Court-ordered visitation establishes legally enforceable schedules to ensure parental access, while informal visitation relies on mutual agreement without legal backing. Explore this article to understand the advantages and challenges of each visitation type.
Table of Comparison
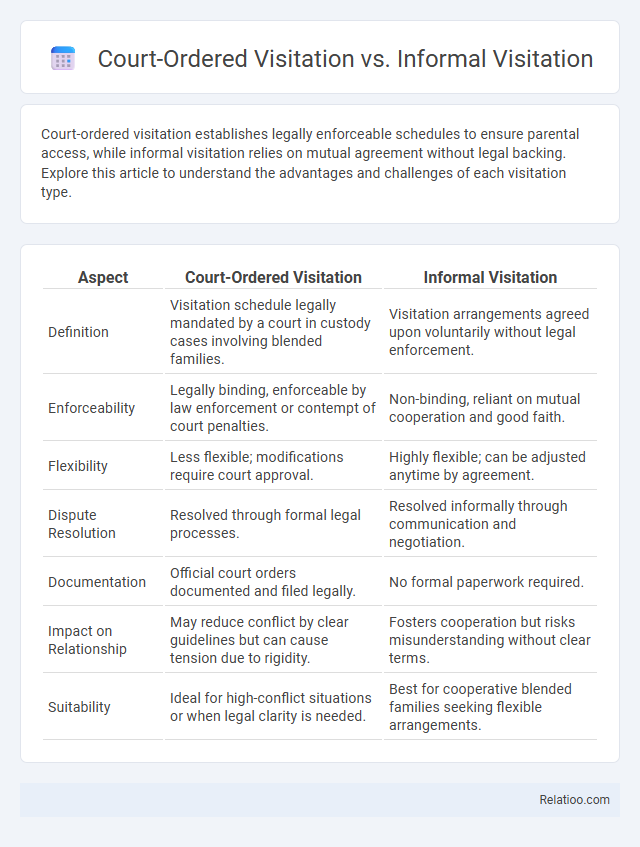
| Aspect | Court-Ordered Visitation | Informal Visitation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Visitation schedule legally mandated by a court in custody cases involving blended families. | Visitation arrangements agreed upon voluntarily without legal enforcement. |
| Enforceability | Legally binding, enforceable by law enforcement or contempt of court penalties. | Non-binding, reliant on mutual cooperation and good faith. |
| Flexibility | Less flexible; modifications require court approval. | Highly flexible; can be adjusted anytime by agreement. |
| Dispute Resolution | Resolved through formal legal processes. | Resolved informally through communication and negotiation. |
| Documentation | Official court orders documented and filed legally. | No formal paperwork required. |
| Impact on Relationship | May reduce conflict by clear guidelines but can cause tension due to rigidity. | Fosters cooperation but risks misunderstanding without clear terms. |
| Suitability | Ideal for high-conflict situations or when legal clarity is needed. | Best for cooperative blended families seeking flexible arrangements. |
Understanding Court-Ordered Visitation
Court-ordered visitation legally establishes a parent or guardian's visitation rights and schedule, ensuring enforcement through the judicial system. Unlike informal visitation, which relies on mutual agreements without legal backing, court-ordered visitation provides clarity and protection for your parental time. Understanding the legal implications and processes of court-ordered visitation helps you safeguard your rights and maintain consistent contact with your child.
What Is Informal Visitation?
Informal visitation refers to parenting time arrangements agreed upon directly between parents without court involvement or legal documentation. Unlike court-ordered visitation, which is mandated and enforceable by the legal system, informal visitation relies on mutual cooperation and flexibility. This type of visitation facilitates more personal and adaptable schedules but lacks the legal protections and enforceability of formal court orders.
Key Differences Between Court-Ordered and Informal Visitation
Court-ordered visitation is a legally binding arrangement determined by a judge to ensure consistent parental access, while informal visitation relies on mutual agreements between parents without legal enforcement. Court orders specify visitation schedules, rights, and responsibilities, protecting your parental time if disputes arise, whereas informal visitation depends on trust and cooperation and lacks official documentation. The key difference lies in legal enforceability and the ability to modify visitation terms through the court system versus the flexibility but potential instability of informal arrangements.
Legal Protections in Court-Ordered Visitation
Court-ordered visitation provides legally enforceable rights ensuring consistent and supervised access to a child, offering protections that informal visitation agreements lack. Your visitation schedule is backed by a court order, allowing modifications only through legal channels, which secures your parental rights and protects the child's best interests. Informal visitation relies on mutual consent without legal oversight, making court-ordered visitation the strongest option for guaranteed legal protections and enforcement.
Flexibility and Limitations of Informal Visitation
Court-ordered visitation establishes legally binding schedules ensuring consistency but can be rigid and difficult to modify without court approval. Informal visitation offers flexibility, allowing parents to adapt plans based on mutual agreement and changing circumstances, but this lack of formal structure risks misunderstandings and potential disputes if communication breaks down. Your ability to negotiate and maintain clear communication is crucial to maximizing the benefits of informal visitation while minimizing its limitations.
Enforcement and Compliance Challenges
Court-ordered visitation mandates specific schedules enforced by legal authorities, reducing ambiguity but often encountering compliance challenges such as missed visits that may require contempt proceedings. Informal visitation relies on mutual agreement, offering flexibility but lacking formal enforcement mechanisms, making it difficult to address non-compliance effectively. Your ability to ensure consistent visitation hinges on understanding these differences, as court orders provide stronger enforcement tools while informal arrangements depend heavily on cooperation.
Impact on Child’s Well-being
Court-ordered visitation provides a structured and legally enforced schedule that ensures consistent parent-child contact, often reducing conflict and promoting stability for the child's emotional well-being. Informal visitation allows for flexibility and may foster a more natural and adaptable parent-child relationship, but it risks irregularity that can cause anxiety or uncertainty for the child. Overall visitation quality, whether formal or informal, significantly influences the child's sense of security, attachment, and behavioral development.
Addressing Parental Disputes
Court-ordered visitation establishes legally binding schedules for non-custodial parents, reducing conflicts by providing clear guidelines enforced by the court system. Informal visitation relies on mutual agreement between parents, requiring effective communication and cooperation to minimize disputes. General visitation practices emphasize consistent contact for maintaining parent-child relationships, with structured arrangements often preventing misunderstandings and fostering smoother dispute resolution.
Modifying Visitation Arrangements
Court-ordered visitation provides legally binding guidelines for modifying visitation arrangements, requiring formal requests and judicial approval to ensure compliance and protect the child's best interests. Informal visitation allows parents flexibility to mutually agree on changes without court intervention, often based on communication and cooperation but lacking legal enforceability. Visitation in general encompasses both structured and flexible approaches, with modifications tailored to evolving family circumstances, prioritizing stability and the child's welfare.
Choosing the Best Visitation Option
Court-ordered visitation provides legally binding guidelines that ensure your parental rights are protected while maintaining consistent contact with your child, whereas informal visitation relies on mutual agreement without legal enforcement, which can sometimes lead to misunderstandings or conflicts. Choosing the best visitation option depends on factors such as the level of cooperation between parents, the child's best interests, and the need for legal clarity to prevent disputes. Your decision should prioritize a stable and supportive environment that fosters healthy relationships while considering the benefits and limitations of court-ordered, informal, and general visitation arrangements.
Infographic: Court-Ordered Visitation vs Informal Visitation
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com