Perception shapes how we initially experience others, while interpretation influences the meaning we assign to those experiences in a relationship. Explore the nuances between perception and interpretation to enhance your understanding of interpersonal dynamics in this article.
Table of Comparison
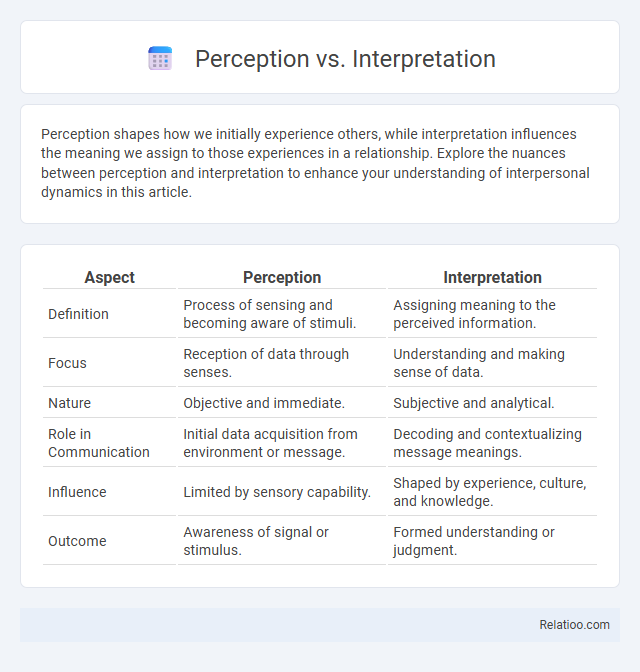
| Aspect | Perception | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Process of sensing and becoming aware of stimuli. | Assigning meaning to the perceived information. |
| Focus | Reception of data through senses. | Understanding and making sense of data. |
| Nature | Objective and immediate. | Subjective and analytical. |
| Role in Communication | Initial data acquisition from environment or message. | Decoding and contextualizing message meanings. |
| Influence | Limited by sensory capability. | Shaped by experience, culture, and knowledge. |
| Outcome | Awareness of signal or stimulus. | Formed understanding or judgment. |
Understanding Perception: The Basics
Perception involves the sensory process of recognizing and organizing stimuli from the environment, forming the foundation for human awareness. Interpretation follows perception by assigning meaning and context to the sensory information, influenced by individual experiences and cultural background. Understanding perception requires studying how the brain processes visual, auditory, and tactile input to create coherent representations of reality.
What Is Interpretation?
Interpretation is the cognitive process of assigning meaning to sensory information that you perceive, transforming raw data into understandable concepts. Unlike perception, which involves detecting stimuli through your senses, interpretation involves analyzing and contextualizing that information based on your knowledge, experiences, and biases. Your ability to interpret influences how you understand and respond to situations, making it a critical step in meaning-making beyond mere perception.
Key Differences Between Perception and Interpretation
Perception is the process through which you receive and organize sensory information from your environment, while interpretation involves assigning meaning or understanding to that sensory input. Perception is largely automatic and based on stimuli, whereas interpretation is influenced by your prior knowledge, experiences, and expectations. The key difference lies in perception being the initial data acquisition and interpretation being the cognitive process that gives that data significance.
The Role of Sensory Input in Perception
Sensory input plays a critical role in perception by providing raw data from the environment through sensory organs such as the eyes, ears, and skin, which the brain processes to form an initial representation of stimuli. Perception transforms these sensory signals into meaningful patterns, enabling the recognition of objects, sounds, and textures, while interpretation involves higher cognitive functions that assign personal or contextual meaning to these perceptions. Accurate perception depends on the quality and clarity of sensory input, as well as neural processing mechanisms that filter and organize sensory information before interpretation occurs.
How Interpretation Shapes Meaning
Interpretation shapes meaning by transforming raw perception into a personalized understanding based on your prior knowledge, experiences, and cultural context. While perception involves the sensory intake of information, interpretation applies cognitive processes that assign significance, influencing how you make sense of what you perceive. This dynamic interplay enhances communication, decision-making, and the construction of reality, emphasizing the subjective nature of meaning-making.
Influences on Perception: Culture and Experience
Culture shapes perception by providing a framework of symbols, values, and norms that influence how individuals interpret sensory information. Personal experience further filters perception, as past encounters and learned behaviors modify the way stimuli are recognized and understood. These cultural and experiential factors interact to create unique perceptual realities, affecting cognitive processing and behavioral responses.
Cognitive Biases in Interpretation
Cognitive biases significantly influence the interpretation stage, where your brain assigns meaning to sensory input received during perception. While perception involves the raw data collected by your senses, interpretation filters this information through prior knowledge, beliefs, and emotions, often causing distortions such as confirmation bias or anchoring. Recognizing these biases can improve your ability to critically analyze and adjust how you interpret sensory data, enhancing decision-making accuracy.
Perception and Interpretation in Communication
Perception in communication refers to the process by which individuals receive and organize sensory information to form an understanding of messages. Interpretation involves assigning meaning to perceived information, influenced by personal experiences, cultural background, and context. Effective communication depends on aligning both perception and interpretation to minimize misunderstandings and enhance message clarity.
Real-World Examples: Perception vs. Interpretation
Perception involves the raw sensory data received from the environment, such as seeing a red traffic light, while interpretation is the cognitive process of assigning meaning to that data, like understanding that the red light means stop. For example, two drivers may perceive the same sunset but interpret its beauty differently based on their experiences or cultural backgrounds. This distinction is crucial in fields like marketing, where consumer perception of an advertisement's visuals can differ from their interpretation of the brand message.
Enhancing Awareness: Bridging Perception and Interpretation
Enhancing awareness involves recognizing the distinct roles of perception and interpretation in shaping your understanding of the world. Perception refers to the sensory input received from the environment, while interpretation is the cognitive process that assigns meaning to those sensory experiences. By improving your ability to consciously bridge perception and interpretation, you can develop more accurate insights and reduce biases in decision-making.
Infographic: Perception vs Interpretation
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com