Engagement in relationships fosters deep connection, trust, and mutual support, while disengagement leads to emotional distance, misunderstandings, and potential conflict. Discover key strategies to enhance engagement and prevent disengagement in your relationships in this article.
Table of Comparison
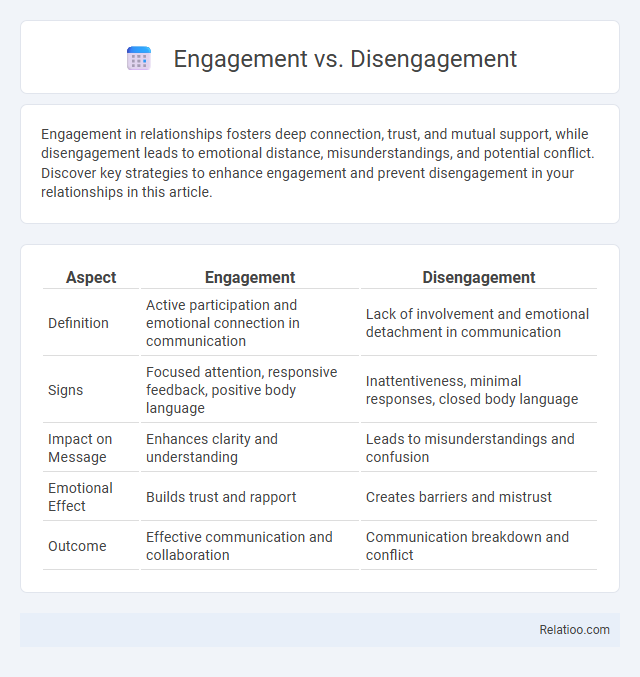
| Aspect | Engagement | Disengagement |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Active participation and emotional connection in communication | Lack of involvement and emotional detachment in communication |
| Signs | Focused attention, responsive feedback, positive body language | Inattentiveness, minimal responses, closed body language |
| Impact on Message | Enhances clarity and understanding | Leads to misunderstandings and confusion |
| Emotional Effect | Builds trust and rapport | Creates barriers and mistrust |
| Outcome | Effective communication and collaboration | Communication breakdown and conflict |
Understanding Engagement vs Disengagement
Understanding engagement vs disengagement involves recognizing how active participation contrasts with withdrawal in workplace or learning environments. Engagement reflects your emotional commitment, motivation, and involvement, leading to higher productivity and satisfaction. Disengagement, marked by apathy and lack of interest, can cause reduced performance and increased turnover risk.
Key Drivers of Engagement
Employee engagement is primarily driven by factors such as meaningful work, recognition, and opportunities for growth, which foster motivation and commitment. Disengagement often stems from poor management, lack of communication, and insufficient support, leading to decreased productivity and morale. Understanding these key drivers enables organizations to implement targeted strategies that enhance engagement and reduce turnover.
Common Causes of Disengagement
Disengagement in the workplace often stems from unclear job expectations, lack of recognition, and insufficient opportunities for growth, which can significantly impact Your motivation and productivity. Low communication quality and inadequate leadership support further contribute to employee disengagement, causing decreased commitment and higher turnover rates. Identifying and addressing these common causes can help improve engagement and foster a more motivated, loyal workforce.
Signs and Symptoms of Disengaged Individuals
Disengaged individuals often exhibit signs such as decreased productivity, lack of enthusiasm, and frequent absenteeism, which negatively impact overall team performance. Symptoms include minimal participation in meetings, reduced communication, and a noticeable decline in quality of work. Identifying these behaviors early is crucial for fostering employee retention and promoting workplace engagement.
Impact of Engagement on Performance
Employee engagement significantly boosts work performance by enhancing motivation, commitment, and productivity within teams. Disengagement, on the other hand, leads to decreased efficiency, higher absenteeism, and increased turnover rates, directly affecting organizational success. Your focus on fostering engagement can transform workplace culture and drive sustainable performance improvements.
Consequences of Persistent Disengagement
Persistent disengagement in the workplace leads to decreased productivity, higher absenteeism, and increased turnover rates, significantly impacting organizational performance. Employees experiencing ongoing disengagement often exhibit reduced motivation, lower job satisfaction, and deteriorating mental health, which can result in costly operational inefficiencies. Addressing persistent disengagement is critical to maintaining employee well-being and sustaining long-term business success.
Strategies to Increase Engagement
Strategies to increase engagement focus on fostering meaningful interaction and connection within your audience or team by creating relevant content, personalized experiences, and active participation opportunities. Implementing regular feedback mechanisms, recognition programs, and clear communication channels significantly boosts motivation and emotional investment. Utilizing data analytics to tailor your approach ensures your efforts effectively address the specific needs and preferences driving engagement rather than disengagement or alienation.
Overcoming Barriers to Engagement
Engagement requires identifying and addressing key barriers such as lack of motivation, unclear goals, and insufficient support systems that hinder active participation. Overcoming these obstacles involves creating personalized strategies that foster a sense of purpose, provide clear communication, and build a supportive environment tailored to Your needs. Consistent feedback and adaptive learning techniques strengthen commitment and reduce tendencies toward disengagement and burnout.
Measuring Engagement and Disengagement
Measuring engagement involves tracking metrics such as active participation rates, time spent on tasks, and emotional investment through surveys or behavioral analytics. Disengagement is assessed by identifying decreased productivity, increased absenteeism, and lower interaction levels within teams or platforms. Accurate measurement of both concepts requires combining quantitative data like click rates or response times with qualitative feedback to capture the full scope of user or employee involvement.
Building a Culture of Lasting Engagement
Building a culture of lasting engagement requires understanding the critical differences between engagement and disengagement, where engagement reflects employees' emotional commitment and proactive participation in their work, while disengagement signifies apathy or withdrawal that can reduce productivity. Organizations should implement continuous feedback systems, promote transparent communication, and foster meaningful recognition to sustain high engagement levels. Cultivating psychological safety and aligning individual roles with organizational values drives long-term employee motivation and reduces turnover rates.
Infographic: Engagement vs Disengagement
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com