Legal guardianship grants an individual the authority to make decisions for a child, including education and healthcare, without necessarily having physical custody. Custody determines where the child lives and who has the right to make day-to-day decisions. Learn more about the differences between legal guardianship and custody in this article.
Table of Comparison
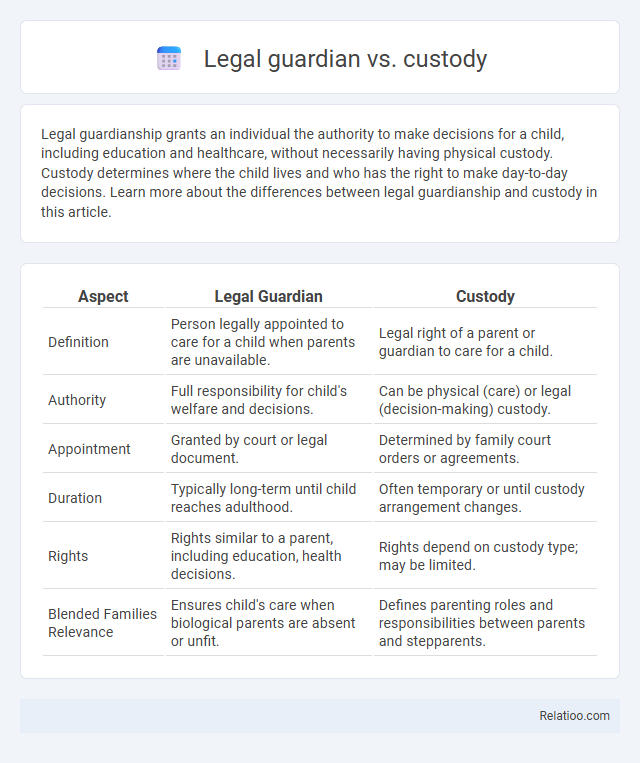
| Aspect | Legal Guardian | Custody |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Person legally appointed to care for a child when parents are unavailable. | Legal right of a parent or guardian to care for a child. |
| Authority | Full responsibility for child's welfare and decisions. | Can be physical (care) or legal (decision-making) custody. |
| Appointment | Granted by court or legal document. | Determined by family court orders or agreements. |
| Duration | Typically long-term until child reaches adulthood. | Often temporary or until custody arrangement changes. |
| Rights | Rights similar to a parent, including education, health decisions. | Rights depend on custody type; may be limited. |
| Blended Families Relevance | Ensures child's care when biological parents are absent or unfit. | Defines parenting roles and responsibilities between parents and stepparents. |
Understanding Legal Guardianship
Legal guardianship grants you the legal authority to make decisions for a minor or incapacitated person, differing from custody, which primarily concerns physical care and living arrangements. Custody is typically assigned through family court to biological parents or guardians, while legal guardianship may be appointed by the court when parents are unable or unfit to care for the child. Understanding legal guardianship is essential for recognizing your rights and responsibilities in providing care, making medical or educational decisions, and ensuring the well-being of the person under your guardianship.
Defining Child Custody
Child custody refers to the legal rights and responsibilities a parent or guardian has regarding the care and control of a child, including decisions about the child's living arrangements, education, and healthcare. Legal guardianship involves a court-appointed individual or entity granted comprehensive authority to make decisions for the child, often in cases where parents are unable or unfit to do so. Unlike general legal guardianship, custody typically emphasizes the physical and legal care provided by a parent, whereas guardianship extends to full responsibility for the child's welfare and legal matters.
Key Differences Between Guardianship and Custody
Guardianship grants a court-appointed individual the legal authority to make decisions for a minor or incapacitated person, including care, education, and healthcare, whereas custody typically involves parental rights and responsibilities in child-rearing following separation or divorce. Custody is divided into physical custody, denoting where the child lives, and legal custody, which involves decision-making rights; guardianship encompasses a broader scope of control that can extend beyond minors to adults unable to care for themselves. Key differences include guardianship often being permanent or long-term and requiring court approval for major decisions, while custody arrangements can be temporary and are primarily focused on the welfare of the child post-parental separation.
Legal Processes for Obtaining Guardianship
Obtaining legal guardianship involves a formal court process where a petitioner must demonstrate the individual's incapacity to care for themselves, providing evidence such as medical or psychological evaluations. Custody typically refers to parental rights over a child's care and decision-making, often determined in family court through considerations of the child's best interests. Legal guardianship establishes a substitute decision-maker when parents are unable or unavailable, requiring a thorough legal review and approval by the court to ensure the guardian meets all responsibilities under state laws.
Legal Procedures for Securing Custody
Securing custody involves complex legal procedures that determine who has the right to make decisions for a child's welfare, while a legal guardian is appointed to manage both personal and financial matters if parents are unable or unfit to do so. Custody typically pertains to the day-to-day care and control of the child, often settled through court hearings that evaluate the best interests of the child based on various factors like parental fitness and stability. You must navigate family court processes, provide evidence supporting your capability, and sometimes attend mediation to establish custody or legal guardianship.
Rights and Responsibilities of Legal Guardians
Legal guardians hold specific rights and responsibilities distinct from custody arrangements; they are authorized to make critical decisions regarding Your child's education, healthcare, and welfare when parents are unable to do so. Unlike custody, which primarily addresses living arrangements and visitation rights, legal guardianship establishes a comprehensive duty to provide for the physical and emotional well-being of the minor. Guardians must act in the child's best interests, ensuring compliance with legal requirements and fostering a stable environment for growth and development.
Parental Rights Under Custody Arrangements
Parental rights under custody arrangements determine the legal authority a parent has to make decisions for their child, while a legal guardian is appointed by the court to assume these responsibilities when parental rights are limited or terminated. Custody defines the specific rights to physical care and decision-making, often divided into legal custody (decision-making) and physical custody (residence). Legal guardianship extends beyond custody by granting broader authority in cases where parents cannot fulfill their roles, ensuring the child's welfare and stability under court oversight.
Factors Courts Consider in Guardianship vs. Custody
Courts evaluate factors such as the child's best interests, emotional bonds, stability, and the capability of the caregiver when deciding between legal guardianship and custody. Your child's safety, health, and well-being are paramount, with courts reviewing the ability of the guardian or parent to provide a stable environment and meet the child's needs. Legal guardianship typically involves a third party appointed to care for the child, while custody generally refers to parental rights and responsibilities.
How Changes in Family Circumstances Affect Guardianship and Custody
Changes in family circumstances, such as divorce, remarriage, or the incapacity of a parent, can significantly impact legal guardianship and custody arrangements, often requiring court modifications to reflect the child's best interests. Legal guardianship grants broader decision-making authority over the child's welfare, including education and healthcare, whereas custody pertains primarily to physical care and visitation rights. Courts assess shifts in family dynamics, parental ability, and the child's well-being to determine necessary adjustments in guardianship or custody orders.
Choosing the Best Legal Option for the Child’s Welfare
Choosing the best legal option for Your child's welfare often involves understanding the differences between legal guardianship and custody, where custody grants parental rights and responsibilities, and legal guardianship assigns care to a non-parent without terminating parental rights. Custody typically focuses on parental decision-making authority and physical care, while legal guardianship offers a longer-term solution when parents are unable to provide adequate care. Evaluating the child's best interests, stability, and the guardian's capabilities ensures the selected arrangement supports the child's safety, emotional well-being, and educational needs.
Infographic: Legal guardian vs custody
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com