Stepparent rights often vary significantly from biological parent rights, with legal recognition typically requiring formal adoption or court approval. Understanding the nuances of custody, visitation, and decision-making authority is essential to navigating these complex family dynamics; discover more details in this article.
Table of Comparison
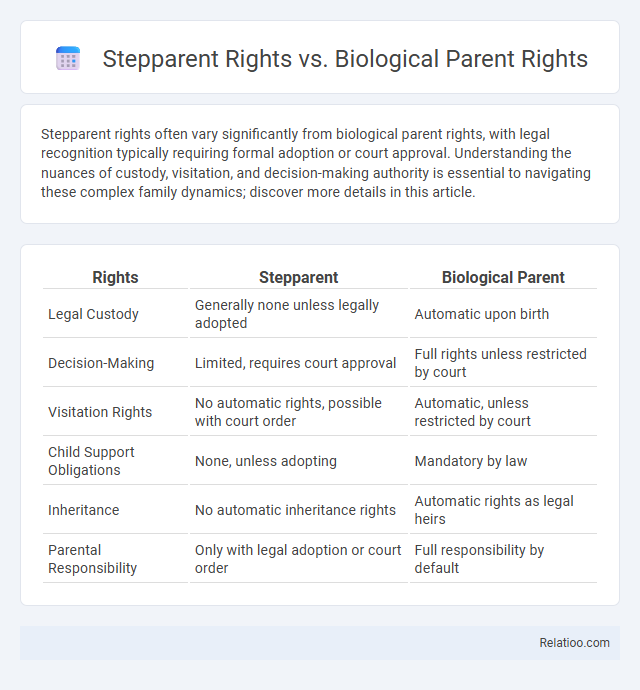
| Rights | Stepparent | Biological Parent |
|---|---|---|
| Legal Custody | Generally none unless legally adopted | Automatic upon birth |
| Decision-Making | Limited, requires court approval | Full rights unless restricted by court |
| Visitation Rights | No automatic rights, possible with court order | Automatic, unless restricted by court |
| Child Support Obligations | None, unless adopting | Mandatory by law |
| Inheritance | No automatic inheritance rights | Automatic rights as legal heirs |
| Parental Responsibility | Only with legal adoption or court order | Full responsibility by default |
Understanding Stepparent Rights: An Overview
Stepparent rights often differ significantly from biological parent rights, primarily because legal recognition of a stepparent's role depends on adoption or court approval rather than biology. Your ability to make decisions for a stepchild typically requires formal guardianship or custody arrangements, which vary by jurisdiction and case specifics. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for navigating responsibilities and legal protections related to stepparent involvement in a child's life.
Defining Biological Parent Rights in Family Law
Biological parent rights in family law primarily establish the legal responsibilities and privileges held by a child's genetic parent, including custody, visitation, and decision-making authority. These rights are protected to ensure the child's welfare and maintain the parental bond unless a court finds reasons to modify or terminate them, such as neglect or abandonment. Your understanding of how biological parent rights interact with stepparent roles is crucial for navigating custody disputes and ensuring the best interests of the child are met.
Custody Battles: Stepparent vs Biological Parent
Custody battles between stepparents and biological parents often hinge on legal rights, with biological parents typically holding primary custody claims unless proven unfit. Stepparents may seek custody or visitation rights by demonstrating a strong emotional bond and involvement in the child's life, but courts prioritize the child's best interests. Your understanding of these distinctions is crucial when navigating custody disputes where stepparent rights challenge biological parent claims.
Legal Adoption and Its Impact on Parental Rights
Legal adoption solidifies stepparent rights by granting them full parental authority, often equalizing their status with the biological parent in custody and decision-making matters. Biological parent rights may be limited or terminated during adoption, particularly if the stepparent assumes legal responsibility for the child's welfare. Understanding how legal adoption affects your parental rights can ensure clarity and security for all parties involved in the child's upbringing.
Visitation Rights: Stepparent Access after Divorce
Stepparent visitation rights after divorce vary significantly by jurisdiction, often requiring courts to balance the biological parent's custodial rights with the stepparent's established relationship with the child. Courts tend to prioritize the child's best interests, considering factors such as the length and quality of the stepparent-child relationship and the biological parent's willingness to facilitate visitation. Legal recognition of stepparent access typically hinges on demonstrating that visitation supports the child's emotional well-being without undermining the rights of the biological parent.
Decision-Making Authority: Medical, Educational, and Religious
Stepparent rights versus biological parent rights in decision-making authority often prioritize the biological parent's legal status for medical, educational, and religious decisions unless the stepparent has obtained legal guardianship or adoption. Medical consent typically requires the biological parent's authorization, but a court may grant stepparents limited authority in emergencies or through power of attorney arrangements. Educational enrollment and participation in religious rites generally hinge on the biological parent's consent, with stepparents needing explicit legal delegation to assume decision-making roles.
Child Support Obligations: Stepparent vs Biological Parent
Stepparent rights regarding child support obligations are typically limited compared to those of biological parents, as biological parents are legally responsible for providing financial support for their children. You may be required to contribute to child support only if you have legally adopted the child or assumed parental responsibilities through a court order, while biological parents remain financially liable by default. Courts prioritize the biological parent's duty to support their child, whereas stepparent involvement depends heavily on legal agreements and custody arrangements.
Stepchild’s Best Interests: The Court’s Perspective
Courts prioritize the stepchild's best interests when balancing stepparent rights versus biological parent rights, often granting stepparents visitation or custody only if it benefits the child's emotional and developmental needs. Legal recognition of stepparent rights typically hinges on established relationships and the biological parent's capability to provide care, with courts examining the stability and continuity offered by the stepparent. State statutes and case law increasingly reflect the importance of protecting the child's welfare above parental status, emphasizing consistent caregiving and nurturing environments.
Navigating Parental Rights in Blended Families
Navigating parental rights in blended families requires understanding the legal distinctions between stepparent rights and biological parent rights, which vary significantly by jurisdiction. Biological parents typically retain primary legal rights, including custody and decision-making authority, unless a court grants stepparents specific rights through adoption or guardianship. Establishing stepparent rights often involves legal processes like stepparent adoption, which transfers parental responsibilities and protections, ensuring clarity and stability within blended family dynamics.
Tips for Resolving Parental Rights Disputes Amicably
Resolving parental rights disputes amicably requires clear communication and a focus on the child's best interests. You can benefit from mediation services or family counseling to facilitate understanding between stepparents and biological parents, ensuring legal rights are respected while maintaining family harmony. Establishing a comprehensive parenting plan that outlines each party's responsibilities and visitation agreements helps prevent conflicts and promotes mutual respect.
Infographic: Stepparent Rights vs Biological Parent Rights
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com