Influence shapes relationships through persuasion and trust, while power relies on authority and control to dictate outcomes. Explore the dynamics of Influence vs Power and their impact on personal and professional relationships in this article.
Table of Comparison
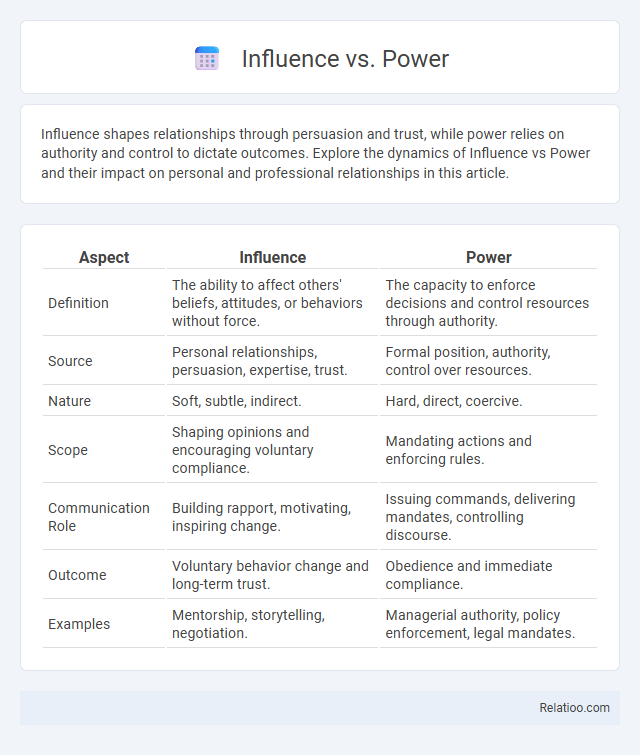
| Aspect | Influence | Power |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The ability to affect others' beliefs, attitudes, or behaviors without force. | The capacity to enforce decisions and control resources through authority. |
| Source | Personal relationships, persuasion, expertise, trust. | Formal position, authority, control over resources. |
| Nature | Soft, subtle, indirect. | Hard, direct, coercive. |
| Scope | Shaping opinions and encouraging voluntary compliance. | Mandating actions and enforcing rules. |
| Communication Role | Building rapport, motivating, inspiring change. | Issuing commands, delivering mandates, controlling discourse. |
| Outcome | Voluntary behavior change and long-term trust. | Obedience and immediate compliance. |
| Examples | Mentorship, storytelling, negotiation. | Managerial authority, policy enforcement, legal mandates. |
Defining Influence and Power
Influence refers to the ability to shape others' thoughts, behaviors, or decisions through persuasion, charisma, or expertise, often operating subtly without formal authority. Power, in contrast, denotes the capacity to enforce actions or control outcomes through authority, coercion, or resource control, typically backed by institutional or hierarchical structures. Understanding the distinction highlights that influence cultivates voluntary compliance, while power demands obedience often linked to position or force.
Key Differences Between Influence and Power
Influence involves the ability to shape others' thoughts, behaviors, or decisions through persuasion, while power is the capacity to enforce commands or control resources often backed by authority. Influence relies on relationship-building and trust, whereas power depends on formal positions, rules, or tangible assets. Understanding these key differences helps you leverage influence for collaborative success and power for organizational control.
Types of Influence in Organizations
Types of influence in organizations include expert influence, where authority is derived from specialized knowledge or skills, and legitimate influence, based on formal position or role within the hierarchy. Referent influence stems from personal traits that inspire admiration and identification, while coercive influence involves the ability to impose sanctions or penalties. Informational influence relies on access to and control of valuable information that affects decision-making and organizational behavior.
Forms of Power and Their Sources
Forms of power include legitimate, reward, coercive, expert, and referent power, each stemming from different sources of influence. Legitimate power arises from formal authority within an organization, while reward and coercive power depend on the ability to provide benefits or impose sanctions. Expert power derives from specialized knowledge or skills, and referent power is based on personal traits that inspire admiration and loyalty.
The Role of Authority in Power Dynamics
Authority fundamentally shapes power dynamics by legitimizing influence within social and organizational hierarchies. Your ability to exercise power increases when authority is recognized, as it grants formal rights to make decisions and enforce compliance. Influence, however, often operates through persuasion and interpersonal relationships, supplementing or challenging authority in complex power structures.
How Influence Shapes Decision-Making
Influence shapes decision-making by subtly guiding opinions and behaviors through persuasion, credibility, and social proof rather than direct authority. Unlike power, which relies on formal control or coercion, influence operates through trust and relationships, enabling lasting change in individual and group choices. Effective use of influence often leads to collaborative, voluntary commitments that align with strategic goals in organizations and social contexts.
Ethical Considerations: Influence vs Power
Ethical considerations distinguish influence and power by emphasizing the intent and methods used to affect others. Influence relies on persuasion and mutual respect, promoting ethical behavior through transparency and consent. Power, when misused, can lead to coercion and manipulation, raising concerns about abuse and ethical responsibility.
Real-World Examples of Influence and Power
Real-world examples of influence include Oprah Winfrey's ability to shape public opinion through media and social platforms, demonstrating persuasive soft power without formal authority. Power is exemplified by political leaders like Angela Merkel, whose official position enabled decisive policy implementations impacting millions. Influence often operates through social capital and credibility, while power relies on institutional authority and control over resources.
Building Influence Without Authority
Building influence without authority relies on establishing trust, demonstrating expertise, and fostering strong relationships within your network. You can enhance your ability to sway decisions and inspire action by consistently delivering value, communicating effectively, and aligning your goals with those of your colleagues. This approach creates a foundation of respect and credibility, enabling you to lead and motivate even without formal power.
Balancing Influence and Power for Effective Leadership
Balancing influence and power is crucial for effective leadership, as influence fosters trust and collaboration while power ensures authority and decision-making capacity. Leaders who skillfully blend influence with legitimate power create environments where team members feel motivated and respected, leading to higher productivity and engagement. Overreliance on power can breed resistance, whereas too much emphasis on influence without authority may undermine decisiveness, highlighting the necessity of equilibrium between the two for sustainable success.
Infographic: Influence vs Power
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com