Empathy involves deeply understanding and sharing another person's feelings, while compassion goes further by motivating actionable support to alleviate their suffering. Discover the key differences and benefits of empathy and compassion in relationships in this article.
Table of Comparison
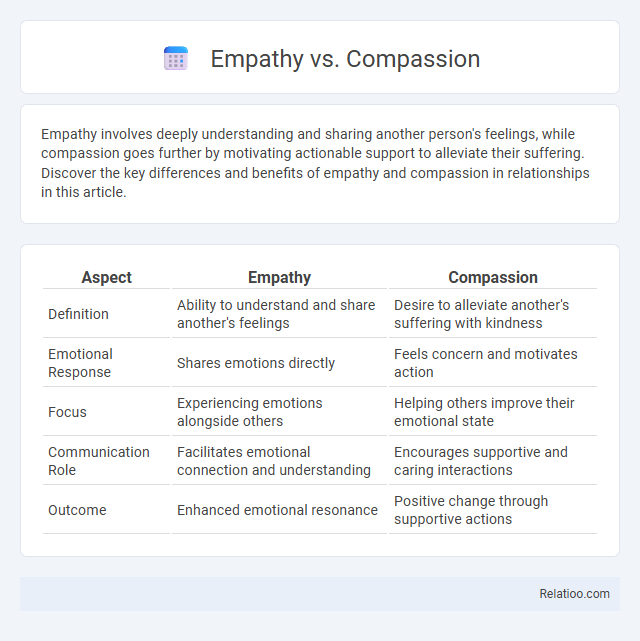
| Aspect | Empathy | Compassion |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Ability to understand and share another's feelings | Desire to alleviate another's suffering with kindness |
| Emotional Response | Shares emotions directly | Feels concern and motivates action |
| Focus | Experiencing emotions alongside others | Helping others improve their emotional state |
| Communication Role | Facilitates emotional connection and understanding | Encourages supportive and caring interactions |
| Outcome | Enhanced emotional resonance | Positive change through supportive actions |
Understanding Empathy: A Deeper Connection
Understanding empathy involves recognizing and sharing the feelings of others on a personal level, which forms a deeper emotional connection compared to compassion or sympathy. While compassion entails a desire to help and sympathy reflects sorrow for someone's situation, empathy requires you to genuinely experience and understand another person's emotions. Developing empathy enhances your ability to connect authentically, fostering stronger relationships and effective communication.
Defining Compassion: Action Beyond Emotion
Compassion involves not only recognizing and sharing another person's emotions but also taking deliberate actions to alleviate their suffering. Unlike empathy, which is the ability to understand and feel what others experience, compassion drives you to provide support and create positive change. Your compassionate response transforms emotional awareness into meaningful help and healing.
Key Differences Between Empathy and Compassion
Empathy involves understanding and sharing another person's emotions by mentally putting yourself in their situation, often feeling their pain or joy. Compassion extends beyond empathy by including a desire to help alleviate the suffering experienced by others through actions or supportive behavior. Key differences lie in empathy being an emotional resonance, while compassion combines that emotional connection with proactive care and kindness.
The Science Behind Empathy and Compassion
Neuroscience reveals that empathy activates brain regions like the anterior insula and anterior cingulate cortex, allowing You to experience others' emotions vicariously. Compassion engages areas such as the ventral striatum and medial orbitofrontal cortex, associated with reward and positive feelings, motivating prosocial behavior. Understanding these distinct neural mechanisms helps clarify how empathy and compassion influence social connection and emotional regulation.
Psychological Benefits of Empathy
Empathy enhances psychological well-being by fostering emotional understanding and reducing feelings of isolation, leading to stronger interpersonal connections and improved mental health. Unlike compassion, which involves a desire to alleviate suffering, empathy primarily involves deeply resonating with another person's emotions, promoting emotional regulation and resilience. Studies demonstrate that cultivating empathy can increase self-awareness, lower stress levels, and boost overall emotional intelligence, which are key factors in psychological benefits.
The Impact of Compassion on Well-being
Compassion enhances well-being by fostering emotional resilience and reducing stress through active concern for others' suffering. Unlike empathy, which involves sharing feelings, compassion motivates prosocial behavior and supportive actions that improve mental health outcomes. Studies show that cultivating compassion correlates with increased happiness, lower anxiety levels, and stronger social connections.
Empathy in Everyday Relationships
Empathy in everyday relationships involves recognizing and understanding another person's emotions, fostering deeper connections through active listening and emotional validation. This emotional awareness enhances communication, reduces conflicts, and builds trust by making others feel genuinely heard and supported. Unlike compassion, which motivates action to alleviate suffering, empathy centers on emotional resonance and perspective-taking, forming the foundation for meaningful interpersonal bonds.
Compassionate Actions in Society
Compassionate actions in society drive meaningful change by transforming empathy into tangible support, addressing the needs of others through purposeful deeds. Unlike empathy, which involves understanding others' emotions, compassion motivates you to actively alleviate suffering and foster well-being within communities. Prioritizing compassionate behaviors strengthens social bonds and promotes collective resilience, resulting in a more caring and responsive society.
Cultivating Empathy and Compassion in Daily Life
Cultivating empathy involves actively listening and understanding others' emotions, fostering deeper connections in daily interactions. Compassion builds upon empathy by motivating altruistic actions to alleviate others' suffering, reinforcing social bonds and emotional well-being. Practicing empathy and compassion regularly enhances emotional intelligence, promotes mental health, and cultivates a supportive, inclusive environment.
Empathy vs Compassion: Finding a Healthy Balance
Empathy involves deeply understanding and sharing another person's emotions, while compassion goes further by motivating a desire to help and alleviate suffering. Maintaining a healthy balance between empathy and compassion prevents emotional burnout and enhances effective support without becoming overwhelmed. Cultivating compassion alongside empathy enables meaningful connections and proactive kindness, fostering resilience in both caregivers and those they assist.
Infographic: Empathy vs Compassion
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com