De-escalation involves calming tensions and reducing conflict intensity, while negotiation focuses on reaching a mutually beneficial agreement through dialogue. Explore effective techniques and strategies for both approaches in this article.
Table of Comparison
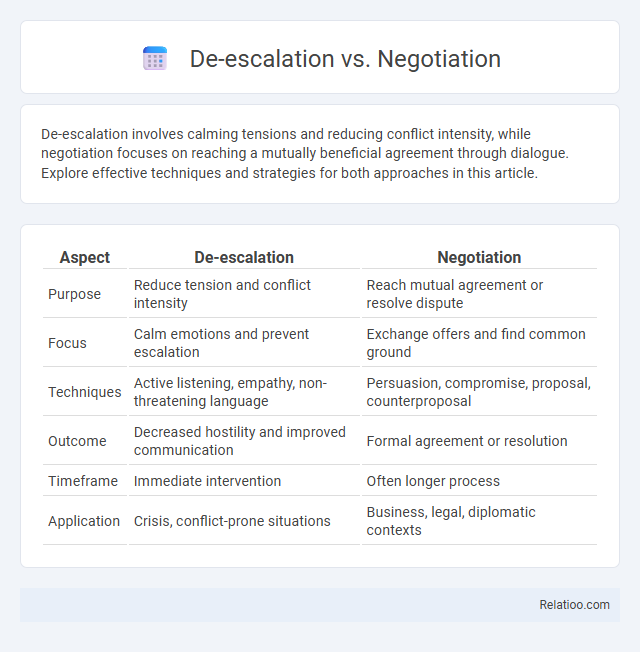
| Aspect | De-escalation | Negotiation |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Reduce tension and conflict intensity | Reach mutual agreement or resolve dispute |
| Focus | Calm emotions and prevent escalation | Exchange offers and find common ground |
| Techniques | Active listening, empathy, non-threatening language | Persuasion, compromise, proposal, counterproposal |
| Outcome | Decreased hostility and improved communication | Formal agreement or resolution |
| Timeframe | Immediate intervention | Often longer process |
| Application | Crisis, conflict-prone situations | Business, legal, diplomatic contexts |
Understanding De-escalation: Definition and Purpose
Understanding de-escalation involves recognizing techniques designed to reduce tension and prevent conflict from intensifying by calming emotions and creating a sense of safety. Unlike negotiation, which aims to reach an agreement between conflicting parties, de-escalation focuses on stabilizing the situation and avoiding immediate confrontation. Your ability to apply de-escalation effectively can defuse potentially volatile encounters and pave the way for constructive dialogue.
Negotiation Explained: Core Concepts
Negotiation involves a strategic dialogue aimed at reaching a mutually beneficial agreement by understanding the interests and needs of all parties involved. Core concepts include preparation, active listening, effective communication, and finding common ground to resolve conflicts without confrontation. Unlike de-escalation, which focuses on calming tensions, negotiation actively seeks solutions through compromise and collaborative problem-solving.
Key Differences Between De-escalation and Negotiation
De-escalation focuses on calming heightened emotions and reducing tension to prevent conflict from escalating, using techniques such as active listening, empathy, and non-threatening body language. Negotiation involves a structured dialogue aimed at reaching a mutual agreement between parties, balancing interests, and addressing specific issues. Key differences include de-escalation prioritizing emotional control and conflict prevention, while negotiation centers on problem-solving and agreement formulation.
Common Goals of De-escalation and Negotiation
De-escalation and negotiation both aim to reduce conflict intensity and promote peaceful resolution by fostering understanding and cooperation between parties. Common goals include building trust, encouraging open communication, and identifying mutually beneficial solutions to prevent further escalation. Both strategies emphasize calming emotions and creating a safe environment for dialogue to achieve long-term conflict resolution.
Techniques and Strategies in De-escalation
De-escalation techniques focus on calming tensions through active listening, empathetic communication, and maintaining non-threatening body language to reduce conflict intensity. Strategies such as setting clear boundaries, using open-ended questions, and allowing space for emotional expression prioritize safety and foster cooperation. Your skillful application of these methods can prevent escalation and create a foundation for successful negotiation.
Essential Negotiation Tactics for Success
Effective negotiation tactics include active listening, clear communication, and understanding the other party's interests to reach a mutually beneficial agreement. De-escalation techniques focus on calming heightened emotions and reducing tension, allowing rational discussion to proceed. By mastering these strategies, you improve your chances of resolving conflicts successfully while maintaining positive relationships.
When to Use De-escalation vs Negotiation
De-escalation is best used when tensions are high and immediate emotional calming is necessary to prevent conflict escalation, focusing on reducing hostility and creating space for dialogue. Negotiation is appropriate once emotions are tempered, aiming to reach a mutually acceptable agreement through communication and compromise. Your choice depends on whether the priority is calming the situation (de-escalation) or resolving underlying issues through discussion (negotiation).
Psychological Principles Behind Each Approach
De-escalation relies on calming techniques rooted in emotional regulation and empathy to reduce immediate tension, while negotiation employs strategic communication and mutual understanding to reach a mutually beneficial agreement. Mediation combines elements of both, emphasizing impartial facilitation and conflict resolution grounded in trust and active listening. Your ability to recognize and apply these psychological principles can effectively manage and resolve conflicts in diverse situations.
Case Studies: Real-world Examples
Case studies highlight that de-escalation techniques effectively reduce tension in high-stress situations, such as law enforcement encounters or emergency healthcare settings. Negotiation strategies play a critical role in resolving conflicts by fostering communication and mutual understanding, evident in hostage crises and labor disputes. Your ability to distinguish between de-escalation and negotiation methods enhances conflict resolution outcomes, with case examples demonstrating their complementary use in real-world scenarios.
Choosing the Right Method for Conflict Resolution
Choosing the right method for conflict resolution depends on the situation's intensity, stakeholders involved, and desired outcome. De-escalation focuses on reducing tension and preventing further conflict, while negotiation aims for a mutual agreement through dialogue and compromise. Understanding when to apply de-escalation techniques or negotiation strategies enhances conflict resolution effectiveness and promotes lasting solutions.
Infographic: De-escalation vs Negotiation
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com