Verbal persuasion in relationships relies on spoken words and clear communication to influence emotions and decisions, while nonverbal persuasion uses body language, facial expressions, and tone to convey feelings and intentions. Explore the distinct impacts of verbal and nonverbal persuasion techniques on relationship dynamics in this article.
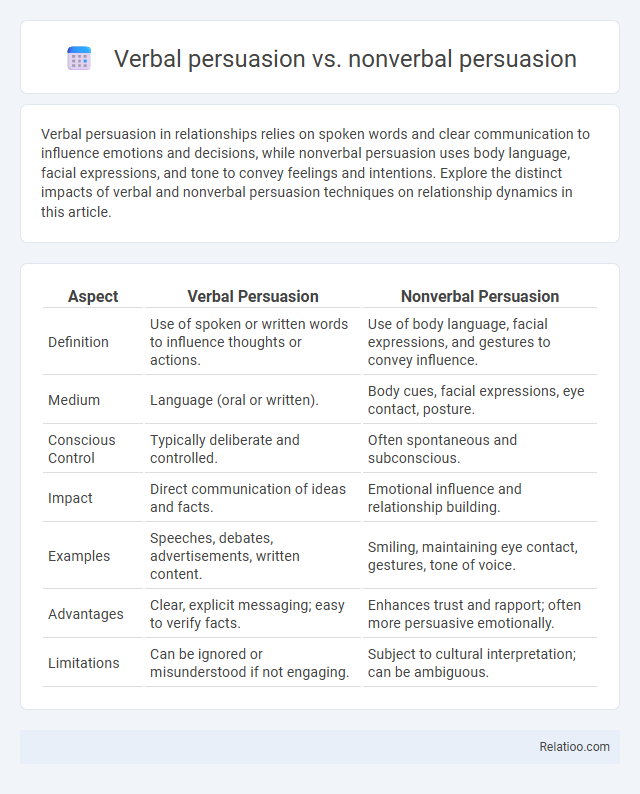
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Verbal Persuasion | Nonverbal Persuasion |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Use of spoken or written words to influence thoughts or actions. | Use of body language, facial expressions, and gestures to convey influence. |
| Medium | Language (oral or written). | Body cues, facial expressions, eye contact, posture. |
| Conscious Control | Typically deliberate and controlled. | Often spontaneous and subconscious. |
| Impact | Direct communication of ideas and facts. | Emotional influence and relationship building. |
| Examples | Speeches, debates, advertisements, written content. | Smiling, maintaining eye contact, gestures, tone of voice. |
| Advantages | Clear, explicit messaging; easy to verify facts. | Enhances trust and rapport; often more persuasive emotionally. |
| Limitations | Can be ignored or misunderstood if not engaging. | Subject to cultural interpretation; can be ambiguous. |
Introduction to Verbal and Nonverbal Persuasion
Verbal persuasion relies on spoken or written language to influence attitudes and behaviors, using carefully chosen words, tone, and rhetorical devices to convey arguments effectively. Nonverbal persuasion involves body language, facial expressions, gestures, and other visual cues that communicate emotions and intentions without verbal communication. Both forms are critical components of overall persuasion, as they complement each other to enhance the impact and credibility of the message.
Defining Verbal Persuasion
Verbal persuasion involves the use of spoken or written language to influence attitudes, beliefs, or behaviors, relying heavily on rhetoric, tone, and choice of words. Nonverbal persuasion uses body language, facial expressions, gestures, and other visual cues to communicate messages and affect opinions without spoken words. Persuasion as a whole encompasses both verbal and nonverbal techniques to effectively shape perceptions and motivate actions.
Defining Nonverbal Persuasion
Nonverbal persuasion leverages body language, facial expressions, and gestures to influence others without spoken words. Unlike verbal persuasion, which relies on language and rhetoric, nonverbal cues communicate emotions and intentions that can significantly impact your message's effectiveness. Mastering nonverbal persuasion enhances your overall persuasive ability by aligning your physical actions with your verbal communication.
Key Differences Between Verbal and Nonverbal Persuasion
Verbal persuasion relies on spoken or written language to influence others through arguments, facts, and emotional appeals, while nonverbal persuasion operates through body language, facial expressions, tone, and gestures that can enhance or contradict verbal messages. The key difference lies in the mode of communication: verbal persuasion depends on explicit content and clarity of message, whereas nonverbal persuasion conveys meaning indirectly and often influences perception subconsciously. Understanding these distinctions empowers your ability to craft more effective persuasive communication tailored to both what you say and how you physically express it.
Psychological Impacts of Verbal Persuasion
Verbal persuasion leverages words, tone, and language to influence your beliefs and behaviors by activating cognitive processes and emotional responses in the brain. Unlike nonverbal persuasion, which relies on body language, facial expressions, and gestures to convey messages, verbal persuasion directly shapes your thoughts through explicit communication and carefully chosen rhetoric. Psychological impacts of verbal persuasion include increased self-efficacy, enhanced motivation, and altered decision-making by reinforcing positive self-perceptions and reducing self-doubt.
Psychological Impacts of Nonverbal Persuasion
Nonverbal persuasion leverages body language, facial expressions, and tone of voice to profoundly influence psychological responses, often bypassing conscious awareness and directly shaping emotions and attitudes. Unlike verbal persuasion, which relies on words and logical arguments, nonverbal cues can trigger subconscious trust or skepticism, making your message more impactful without explicit statements. Research shows that up to 70% of communication effectiveness stems from nonverbal elements, highlighting their critical role in shaping decision-making and behavior.
Real-Life Examples of Verbal Persuasion
Verbal persuasion leverages spoken or written language to influence attitudes and behaviors, such as a politician delivering a compelling speech to gain voter support. Nonverbal persuasion relies on body language, facial expressions, and gestures, exemplified by a confident handshake that establishes trust during a business meeting. Persuasion overall combines both verbal and nonverbal cues, seen when a teacher uses encouraging words and a warm tone to motivate students.
Real-Life Examples of Nonverbal Persuasion
Nonverbal persuasion leverages body language, facial expressions, and gestures to influence others unconsciously, often more effectively than verbal communication alone. Real-life examples include a manager using confident posture and direct eye contact to inspire trust during a presentation, or a salesperson nodding while listening to demonstrate empathy and encourage customer openness. Understanding how your nonverbal cues impact persuasion can enhance your ability to influence outcomes without relying solely on words.
Combining Verbal and Nonverbal Persuasion for Maximum Effect
Combining verbal and nonverbal persuasion leverages both the explicit clarity of spoken or written words and the powerful impact of body language, facial expressions, and tone, creating a more compelling and credible message. Your persuasive efforts become significantly more effective when verbal arguments are reinforced by confident eye contact, gestures, and vocal intonation that convey sincerity and conviction. This synergy enhances your ability to influence, making your communication more engaging and convincing in diverse contexts, from negotiations to presentations.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Persuasion Strategy
Selecting the right persuasion strategy hinges on understanding the context and audience, where verbal persuasion leverages language and rhetoric to influence beliefs, while nonverbal persuasion utilizes body language, facial expressions, and tone to convey credibility and emotion. Effective persuasion often combines both verbal and nonverbal cues to enhance trust and engagement, maximizing the impact of the message. Tailoring the approach based on the communication environment and psychological factors ensures the highest likelihood of achieving desired outcomes.
Infographic: Verbal Persuasion vs Nonverbal Persuasion
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com