Physical custody determines where the child resides daily, while full custody grants one parent both physical and legal decision-making rights. Explore this article to understand the key differences and implications of physical custody versus full custody.
Table of Comparison
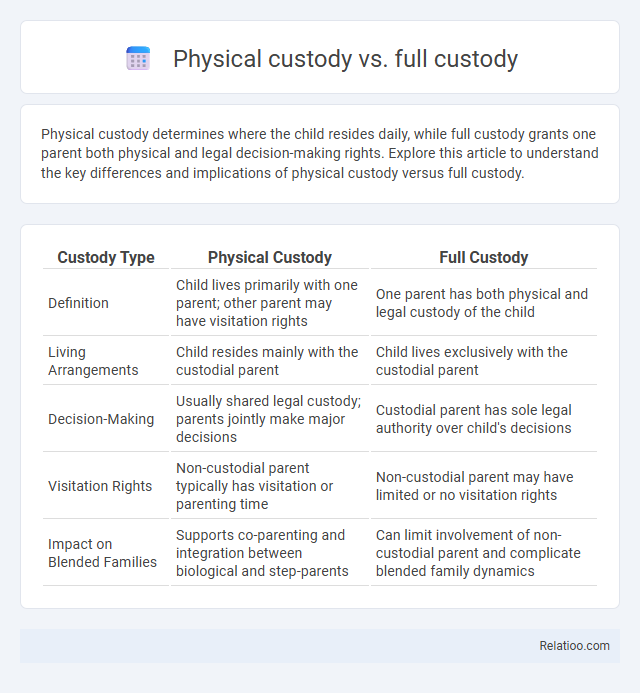
| Custody Type | Physical Custody | Full Custody |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Child lives primarily with one parent; other parent may have visitation rights | One parent has both physical and legal custody of the child |
| Living Arrangements | Child resides mainly with the custodial parent | Child lives exclusively with the custodial parent |
| Decision-Making | Usually shared legal custody; parents jointly make major decisions | Custodial parent has sole legal authority over child's decisions |
| Visitation Rights | Non-custodial parent typically has visitation or parenting time | Non-custodial parent may have limited or no visitation rights |
| Impact on Blended Families | Supports co-parenting and integration between biological and step-parents | Can limit involvement of non-custodial parent and complicate blended family dynamics |
Understanding Physical Custody
Physical custody refers to the time a child spends living with a parent, impacting day-to-day care and routines. Full custody means one parent has both physical custody and legal custody, granting them sole decision-making authority regarding the child's welfare. Understanding physical custody helps you recognize how parenting time arrangements affect your child's stability and emotional well-being.
Defining Full Custody
Full custody grants one parent both physical and legal custody, giving them the exclusive right to make major decisions regarding the child's education, healthcare, and welfare while the child primarily lives with them. Physical custody defines where the child resides, which can be shared or awarded to one parent, while legal custody involves decision-making authority. Understanding full custody as encompassing both physical and legal responsibilities is crucial for clarifying parental rights and obligations post-divorce or separation.
Key Differences Between Physical and Full Custody
Physical custody refers to the parent with whom the child primarily resides, emphasizing day-to-day care and living arrangements. Full custody encompasses both physical custody and legal custody, granting one parent exclusive rights to make major decisions regarding the child's education, health, and welfare. The key difference lies in legal authority: physical custody affects the child's residence, while full custody includes both the child's residence and comprehensive legal decision-making power.
Legal Rights in Physical vs Full Custody
Physical custody refers to the right of a parent to have their child live with them, whereas full custody includes both physical custody and legal custody, meaning the parent has authority to make major decisions about the child's welfare, education, and healthcare. Legal rights in physical custody are typically limited to day-to-day care, while full custody grants comprehensive decision-making power, allowing you to control all aspects of your child's life. Understanding these distinctions is crucial when navigating custody agreements to ensure your child's best interests are protected.
Factors Courts Consider in Custody Decisions
Courts evaluate physical custody, full custody, and shared custody primarily based on the child's best interests, considering factors such as the child's age, emotional needs, and the parents' ability to provide a stable environment. Physical custody focuses on where the child lives, while full custody grants one parent both physical and legal decision-making authority. Judges assess each parent's mental and physical health, history of caregiving, and willingness to support the child's relationship with the other parent when determining custody arrangements.
Impact on Child’s Well-Being
Physical custody determines where Your child lives and how daily routines are managed, directly influencing their stability and comfort. Full custody, whether physical or legal, grants one parent primary decision-making power, impacting the child's emotional security and consistency in care. Understanding these custody types helps prioritize Your child's well-being by ensuring a supportive, nurturing environment tailored to their needs.
Parental Responsibilities and Limitations
Physical custody determines where the child lives and who provides day-to-day care, while full custody grants one parent both physical and legal custody, giving them sole decision-making authority. Parental responsibilities in physical custody involve routine caregiving tasks and supporting the child's well-being during their custodial time. Full custody limits the non-custodial parent's involvement by restricting their decision-making rights and physical access to the child unless otherwise specified by court order.
Modifying Custody Arrangements
Modifying custody arrangements involves changing the legal or physical custody terms based on new circumstances affecting the child's best interests. Physical custody determines where the child lives, while full custody usually grants one parent exclusive physical and legal rights. Courts assess factors such as parental stability, child's needs, and any changes in family dynamics to approve custody modifications.
Common Myths About Custody Types
Common myths about custody types often confuse physical custody with full custody, but they refer to different aspects of child care and decision-making authority. Physical custody involves where the child lives, while full custody includes both physical and legal custody, giving one parent complete control over the child's residence and major decisions. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for your custody arrangements to ensure the child's best interests are prioritized without falling for misinformation.
Seeking Legal Guidance for Custody Issues
Understanding the distinctions between physical custody, full custody, and legal custody is crucial when navigating family law matters. Physical custody refers to the child living arrangements, while full custody typically grants one parent both physical and legal decision-making authority. You should seek professional legal guidance to ensure your rights and your child's best interests are effectively represented during custody disputes.
Infographic: Physical custody vs full custody
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com