Affection involves deep emotional connection and care, while attraction often centers on physical or superficial appeal. Explore this article to understand how these elements influence lasting relationships.
Table of Comparison
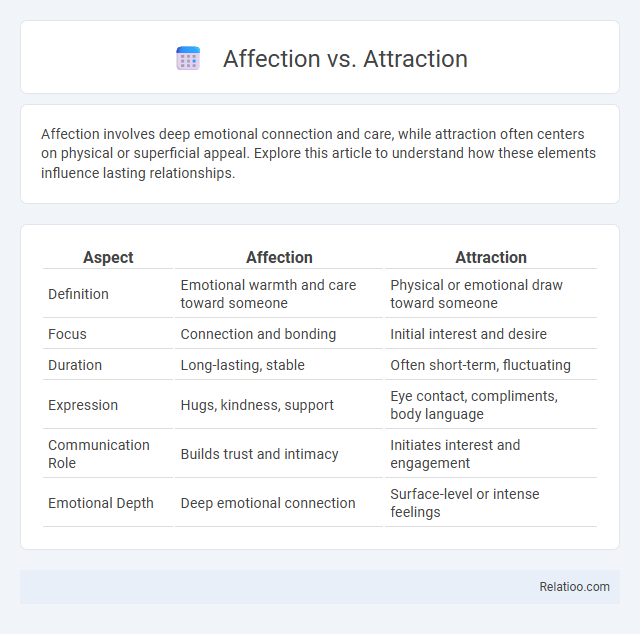
| Aspect | Affection | Attraction |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Emotional warmth and care toward someone | Physical or emotional draw toward someone |
| Focus | Connection and bonding | Initial interest and desire |
| Duration | Long-lasting, stable | Often short-term, fluctuating |
| Expression | Hugs, kindness, support | Eye contact, compliments, body language |
| Communication Role | Builds trust and intimacy | Initiates interest and engagement |
| Emotional Depth | Deep emotional connection | Surface-level or intense feelings |
Understanding Affection: Definition and Core Elements
Understanding affection involves recognizing it as a deep emotional connection characterized by warmth, care, and genuine concern for someone's well-being. Core elements of affection include physical touch, verbal expressions of love, and acts of kindness that reinforce emotional bonds. Your ability to identify and express affection enhances relationships by fostering trust, comfort, and mutual respect.
What is Attraction? Key Differences from Affection
Attraction is a powerful emotional or physical pull towards someone, often driven by biological, psychological, or social factors, while affection is a gentle feeling of fondness and care towards another. Attraction tends to be more immediate and intense, often linked to desire and interest, whereas affection grows over time, rooted in warmth and attachment. Your understanding of both can help distinguish a fleeting connection from a lasting emotional bond.
Types of Affection: Emotional, Platonic, and Familial
Types of affection encompass emotional, platonic, and familial dimensions, each shaping human connections uniquely. Emotional affection involves deep feelings of attachment and care, often linked to romantic partnerships and close friendships. Platonic affection is characterized by non-romantic bonds marked by trust and mutual respect, while familial affection represents the inherent love and support within family relationships.
Forms of Attraction: Romantic, Physical, and Emotional
Romantic attraction involves a desire for a committed relationship or deep emotional connection with another person, often leading to feelings of love and intimacy. Physical attraction centers on the aesthetic appeal or sexual desire one feels towards another, driven by visual or sensory stimuli. Emotional attraction arises from a connection to someone's personality, kindness, or shared values, fostering closeness and empathy beyond the physical or romantic realms.
Psychological Foundations: How Affection Develops
Affection develops through consistent positive interactions and emotional bonding, rooted in attachment theory and neurochemical responses involving oxytocin and dopamine. Unlike attraction, which is often triggered by physical or superficial cues, affection grows from trust, empathy, and shared experiences that strengthen relational security. Psychological studies highlight that affection supports mental well-being by fostering a sense of belonging and emotional safety within interpersonal relationships.
The Science Behind Attraction: Biological and Chemical Factors
Attraction involves complex biological and chemical factors such as pheromones, dopamine, and oxytocin that influence your brain's reward system and emotional responses. Affection is the expression of warmth and care, often driven by oxytocin, which promotes bonding and trust between individuals. Understanding these scientific elements helps differentiate attraction, the initial biological pull, from affection, the emotional connection that deepens over time.
Signs of Affection vs. Signs of Attraction
Signs of affection often include caring gestures, physical touch like hugs, and verbal expressions of love that emphasize emotional connection and comfort. In contrast, signs of attraction tend to involve intense eye contact, flirting, and heightened physical awareness signaling romantic or sexual interest. Understanding the subtle differences can help you interpret the intentions behind someone's actions more accurately.
Affection and Attraction in Healthy Relationships
Affection in healthy relationships involves genuine expressions of care, warmth, and emotional support that strengthen the bond between partners. Attraction often initiates connection through physical or emotional appeal, but sustained affection is essential for deepening trust and intimacy. Your understanding of these dynamics helps nurture a balanced, fulfilling relationship where both affection and attraction coexist harmoniously.
When Affection Transforms into Attraction
Affection transforms into attraction when emotional warmth deepens into physical or romantic desire, often marked by increased attention to the other's presence and qualities. Neurological responses involving dopamine and oxytocin surge, signaling a shift from platonic feelings to passionate interest. Recognizing this change is key in relationships, as affection fosters connection, while attraction drives intimacy and romantic progression.
Navigating Boundaries: Balancing Affection and Attraction
Navigating boundaries between affection and attraction requires understanding the distinct emotional and physical components involved; affection typically involves warmth and care without necessarily implying romantic interest, while attraction often includes desire and longing. Balancing these feelings involves clear communication and self-awareness to respect personal limits and avoid misunderstandings in relationships. Recognizing when affection may lead to attraction or vice versa helps maintain healthy interactions and emotional clarity.
Infographic: Affection vs Attraction
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com