approach supports enduring resolution and positive outcomes.
Infographic: Escalation vs Negotiation
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com