Emotional intelligence involves recognizing and understanding emotions in oneself and others, while emotional regulation refers to effectively managing and responding to those emotions. Explore this article to learn how mastering both can strengthen your relationships.
Table of Comparison
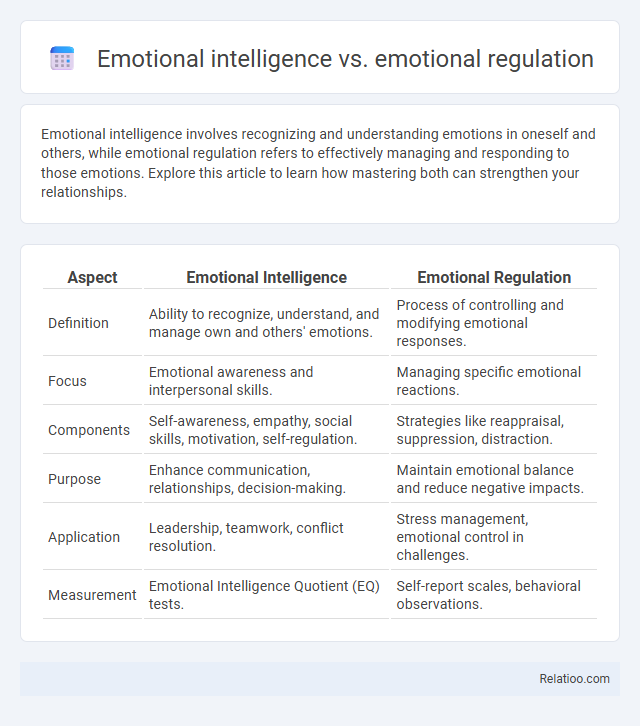
| Aspect | Emotional Intelligence | Emotional Regulation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Ability to recognize, understand, and manage own and others' emotions. | Process of controlling and modifying emotional responses. |
| Focus | Emotional awareness and interpersonal skills. | Managing specific emotional reactions. |
| Components | Self-awareness, empathy, social skills, motivation, self-regulation. | Strategies like reappraisal, suppression, distraction. |
| Purpose | Enhance communication, relationships, decision-making. | Maintain emotional balance and reduce negative impacts. |
| Application | Leadership, teamwork, conflict resolution. | Stress management, emotional control in challenges. |
| Measurement | Emotional Intelligence Quotient (EQ) tests. | Self-report scales, behavioral observations. |
Understanding Emotional Intelligence
Understanding emotional intelligence involves recognizing your ability to perceive, assess, and manage emotions effectively. Emotional regulation is a component of emotional intelligence, focusing specifically on controlling and adjusting your emotional responses in various situations. Mastering both emotional intelligence and emotional regulation enhances interpersonal skills and improves decision-making.
Defining Emotional Regulation
Emotional regulation refers to the processes by which individuals influence their emotions, how they experience and express them, aiming to maintain psychological balance and achieve adaptive outcomes. Unlike emotional intelligence, which involves recognizing, understanding, and managing emotions overall, emotional regulation specifically targets the modulation and control of emotional responses in real-time situations. Effective emotional regulation techniques include cognitive reappraisal, suppression, and mindfulness, which help reduce emotional distress and improve interpersonal functioning.
Key Differences Between Emotional Intelligence and Emotional Regulation
Emotional intelligence involves the ability to recognize, understand, and manage one's own emotions and the emotions of others, encompassing skills like empathy, social awareness, and emotional expression. Emotional regulation specifically refers to the processes and strategies used to control and modify emotional responses, including techniques like cognitive reappraisal and suppression to maintain emotional balance. The key difference lies in scope: emotional intelligence is a broader capacity for emotional awareness and interaction, while emotional regulation is a subset focused on managing emotional intensity and duration in various contexts.
Components of Emotional Intelligence
Emotional intelligence comprises key components such as self-awareness, self-regulation, motivation, empathy, and social skills, enabling you to understand and manage your emotions effectively. Emotional regulation, a subset of emotional intelligence, specifically focuses on controlling and modulating your emotional responses to adapt to various situations. Mastering these components enhances your interpersonal relationships, decision-making, and overall mental well-being.
Core Skills of Emotional Regulation
Emotional regulation centers on core skills such as self-awareness, impulse control, and adaptive coping strategies to manage intense emotions effectively. Emotional intelligence encompasses these regulation abilities along with empathy, social skills, and emotional awareness, enabling individuals to navigate interpersonal dynamics smoothly. Distinguishing emotional regulation involves focusing on specific techniques like mindfulness, cognitive reappraisal, and stress management that directly influence emotional responses and behavioral outcomes.
How Emotional Intelligence Influences Behavior
Emotional intelligence directly impacts your behavior by enabling better recognition, understanding, and management of emotions in yourself and others. It enhances interpersonal skills and decision-making by allowing you to respond thoughtfully rather than react impulsively to emotional stimuli. Emotional regulation, a component of emotional intelligence, specifically involves controlling your emotional responses to maintain composure and act appropriately in various situations.
The Role of Emotional Regulation in Decision-Making
Emotional regulation plays a critical role in decision-making by allowing individuals to manage and adjust their emotional responses to achieve more rational and goal-oriented outcomes. Unlike emotional intelligence, which encompasses recognizing and understanding emotions, emotional regulation specifically involves controlling impulses and stress that can cloud judgment. Effective emotional regulation enhances cognitive flexibility and reduces bias, leading to better choices under pressure.
Emotional Intelligence vs Emotional Regulation: Real-World Examples
Emotional intelligence involves recognizing, understanding, and managing one's emotions while interpreting others' feelings, crucial in leadership and team collaboration scenarios. Emotional regulation specifically refers to controlling and modifying emotional responses to maintain composure during stressful events, such as negotiations or conflict resolution. Real-world examples include a manager using emotional intelligence to empathize with employee concerns and applying emotional regulation to stay calm when delivering critical feedback.
Developing Emotional Intelligence and Regulation Skills
Developing emotional intelligence enhances your ability to recognize, understand, and manage your emotions effectively, leading to improved interpersonal relationships and decision-making. Emotional regulation focuses specifically on controlling and modulating emotional responses to reduce stress and maintain composure in challenging situations. Strengthening both emotional intelligence and emotional regulation skills supports better mental health, resilience, and overall well-being.
Impact on Personal and Professional Relationships
Emotional intelligence enhances interpersonal communication and empathy, fostering trust and collaboration in personal and professional relationships. Emotional regulation controls impulsive reactions and manages stress, promoting stability and constructive conflict resolution. Together, strong emotional intelligence and effective emotional regulation improve relationship quality, teamwork, and leadership success.
Infographic: Emotional intelligence vs Emotional regulation
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com