Shared custody allows both parents to actively participate in their child's life, promoting balanced involvement and decision-making. Explore this article to understand the differences and benefits of shared custody versus full custody arrangements.
Table of Comparison
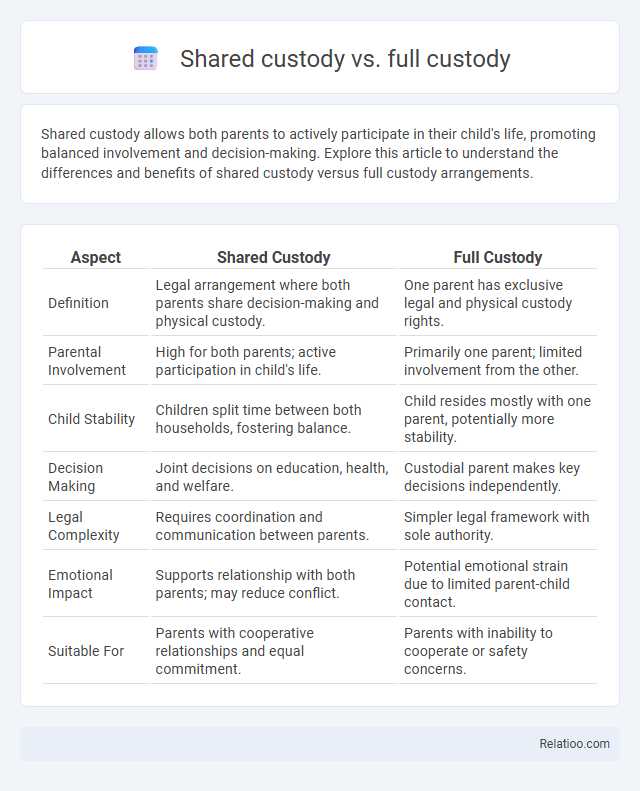
| Aspect | Shared Custody | Full Custody |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Legal arrangement where both parents share decision-making and physical custody. | One parent has exclusive legal and physical custody rights. |
| Parental Involvement | High for both parents; active participation in child's life. | Primarily one parent; limited involvement from the other. |
| Child Stability | Children split time between both households, fostering balance. | Child resides mostly with one parent, potentially more stability. |
| Decision Making | Joint decisions on education, health, and welfare. | Custodial parent makes key decisions independently. |
| Legal Complexity | Requires coordination and communication between parents. | Simpler legal framework with sole authority. |
| Emotional Impact | Supports relationship with both parents; may reduce conflict. | Potential emotional strain due to limited parent-child contact. |
| Suitable For | Parents with cooperative relationships and equal commitment. | Parents with inability to cooperate or safety concerns. |
Understanding Shared Custody
Shared custody involves both parents having legal and/or physical custody of a child, promoting joint decision-making and time-sharing that benefits the child's well-being. Full custody grants one parent sole legal and physical responsibility, limiting the other parent's involvement to visitation rights or none at all. Understanding shared custody emphasizes balanced parental involvement, fostering consistent emotional support and stability essential for a child's development.
What Is Full Custody?
Full custody grants one parent exclusive legal and physical responsibility for the child, allowing them to make major decisions about healthcare, education, and welfare without requiring consent from the other parent. Shared custody involves both parents having legal rights and physical time with the child, promoting joint decision-making and involvement in the child's life. Your understanding of full custody is critical, as it directly affects your parental rights and your child's living arrangements.
Legal Definitions: Shared vs Full Custody
Shared custody involves both parents legally sharing decision-making responsibilities and physical time with the child, fostering cooperation and balanced involvement. Full custody grants one parent exclusive rights to make major decisions and primary physical custody, often limiting the other parent's involvement to visitation. Understanding these legal definitions helps you navigate custody arrangements tailored to your child's best interests.
Benefits of Shared Custody Arrangements
Shared custody arrangements promote equal parental involvement, fostering stronger relationships between children and both parents. Children benefit from consistent emotional support and stability by maintaining regular contact with each parent. Shared custody also reduces parental conflict and encourages cooperative co-parenting, leading to a healthier family dynamic and improved child well-being.
Advantages of Full Custody
Full custody grants one parent the exclusive legal and physical responsibility for a child, providing stability and clear decision-making authority in education, healthcare, and daily activities. This arrangement can reduce conflict and confusion for the child, fostering a consistent routine and environment essential for their well-being. Your ability to make unilateral decisions ensures that the child's best interests are prioritized without the delay or dispute often associated with shared custody.
Factors Courts Consider in Custody Decisions
Courts evaluate several key factors when deciding between shared custody, full custody, or sole custody arrangements, including the child's best interests, the parents' ability to cooperate, and the stability of the home environment. They assess each parent's mental and physical health, history of caregiving, and the child's relationship with each parent to determine which custody form supports the child's emotional and developmental needs. Proximity of the parents' residences, the child's preferences when appropriate, and any history of abuse or neglect also heavily influence custody decisions.
Impact on Child’s Wellbeing
Shared custody promotes stability by allowing the child frequent and meaningful contact with both parents, which supports emotional balance and a stronger sense of security. Full custody can provide a consistent and predictable environment, beneficial for children needing structure or in cases of parental conflict, but may limit the child's relationship with the non-custodial parent. Research indicates that the quality of parenting and interparental cooperation significantly outweighs custody type in determining the child's overall wellbeing.
Parental Rights and Responsibilities
Shared custody grants both parents equal decision-making authority and time with the child, ensuring active involvement in education, healthcare, and daily activities. Full custody awards one parent primary physical and legal control, allowing them to make major decisions independently while the non-custodial parent may have limited visitation rights. Parental rights under shared custody emphasize cooperative co-parenting, while full custody centralizes responsibilities and rights in one parent, affecting child support and legal obligations.
Co-Parenting Challenges and Solutions
Shared custody involves both parents actively participating in decision-making and parenting time, which can lead to challenges like communication breakdowns and inconsistent parenting styles. Full custody grants one parent primary decision-making authority and physical care, often simplifying logistics but potentially limiting the non-custodial parent's involvement. You can improve co-parenting by establishing clear boundaries, maintaining open communication, and using mediation tools to resolve conflicts efficiently.
Choosing the Best Custody Arrangement
Choosing the best custody arrangement depends on the child's needs, parental involvement, and legal considerations. Shared custody allows both parents to participate actively in the child's life, promoting a balanced upbringing and minimizing emotional disruption. Full custody entrusts one parent with primary decision-making and residence, often chosen when one parent provides greater stability or the other is unfit or unavailable.
Infographic: Shared custody vs full custody
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com