Primary custody grants one parent exclusive decision-making authority and residency rights, while shared parenting involves joint custody responsibilities and equitable time distribution. Explore the benefits and challenges of each arrangement in this article.
Table of Comparison
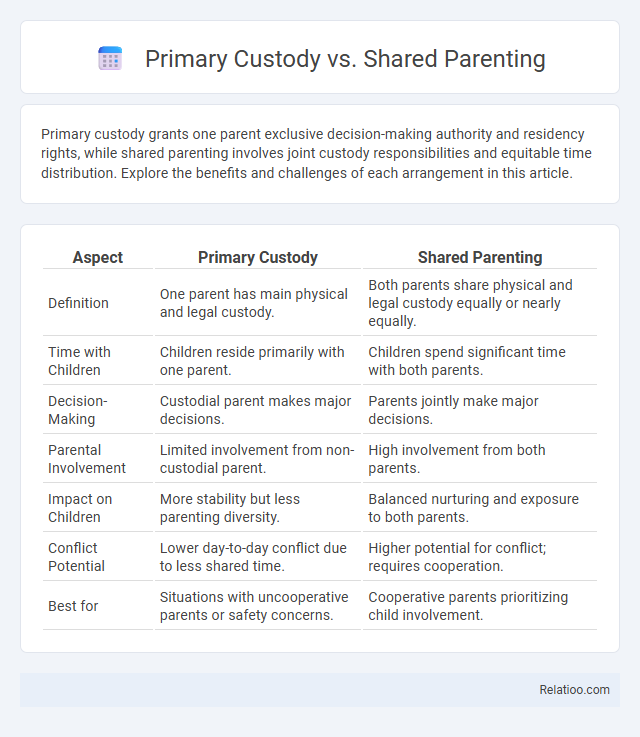
| Aspect | Primary Custody | Shared Parenting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | One parent has main physical and legal custody. | Both parents share physical and legal custody equally or nearly equally. |
| Time with Children | Children reside primarily with one parent. | Children spend significant time with both parents. |
| Decision-Making | Custodial parent makes major decisions. | Parents jointly make major decisions. |
| Parental Involvement | Limited involvement from non-custodial parent. | High involvement from both parents. |
| Impact on Children | More stability but less parenting diversity. | Balanced nurturing and exposure to both parents. |
| Conflict Potential | Lower day-to-day conflict due to less shared time. | Higher potential for conflict; requires cooperation. |
| Best for | Situations with uncooperative parents or safety concerns. | Cooperative parents prioritizing child involvement. |
Understanding Primary Custody
Primary custody refers to the parent who has the predominant responsibility for the child's day-to-day care and decision-making, often involving the child residing primarily with this parent. Understanding primary custody is crucial for determining legal and physical custody arrangements, as it affects the child's stability, schooling, and medical care. Courts assess factors such as the child's best interests, parental capability, and existing emotional bonds when awarding primary custody.
What Is Shared Parenting?
Shared parenting is a legal arrangement where both parents share decision-making responsibilities and physical custody of their child, promoting active involvement from both sides. This approach ensures that Your child maintains a stable relationship with each parent while balancing time spent at each residence. Courts prioritize shared parenting to support the child's well-being, development, and emotional stability.
Legal Definitions and Differences
Primary custody legally grants one parent the exclusive right to make major decisions regarding the child's welfare while the other parent may have visitation rights. Shared parenting, also known as joint custody, involves both parents sharing decision-making responsibilities and physical custody, promoting equal involvement in the child's life. Visitation refers to the non-custodial parent's scheduled time with the child, which is legally defined but does not confer decision-making authority.
Factors Courts Consider in Custody Decisions
Courts prioritize the child's best interests when deciding on primary custody, shared parenting, or visitation arrangements, analyzing factors such as the child's age, emotional needs, and each parent's ability to provide stability and care. Parenting history, including each parent's involvement in daily activities and capacity to support the child's development, plays a crucial role. Courts also consider the child's preference, sibling relationships, and any history of abuse or neglect to ensure a safe and nurturing environment.
Pros and Cons of Primary Custody
Primary custody grants one parent the legal right to make significant decisions regarding the child's education, healthcare, and welfare, ensuring consistency and stability in the child's daily routine. However, this arrangement may limit the non-custodial parent's involvement, potentially impacting the child's emotional connection and access to both parents. Courts often favor arrangements that foster strong, ongoing relationships with both parents unless safety or well-being concerns dictate otherwise.
Pros and Cons of Shared Parenting
Shared parenting allows both parents to actively participate in their child's life, fostering strong emotional bonds and balanced decision-making, which often supports the child's well-being and stability. However, shared parenting requires effective communication and cooperation between parents, and conflicts or logistical challenges can negatively impact the child's routine and emotional health. You must evaluate whether shared parenting suits your family's dynamics before committing to it, considering factors like work schedules, parental proximity, and the child's needs.
Emotional Impact on Children
Primary custody often leads to a stronger emotional bond with the custodial parent but may cause feelings of abandonment or loss with the non-custodial parent. Shared parenting tends to promote emotional stability by allowing children consistent contact with both parents, fostering a sense of security and balanced support. Visitation arrangements can result in emotional distress if the child's time with one parent is limited or unpredictable, potentially undermining the child's sense of continuity and attachment.
Co-Parenting Communication Strategies
Effective co-parenting communication strategies involve clear, consistent, and respectful dialogue regardless of whether you have primary custody, shared parenting, or visitation arrangements. Establishing boundaries, using neutral language, and prioritizing the child's needs help reduce conflicts and promote collaboration between parents. Utilizing tools like shared calendars and regular check-ins ensures both parties stay informed and coordinated for the child's well-being.
Transitioning Between Custody Arrangements
Transitioning between primary custody, shared parenting, and visitation arrangements requires clear communication and detailed parenting plans to minimize disruptions for the child. You should work with legal professionals to ensure all custody modifications comply with state laws and prioritize the child's best interests during transitions. Consistent routines and cooperative co-parenting strategies help ease adjustment periods and support emotional stability for your family.
Deciding What’s Best for Your Family
Primary custody grants one parent the majority of physical and legal decision-making responsibilities, ensuring stability and consistency for the child. Shared parenting promotes balanced involvement by both parents, fostering strong relationships and cooperation in upbringing. Visitation rights allow the non-custodial parent regular contact, maintaining emotional bonds while respecting the primary custodian's role, making the family's unique dynamics and child's best interests central to the decision.
Infographic: Primary Custody vs Shared Parenting
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com