Parental alienation involves one parent undermining a child's relationship with the other parent, while gatekeeping refers to one parent's control over the child's access to the other parent. Explore the distinctions and impacts of parental alienation versus gatekeeping in this article.
Table of Comparison
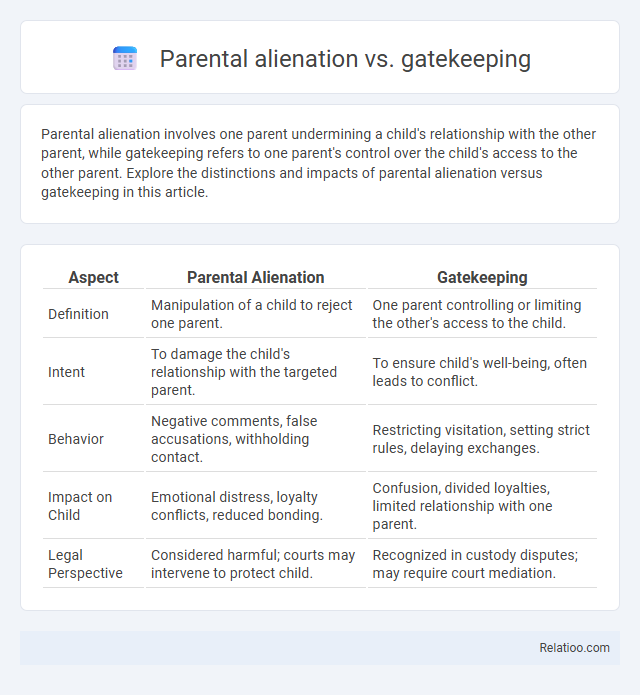
| Aspect | Parental Alienation | Gatekeeping |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Manipulation of a child to reject one parent. | One parent controlling or limiting the other's access to the child. |
| Intent | To damage the child's relationship with the targeted parent. | To ensure child's well-being, often leads to conflict. |
| Behavior | Negative comments, false accusations, withholding contact. | Restricting visitation, setting strict rules, delaying exchanges. |
| Impact on Child | Emotional distress, loyalty conflicts, reduced bonding. | Confusion, divided loyalties, limited relationship with one parent. |
| Legal Perspective | Considered harmful; courts may intervene to protect child. | Recognized in custody disputes; may require court mediation. |
Understanding Parental Alienation
Understanding parental alienation involves recognizing a psychological manipulation where one parent undermines the child's relationship with the other parent, often leading to emotional estrangement. It differs from gatekeeping, which is typically the protective or controlling behavior of one parent limiting the other's access based on concerns about the child's well-being. Parental alienation presents more severe long-term emotional damage and legal challenges as it intentionally damages the parent-child bond beyond mere supervision or safety measures seen in gatekeeping.
Defining Gatekeeping in Parenting
Gatekeeping in parenting refers to the control or regulation of a non-custodial parent's time and involvement with their child by the custodial parent, often limiting access and communication. Unlike parental alienation, which involves manipulating a child to reject the other parent, gatekeeping centers on managing or restricting parenting roles and responsibilities without necessarily inducing child hostility. Understanding gatekeeping is crucial for addressing conflicts in co-parenting arrangements and promoting balanced parental involvement.
Key Differences Between Parental Alienation and Gatekeeping
Parental alienation involves one parent deliberately undermining the child's relationship with the other parent, often through manipulation and false accusations, whereas gatekeeping refers to a parent's restrictive behavior that limits the other parent's access or involvement without necessarily damaging the child's feelings. Key differences include the intent and impact: alienation aims to sever the parent-child bond, while gatekeeping centers on controlling participation in parenting decisions. Understanding these distinctions helps Your family navigate custody and visitation conflicts more effectively.
Common Signs of Parental Alienation
Common signs of parental alienation include a child's unjustified fear, disrespect, or hostility toward one parent, often influenced by the other parent's negative comments or restrictions on contact. Gatekeeping involves one parent controlling or limiting the other's access and involvement, affecting visitation and decision-making rights without necessarily fostering animosity. Recognizing these behaviors can help you address and mitigate the emotional impact on the child and improve co-parenting dynamics.
Types of Parental Gatekeeping Behaviors
Parental gatekeeping behaviors manifest in various forms such as communication interference, where one parent limits or controls the other's access to the child, and direct obstruction, involving active prevention of visitation or interaction. These behaviors differ from parental alienation, which aims to estrange the child from the other parent by fostering negative beliefs, whereas gatekeeping primarily regulates parental involvement and participation. Understanding the types of gatekeeping, including psychological control, restricting involvement in decision-making, and undermining authority, is crucial for addressing family dynamics and promoting balanced co-parenting.
Psychological Impact on Children
Parental alienation, gatekeeping, and parental alienation all profoundly affect the psychological well-being of children, often leading to confusion, anxiety, and damaged self-esteem. Your child's emotional development may suffer as these behaviors create loyalty conflicts, hinder healthy parent-child relationships, and foster feelings of abandonment or rejection. Understanding these distinctions is vital for fostering a supportive environment that prioritizes your child's mental health and stability.
Legal Perspectives on Parental Alienation and Gatekeeping
Legal perspectives on parental alienation and gatekeeping emphasize the protection of the child's best interests and the fair allocation of parental responsibilities. Parental alienation is often viewed as a form of emotional abuse involving one parent intentionally undermining the child's relationship with the other parent, which can lead to court interventions including custody modifications. Gatekeeping, while less overtly hostile, involves one parent's control or limitation of the other parent's access and influence, and courts evaluate such behavior based on whether it restricts the child's meaningful contact and harms the parent-child relationship.
Addressing Parental Gatekeeping in Co-Parenting
Parental gatekeeping involves one parent limiting the other's access to their child, often under the guise of concern for the child's wellbeing, which differs from parental alienation where one parent manipulates the child to reject the other parent. Addressing parental gatekeeping in co-parenting requires establishing clear communication, leveraging legal frameworks like custody agreements, and promoting mutual respect to ensure both parents have equitable involvement in the child's life. Effective interventions include family therapy and mediation aimed at reducing control dynamics and fostering cooperative parenting strategies for the child's best interests.
Strategies to Prevent Parental Alienation
Effective strategies to prevent parental alienation include fostering open communication and encouraging positive co-parenting relationships, which help maintain strong bonds between children and both parents. Implementing clear, consistent visitation schedules and involving neutral third parties, such as family therapists or mediators, can reduce conflicts and prevent manipulation. Your proactive efforts in promoting respect and cooperation between parents significantly contribute to shielding children from the harmful effects of parental alienation.
Resources for Families Facing Alienation or Gatekeeping
Families facing parental alienation or gatekeeping can access specialized counseling services and support groups to navigate emotional challenges effectively. Legal resources, including family law attorneys experienced in alienation and gatekeeping cases, help protect your parental rights and foster healthy family dynamics. Online platforms and organizations such as the Parental Alienation Awareness Organization provide educational materials and advocacy tools tailored to these complex family issues.
Infographic: Parental alienation vs Gatekeeping
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com