Mediation involves a neutral third party facilitating negotiation between disputing parties to reach a mutual agreement, while arbitration entails a third party making a binding decision after evaluating evidence. Explore this article to understand the key differences and benefits of mediation versus arbitration in dispute resolution.
Table of Comparison
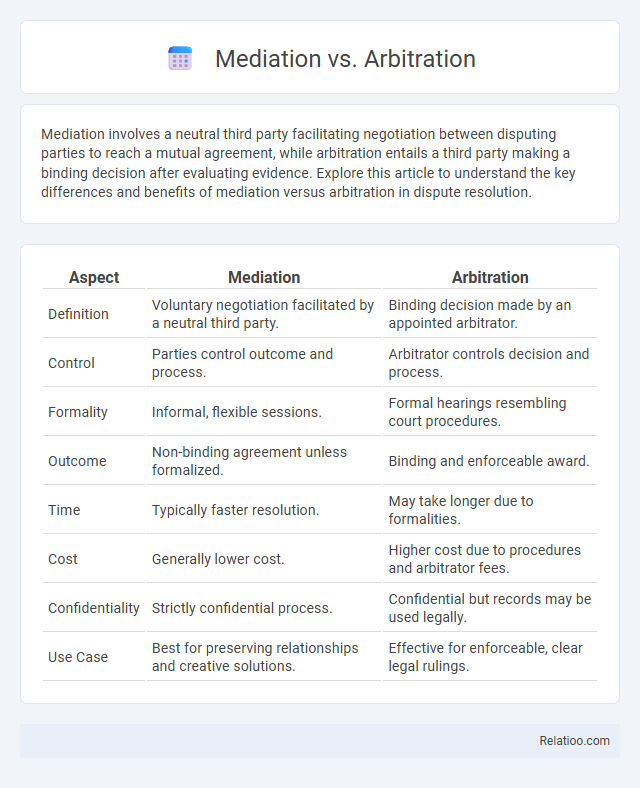
| Aspect | Mediation | Arbitration |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Voluntary negotiation facilitated by a neutral third party. | Binding decision made by an appointed arbitrator. |
| Control | Parties control outcome and process. | Arbitrator controls decision and process. |
| Formality | Informal, flexible sessions. | Formal hearings resembling court procedures. |
| Outcome | Non-binding agreement unless formalized. | Binding and enforceable award. |
| Time | Typically faster resolution. | May take longer due to formalities. |
| Cost | Generally lower cost. | Higher cost due to procedures and arbitrator fees. |
| Confidentiality | Strictly confidential process. | Confidential but records may be used legally. |
| Use Case | Best for preserving relationships and creative solutions. | Effective for enforceable, clear legal rulings. |
Introduction to Mediation and Arbitration
Mediation involves a neutral third party, the mediator, who facilitates communication and negotiation between disputing parties to help them reach a mutually acceptable agreement without imposing a decision. Arbitration, in contrast, assigns an arbitrator the authority to review evidence and make a binding decision that resolves the conflict, similar to a private judge. Understanding the distinctions between mediation's collaborative approach and arbitration's authoritative resolution helps you select the most effective method for your specific conflict resolution needs.
Defining Mediation: Key Features
Mediation is a voluntary, confidential process where a neutral third-party facilitates communication between disputing parties to help them reach a mutually acceptable agreement. Key features include its non-binding nature, emphasis on collaboration, and empowerment of parties to control the outcome without a judge or arbitrator imposing decisions. Mediation promotes preserving relationships and often serves as a cost-effective, timely alternative to litigation or arbitration.
What is Arbitration? Core Principles
Arbitration is a form of alternative dispute resolution where an impartial arbitrator renders a binding decision after hearing evidence and arguments from the parties involved. The core principles of arbitration include neutrality, confidentiality, and finality, ensuring that disputes are resolved efficiently without involving the court system. Understanding how arbitration works can help you choose the best method for resolving your conflicts.
Process Differences: Mediation vs Arbitration
Mediation involves a neutral third party facilitating open dialogue to help You and the other party reach a mutually agreeable solution without imposing a decision. Arbitration, by contrast, features an arbitrator who listens to both sides and delivers a binding verdict, similar to a court judgment. The key process difference lies in mediation's collaborative approach versus arbitration's formal, adjudicative procedure.
Role of the Neutral Third Party
The role of the neutral third party varies significantly across mediation, arbitration, and conflict resolution processes. In mediation, the neutral third party facilitates communication and negotiation between disputing parties without imposing a decision, aiming for a mutually acceptable agreement. Arbitration involves the neutral third party acting as a private judge who listens to evidence and arguments before issuing a binding decision, while conflict resolution encompasses a broader range of methods where the neutral party guides the process to help parties identify underlying issues and reach a resolution.
Advantages of Mediation
Mediation offers a confidential and flexible approach to dispute resolution, allowing you to maintain control over the outcome while preserving relationships. Unlike arbitration or litigation, mediation typically requires less time and expense, providing a cost-effective solution. The collaborative environment encourages open communication and creative problem-solving tailored to the needs of both parties.
Benefits of Arbitration
Arbitration offers a legally binding resolution process that is faster and more cost-effective than traditional court litigation, providing you with a definitive outcome. It ensures confidentiality, preserving the reputation and privacy of all parties involved while allowing specialized arbitrators with industry expertise to handle complex disputes. This efficient method reduces court backlog and promotes enforceability of awards internationally under treaties like the New York Convention, enhancing global business confidence.
Cost and Time Comparison
Mediation typically costs less and resolves disputes faster by facilitating direct communication between parties, often concluding in a few hours or days. Arbitration involves higher expenses, including arbitrator fees and formal procedures, and can extend over weeks or months depending on case complexity. Your choice between mediation, arbitration, and other conflict resolution methods should consider the trade-offs between the urgency for a swift resolution and the budget you can allocate.
Legal Binding Nature: Outcomes Explained
Mediation involves a non-binding process where a neutral third party assists disputing individuals in reaching a mutually acceptable agreement, leaving final decisions up to the parties involved. Arbitration produces legally binding outcomes as the arbitrator's decision is enforceable by courts, similar to a judge's ruling, providing a resolution that you must adhere to. Conflict resolution encompasses various strategies, including mediation and arbitration, with outcomes differing based on the method chosen and whether parties agree to legal binding or informal agreements.
Choosing Between Mediation and Arbitration
Choosing between mediation and arbitration depends on the desired level of formality and control over the outcome. Mediation offers a collaborative approach where parties retain decision-making power, aiming for a mutually agreeable solution through facilitated negotiation. Arbitration involves a neutral arbitrator who listens to both sides and renders a binding decision, providing a more structured and enforceable resolution for disputes.
Infographic: Mediation vs Arbitration
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com