Nuclear families consist of two parents and their biological children, offering a traditional family structure, while blended families combine members from previous relationships, creating diverse dynamics. Explore the benefits and challenges of both family types in this article.
Table of Comparison
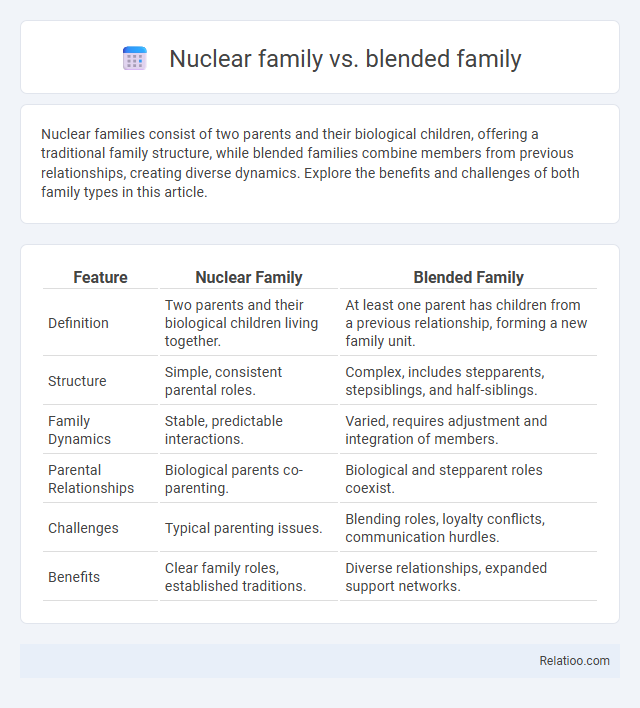
| Feature | Nuclear Family | Blended Family |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Two parents and their biological children living together. | At least one parent has children from a previous relationship, forming a new family unit. |
| Structure | Simple, consistent parental roles. | Complex, includes stepparents, stepsiblings, and half-siblings. |
| Family Dynamics | Stable, predictable interactions. | Varied, requires adjustment and integration of members. |
| Parental Relationships | Biological parents co-parenting. | Biological and stepparent roles coexist. |
| Challenges | Typical parenting issues. | Blending roles, loyalty conflicts, communication hurdles. |
| Benefits | Clear family roles, established traditions. | Diverse relationships, expanded support networks. |
Defining Nuclear and Blended Families
A nuclear family consists of two parents and their biological or adopted children living together as a single unit, emphasizing strong familial bonds and clear parental roles. A blended family forms when partners bring children from previous relationships into a new, combined household, creating complex family dynamics and the need for adaptive cohesion strategies. Family cohesion refers to the emotional bonding and support among family members, which varies in intensity and structure between nuclear and blended family types.
Historical Evolution of Family Structures
The historical evolution of family structures reveals the nuclear family as the dominant model in industrial societies, characterized by two parents and their biological children, emphasizing economic self-sufficiency and privacy. Blended families emerged more frequently due to higher divorce rates and remarriage, creating diverse family units with stepparents and stepsiblings that challenge traditional norms. Your understanding of family cohesion must consider how these structural shifts impact emotional bonds, communication patterns, and stability within both nuclear and blended families.
Core Characteristics of Nuclear Families
Nuclear families consist of two parents and their biological or adopted children living together, emphasizing strong parental roles and exclusive kinship bonds. Blended families form when partners merge their children from previous relationships, creating complex familial ties and varied household dynamics. Family cohesion measures emotional bonding and support within these structures, often strongest in nuclear families due to clear role definitions and shared responsibilities.
Core Characteristics of Blended Families
Blended families consist of partners bringing children from previous relationships, creating complex family dynamics that require strong communication and flexibility. Unlike nuclear families, which typically involve two parents and their biological children, blended families navigate the integration of multiple familial bonds and adjust roles to foster Unity. Your ability to maintain family cohesion in a blended family hinges on establishing trust, shared responsibilities, and emotional support among all members.
Emotional Dynamics in Nuclear vs Blended Families
Nuclear families typically experience stable emotional dynamics due to consistent parental roles and established routines, fostering secure attachments and predictable conflict resolution patterns. Blended families often face complex emotional dynamics as members navigate loyalty conflicts, role ambiguity, and integration challenges, requiring enhanced communication and adaptability to maintain harmony. Family cohesion in both family types hinges on effective emotional regulation and mutual support, but blended families demand greater flexibility to reconcile diverse emotional needs and histories.
Social Advantages and Challenges
Nuclear families often provide focused emotional support and clearer role definitions, enhancing family cohesion through stability and consistency in daily routines. Blended families offer rich social advantages by integrating diverse perspectives and fostering adaptability but may face challenges in establishing trust and managing complex relationships. Your ability to navigate these dynamics influences overall family cohesion, impacting communication, conflict resolution, and emotional bonding.
Parenting Roles and Responsibilities
Nuclear families typically feature clearly defined parenting roles, with both parents sharing responsibilities for child-rearing and household management, fostering stability and consistent guidance. Blended families often navigate more complex parenting dynamics, requiring effective communication and flexibility as stepparents and biological parents collaborate to maintain family cohesion. Your ability to balance these roles directly impacts family cohesion, promoting emotional bonding and a supportive environment essential for children's development.
Financial Implications and Resource Sharing
Nuclear families typically have a straightforward financial structure with income and expenses managed by fewer adults, while blended families often face complex financial implications due to multiple income sources, child support arrangements, and shared expenses among step-relatives. Family cohesion plays a crucial role in resource sharing by fostering cooperation and ensuring fair distribution of finances, which can reduce conflicts and promote financial stability. Understanding these dynamics helps you optimize budgeting strategies and effectively allocate resources within diverse family structures.
Impact on Child Development
Nuclear families often provide a stable environment that supports consistent parenting and clear role definitions, positively influencing child development. Blended families can offer enriched social experiences but may face challenges in establishing family cohesion, which can affect a child's emotional adjustment. Your child's growth benefits most from strong family cohesion, fostering secure attachments and emotional resilience regardless of family structure.
Navigating Conflicts and Building Strong Bonds
Nuclear families often rely on consistent routines to navigate conflicts and build strong bonds, fostering clarity and stability among members. Blended families face unique challenges requiring adaptive communication strategies to integrate diverse backgrounds and create cohesive relationships. Strong family cohesion enhances emotional support and resilience, promoting effective conflict resolution and lasting connections regardless of family structure.
Infographic: Nuclear family vs Blended family
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com