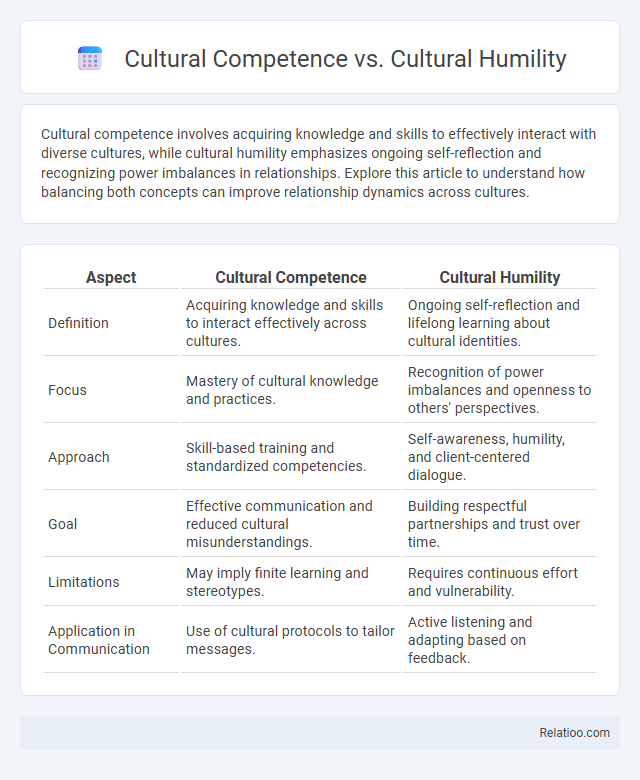
Cultural competence involves acquiring knowledge and skills to effectively interact with diverse cultures, while cultural humility emphasizes ongoing self-reflection and recognizing power imbalances in relationships. Explore this article to understand how balancing both concepts can improve relationship dynamics across cultures.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Cultural Competence | Cultural Humility |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Acquiring knowledge and skills to interact effectively across cultures. | Ongoing self-reflection and lifelong learning about cultural identities. |
| Focus | Mastery of cultural knowledge and practices. | Recognition of power imbalances and openness to others' perspectives. |
| Approach | Skill-based training and standardized competencies. | Self-awareness, humility, and client-centered dialogue. |
| Goal | Effective communication and reduced cultural misunderstandings. | Building respectful partnerships and trust over time. |
| Limitations | May imply finite learning and stereotypes. | Requires continuous effort and vulnerability. |
| Application in Communication | Use of cultural protocols to tailor messages. | Active listening and adapting based on feedback. |
Understanding Cultural Competence: Definition and Origins
Cultural competence refers to the ability of individuals and organizations to effectively interact with people from diverse cultural backgrounds by acquiring relevant knowledge, attitudes, and skills. Originating from healthcare and social work fields, this concept emphasizes understanding cultural differences to improve communication and service delivery. Unlike cultural humility, which focuses on self-reflection and lifelong learning, cultural competence aims at achieving measurable proficiency in cross-cultural interactions, supporting inclusive environments.
Exploring Cultural Humility: A Paradigm Shift
Cultural humility involves a lifelong commitment to self-evaluation and critique, emphasizing the importance of acknowledging power imbalances and learning from diverse cultural experiences. Unlike cultural competence, which focuses on acquiring specific knowledge and skills about different cultures, cultural humility prioritizes openness and respect for others' cultural identities. Your ability to practice cultural humility fosters authentic inclusion by valuing individual perspectives and promoting equitable interactions in diverse environments.
Key Differences Between Cultural Competence and Cultural Humility
Cultural competence involves acquiring knowledge and skills to effectively interact with diverse cultures, emphasizing measurable proficiency and expertise in cultural practices. Cultural humility requires continuous self-reflection and recognizing personal biases, fostering an open mindset that prioritizes listening and learning from others' experiences. You develop inclusion by integrating both approaches, ensuring respectful engagement and equitable participation within diverse environments.
The Role of Self-Reflection in Cultural Humility
Self-reflection plays a crucial role in cultural humility by encouraging individuals to critically examine their own biases, assumptions, and cultural identities. This process fosters continuous personal growth and adaptability, allowing for more genuine and respectful interactions in diverse environments. Unlike cultural competence, which focuses on acquiring knowledge about cultures, cultural humility emphasizes an ongoing commitment to self-awareness and openness to learning from others.
Limitations of Cultural Competence in Practice
Cultural competence often emphasizes acquiring knowledge about different cultures, but it risks oversimplifying complex identities and perpetuating stereotypes, limiting genuine understanding. Your ability to adapt and respond to diverse individuals may be constrained when relying solely on static cultural facts rather than engaging in ongoing self-reflection and learning. Unlike cultural humility and inclusion, which prioritize continuous growth and equitable participation, cultural competence in practice may fail to address power imbalances and systemic barriers effectively.
Benefits of Embracing Cultural Humility in Diverse Settings
Embracing cultural humility fosters genuine respect and continuous self-evaluation, enhancing communication and trust in diverse settings. This approach benefits your organization by promoting collaboration and reducing biases, resulting in more equitable and effective interactions. Prioritizing cultural humility supports a dynamic environment where diverse perspectives are valued, driving innovation and social cohesion.
Practical Strategies for Developing Cultural Humility
Developing cultural humility requires continuous self-reflection, recognizing personal biases, and actively seeking to understand diverse cultural perspectives through open dialogue and feedback. Practical strategies include engaging in immersive cultural experiences, participating in training programs that emphasize empathy and listening skills, and building long-term relationships with individuals from different backgrounds. Emphasizing humility over competence fosters adaptability and respect, creating inclusive environments that value ongoing learning and equitable collaboration.
Impact on Healthcare, Education, and Social Services
Cultural competence equips healthcare, education, and social services professionals with the skills to recognize and respect diverse cultural backgrounds, improving communication and outcomes. Cultural humility encourages ongoing self-reflection and learning, fostering deeper trust and reducing disparities in service delivery. Inclusion ensures that diverse perspectives are actively valued and integrated, enhancing Your ability to create equitable environments that address systemic inequities effectively.
Overcoming Challenges in Cultural Competence and Humility
Overcoming challenges in cultural competence requires continuous education and self-awareness to recognize implicit biases and avoid stereotyping, while cultural humility emphasizes ongoing self-reflection and openness to learning from diverse cultural experiences. Both approaches demand effective communication skills and empathy to build trust and meaningful relationships across cultural boundaries. Inclusion complements these efforts by fostering environments where diverse perspectives are valued, reducing systemic barriers, and promoting equity in workplaces and communities.
Moving Toward Culturally Responsive Practices
Cultural competence emphasizes understanding and effectively interacting with diverse cultural groups, while cultural humility focuses on lifelong self-reflection and recognizing power imbalances in cross-cultural interactions. Inclusion involves creating environments where all individuals feel valued and respected, fostering equitable participation. Moving toward culturally responsive practices requires integrating these approaches to better support Your engagement with diverse communities, promoting understanding, respect, and equity.
Infographic: Cultural Competence vs Cultural Humility
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com