Formal communication in relationships ensures clarity and professionalism through structured, respectful language, while informal communication fosters intimacy and spontaneity using casual, conversational tones. Discover how balancing both styles can enhance your personal and professional connections in this article.
Table of Comparison
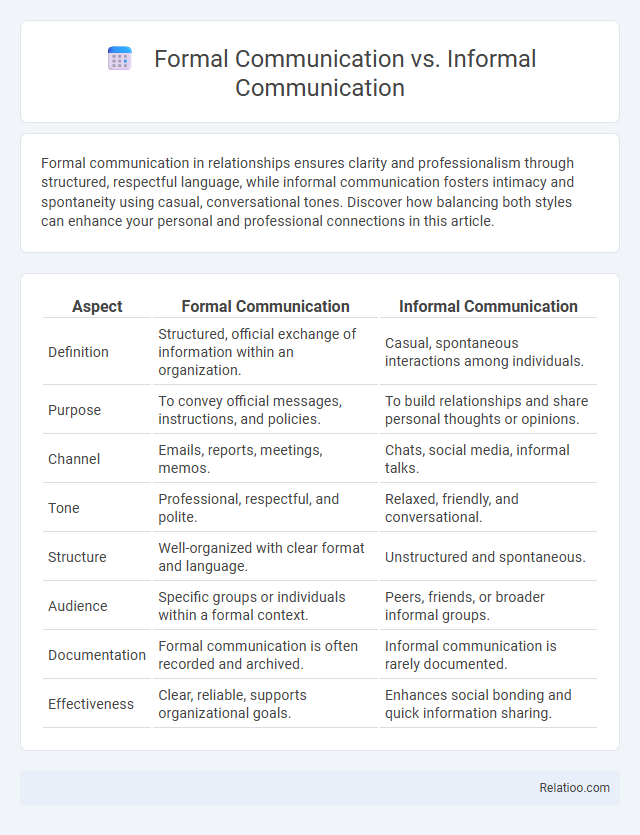
| Aspect | Formal Communication | Informal Communication |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Structured, official exchange of information within an organization. | Casual, spontaneous interactions among individuals. |
| Purpose | To convey official messages, instructions, and policies. | To build relationships and share personal thoughts or opinions. |
| Channel | Emails, reports, meetings, memos. | Chats, social media, informal talks. |
| Tone | Professional, respectful, and polite. | Relaxed, friendly, and conversational. |
| Structure | Well-organized with clear format and language. | Unstructured and spontaneous. |
| Audience | Specific groups or individuals within a formal context. | Peers, friends, or broader informal groups. |
| Documentation | Formal communication is often recorded and archived. | Informal communication is rarely documented. |
| Effectiveness | Clear, reliable, supports organizational goals. | Enhances social bonding and quick information sharing. |
Introduction to Formal and Informal Communication
Formal communication follows structured channels within organizations, ensuring clarity, accountability, and consistency through official reports, meetings, and emails. Informal communication occurs spontaneously among employees, fostering quick information exchange and relationship-building via casual conversations, social interactions, and unofficial messaging. Recognizing the boundary between these modes helps maintain professionalism while encouraging collaboration and team cohesion.
Defining Formal Communication
Formal communication refers to the structured exchange of information within established organizational channels, following predefined rules and protocols. It typically involves official documents, emails, reports, and meetings that maintain professionalism and clarity. Boundaries in formal communication ensure message consistency, authority, and accountability, distinguishing it from informal interactions.
Defining Informal Communication
Informal communication is the spontaneous, unofficial exchange of information that occurs without prescribed channels or protocols, typically through casual conversations, social interactions, or personal networks. This mode of communication fosters a relaxed atmosphere, enabling quicker information flow, relationship building, and immediate feedback, often transcending hierarchical boundaries within an organization. Unlike formal communication, informal communication lacks structured documentation and is characterized by its fluid, dynamic nature, making it essential for fostering workplace culture and enhancing collaboration.
Key Differences Between Formal and Informal Communication
Formal communication follows predefined channels and structured formats, ensuring clarity and accountability within organizational hierarchies. Informal communication occurs spontaneously through personal interactions, fostering quicker information exchange but lacking official documentation. Understanding these key differences helps you navigate workplace dynamics effectively by recognizing when to use formal procedures or informal conversations.
Advantages of Formal Communication
Formal communication ensures clarity and consistency in transmitting important organizational information, reducing misunderstandings. It establishes clear boundaries and protocols, which enhances accountability and maintains professionalism within teams. Your ability to rely on structured communication channels leads to improved coordination and efficient decision-making.
Advantages of Informal Communication
Informal communication facilitates faster information exchange and fosters stronger interpersonal relationships within teams, enhancing collaboration and creativity. Your ability to leverage informal channels, such as casual conversations or instant messaging, can lead to increased trust and morale among colleagues. This communication style often bridges hierarchical gaps, making it easier to address issues promptly without the rigidity of formal boundaries.
Disadvantages of Formal Communication
Formal communication often limits spontaneity and restricts the flow of creative ideas due to rigid structures and protocols. Employees may experience delays in decision-making and feedback, reducing overall efficiency and responsiveness within the organization. The established boundaries in formal communication can also create a sense of hierarchy that discourages open dialogue and collaboration.
Disadvantages of Informal Communication
Informal communication often leads to misinformation due to its reliance on unofficial channels and lack of verification. It can cause misunderstandings and rumors, which disrupt team cohesion and reduce overall productivity. The absence of clear boundaries in informal communication may result in breaches of confidentiality and unprofessional behavior.
Choosing the Right Communication Channel
Choosing the right communication channel depends on the context, audience, and purpose of your message, balancing formal and informal communication styles. Formal communication, used for official, professional, or sensitive information, requires clarity, structure, and often written documentation, while informal communication suits casual, quick interactions and fosters rapport. Understanding boundaries ensures you select channels that respect privacy, maintain professionalism, and promote effective information flow tailored to your communication goals.
Conclusion: Balancing Formal and Informal Communication
Balancing formal and informal communication enhances organizational effectiveness by fostering clarity while promoting interpersonal relationships. Your ability to navigate these communication styles ensures boundaries are respected without stifling collaboration or creativity. Maintaining this equilibrium drives productivity, trust, and a positive work environment.
Infographic: Formal vs Informal Communication
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com