Emotional intelligence enhances relationship management by recognizing and regulating emotions, while empathy involves understanding and sharing others' feelings. Discover how mastering both skills can transform your connections in this article.
Table of Comparison
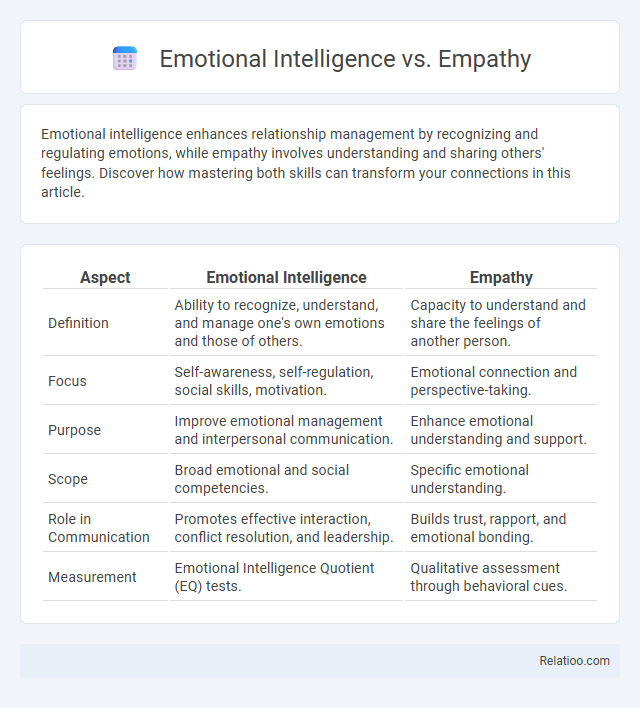
| Aspect | Emotional Intelligence | Empathy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Ability to recognize, understand, and manage one's own emotions and those of others. | Capacity to understand and share the feelings of another person. |
| Focus | Self-awareness, self-regulation, social skills, motivation. | Emotional connection and perspective-taking. |
| Purpose | Improve emotional management and interpersonal communication. | Enhance emotional understanding and support. |
| Scope | Broad emotional and social competencies. | Specific emotional understanding. |
| Role in Communication | Promotes effective interaction, conflict resolution, and leadership. | Builds trust, rapport, and emotional bonding. |
| Measurement | Emotional Intelligence Quotient (EQ) tests. | Qualitative assessment through behavioral cues. |
Understanding Emotional Intelligence
Understanding Emotional Intelligence involves recognizing your ability to perceive, control, and evaluate emotions effectively in yourself and others. Empathy, a core component of Emotional Intelligence, specifically refers to the capacity to understand and share the feelings of another person. By developing your Emotional Intelligence, you enhance interpersonal skills, improve conflict resolution, and foster stronger emotional connections.
Defining Empathy: A Core Component
Empathy is a fundamental aspect of emotional intelligence, involving the ability to understand and share the feelings of others. It enables individuals to perceive emotions accurately, fostering deeper interpersonal connections and effective communication. As a core component, empathy bridges cognitive recognition of emotions with emotional responsiveness, enhancing social awareness and relationship management.
Key Differences Between Emotional Intelligence and Empathy
Emotional Intelligence involves your ability to recognize, understand, and manage your own emotions and those of others, while empathy specifically refers to the capacity to feel and share another person's emotional experience. Key differences between Emotional Intelligence and empathy lie in scope and application: Emotional Intelligence encompasses emotional regulation, social skills, and self-awareness, whereas empathy primarily focuses on emotional connection and perspective-taking. Mastering Emotional Intelligence allows you to use empathy effectively within broader interpersonal interactions and decision-making processes.
The Role of Self-Awareness in Emotional Intelligence
Self-awareness is a fundamental component of emotional intelligence, enabling individuals to recognize and understand their own emotions, which is crucial for managing reactions and making informed decisions. Unlike empathy, which involves sensing and relating to others' emotions, self-awareness focuses inward, providing clarity about personal emotional states and triggers. Developing self-awareness enhances emotional intelligence by fostering greater emotional regulation, interpersonal skills, and overall psychological resilience.
How Empathy Drives Human Connection
Empathy, a core component of emotional intelligence (EI), enables individuals to understand and share the feelings of others, fostering deeper human connections and trust. Unlike general EI, which encompasses self-awareness, self-regulation, and social skills, empathy specifically drives interpersonal bonding by facilitating genuine emotional resonance. This emotional attunement strengthens relationships, enhances communication, and improves collaborative outcomes in both personal and professional contexts.
Emotional Intelligence in Leadership and Relationships
Emotional Intelligence in leadership enhances decision-making, conflict resolution, and team motivation by enabling leaders to recognize, understand, and manage their own emotions while effectively responding to the emotions of others. Empathy, a key component of Emotional Intelligence, allows leaders to build trust and foster strong relationships by genuinely understanding and validating the feelings of team members. In personal and professional relationships, high Emotional Intelligence improves communication, reduces misunderstandings, and promotes emotional support, creating a foundation for healthy and productive interactions.
Types of Empathy: Cognitive, Emotional, and Compassionate
Emotional intelligence encompasses the ability to recognize, understand, and manage your own emotions as well as others' feelings, while empathy specifically refers to the capacity to sense and share another person's emotional experience. Types of empathy include cognitive empathy, which involves intellectually understanding someone else's perspective; emotional empathy, characterized by physically feeling another's emotions; and compassionate empathy, which combines understanding and feeling with the motivation to take action and help. Developing these distinct forms of empathy enhances your emotional intelligence by improving interpersonal communication and fostering deeper connections.
Developing Emotional Intelligence: Practical Strategies
Developing emotional intelligence involves enhancing self-awareness, self-regulation, motivation, empathy, and social skills through deliberate practice and reflection. Practical strategies include active listening, mindfulness meditation, journaling emotions, and seeking feedback to recognize and manage emotional responses effectively. Empathy, a key component of emotional intelligence, can be strengthened by perspective-taking exercises and engaging in meaningful interpersonal interactions to better understand and respond to others' feelings.
Empathy Training: Building Better Social Skills
Empathy training enhances emotional intelligence by improving the ability to understand and share the feelings of others, which is crucial for effective social interactions. Developing empathy skills fosters better communication, reduces conflicts, and strengthens relationships in both personal and professional settings. Research shows that targeted empathy exercises, such as perspective-taking and active listening, significantly boost social competence and emotional regulation.
Integrating Emotional Intelligence and Empathy for Success
Integrating emotional intelligence and empathy enhances your ability to understand and manage both your emotions and those of others, fostering stronger relationships and effective communication. Emotional intelligence equips you with self-awareness and emotional regulation skills, while empathy deepens your capacity to connect and respond to the feelings of others authentically. This synergy boosts collaboration, conflict resolution, and overall success in personal and professional environments.
Infographic: Emotional Intelligence vs Empathy
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com