Active listening involves fully engaging with the speaker's message, emotions, and intentions, while hearing is merely the passive perception of sound. Discover how mastering active listening can transform your relationships in this article.
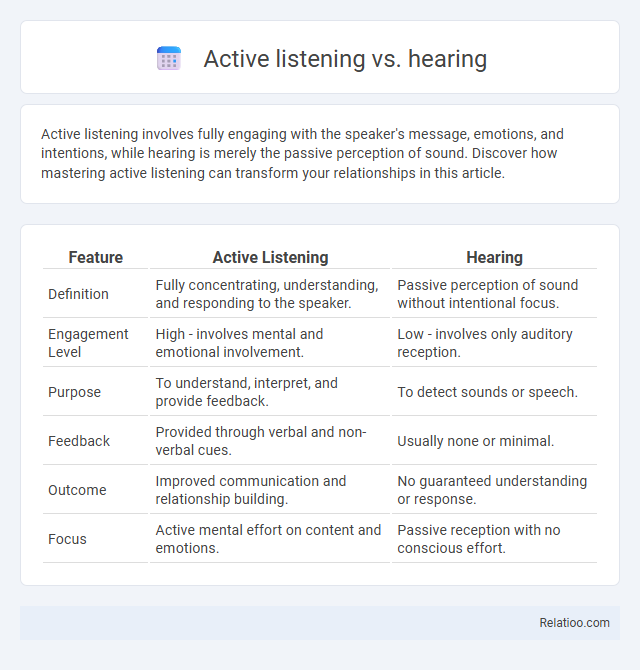
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Active Listening | Hearing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Fully concentrating, understanding, and responding to the speaker. | Passive perception of sound without intentional focus. |
| Engagement Level | High - involves mental and emotional involvement. | Low - involves only auditory reception. |
| Purpose | To understand, interpret, and provide feedback. | To detect sounds or speech. |
| Feedback | Provided through verbal and non-verbal cues. | Usually none or minimal. |
| Outcome | Improved communication and relationship building. | No guaranteed understanding or response. |
| Focus | Active mental effort on content and emotions. | Passive reception with no conscious effort. |
Understanding the Basics: Active Listening vs Hearing
Active listening involves fully engaging with the speaker by focusing on their words, tone, and body language to ensure comprehension, unlike hearing, which is simply the passive act of perceiving sound. Your ability to practice active listening enhances communication effectiveness by minimizing misunderstandings and fostering meaningful connections. Understanding these basics improves interpersonal skills and promotes empathy in conversations.
The Science Behind Hearing and Listening
Hearing is the passive process of perceiving sound waves by the ear, while active listening involves intentional focus, cognitive processing, and interpreting the auditory information received. Neuroscientific studies show that active listening engages brain regions such as the prefrontal cortex and auditory cortex, facilitating comprehension and memory retention beyond mere sound detection. This distinction underscores how active listening enhances communication effectiveness by transforming raw auditory input into meaningful understanding.
Key Differences Between Hearing and Active Listening
Hearing is the passive perception of sound without engagement or processing, while active listening involves fully concentrating, understanding, and responding to the speaker's message. Key differences include attention level, where hearing requires minimal focus and active listening demands intentional mental effort, and response, as active listening includes providing feedback or clarification. Active listening enhances communication effectiveness, fosters empathy, and improves problem-solving, unlike mere hearing which is a basic sensory experience.
Psychological Importance of Active Listening
Active listening involves fully engaging with the speaker by interpreting verbal and non-verbal cues, which significantly enhances understanding and emotional connection. Unlike hearing, which is passive and merely registers sounds, active listening promotes empathy, reduces misunderstandings, and strengthens interpersonal relationships. Psychological research highlights that active listening supports mental health by fostering trust, validating emotions, and improving communication skills in both personal and professional settings.
Common Barriers to Effective Listening
Common barriers to effective listening include distractions, preconceived notions, and emotional interference, which can impede both hearing and active listening processes. Hearing is the passive reception of sound, while active listening involves fully concentrating, understanding, and responding, requiring intentional effort to overcome these obstacles. Recognizing psychological, environmental, and physiological barriers helps improve active listening skills and facilitates clearer communication.
Benefits of Practicing Active Listening
Active listening enhances communication by improving understanding, fostering trust, and reducing misunderstandings compared to passive hearing. Practicing active listening increases empathy, strengthens relationships, and promotes effective problem-solving. Integrating active listening skills in personal and professional settings leads to higher engagement and collaboration.
Signs You’re Only Hearing, Not Listening
Hearing is the passive process of perceiving sound, while active listening requires full attention and engagement to understand the message being communicated. Signs you're only hearing, not listening, include frequent distractions, lack of response or feedback, and missing key details or emotional cues in the conversation. To improve your communication skills, you must focus on maintaining eye contact, asking clarifying questions, and providing thoughtful responses that show genuine understanding.
Techniques to Improve Active Listening Skills
Active listening involves fully concentrating, understanding, and responding to your speaker, whereas hearing is merely the passive perception of sound without engagement. Techniques to improve active listening skills include maintaining eye contact, providing feedback through nodding or paraphrasing, and minimizing distractions to focus your attention entirely on the speaker. Your ability to practice these techniques enhances communication, ensuring that you accurately interpret and respond to the message being conveyed.
Active Listening in Professional and Personal Relationships
Active listening involves fully concentrating, understanding, and responding to speakers, distinguishing it from passive hearing which is merely perceiving sound without engagement. In professional settings, active listening enhances workplace communication by fostering trust, preventing misunderstandings, and improving conflict resolution. In personal relationships, it strengthens emotional bonds by showing empathy, validating feelings, and encouraging open dialogue, making it a critical skill for effective interpersonal interactions.
Transforming Communication with Active Listening Strategies
Active listening transforms communication by engaging fully with the speaker through focused attention, feedback, and clarification, unlike passive hearing which involves merely perceiving sound without comprehension. Employing active listening strategies such as paraphrasing, asking open-ended questions, and providing nonverbal affirmations fosters deeper understanding and trust in conversations. This approach enhances interpersonal relationships, reduces misunderstandings, and promotes effective problem-solving by truly connecting with the speaker's message and emotions.
Infographic: Active listening vs Hearing
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com