Joint custody allows both parents to share legal and physical custody of a child, promoting cooperative parenting and consistent involvement. Full custody grants one parent sole legal and physical responsibility, often due to concerns about the other parent's ability to care for the child. Discover detailed insights and legal implications of joint custody versus full custody in this article.
Table of Comparison
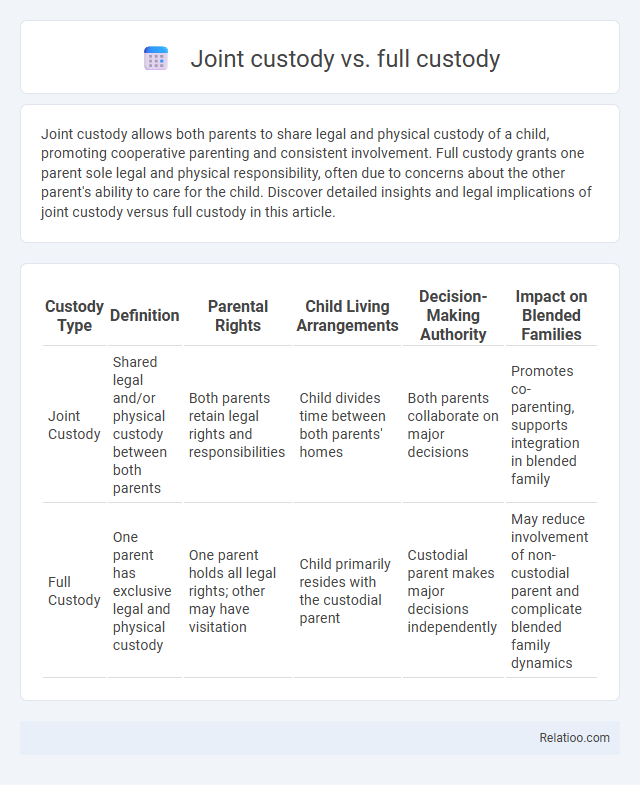
| Custody Type | Definition | Parental Rights | Child Living Arrangements | Decision-Making Authority | Impact on Blended Families |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Joint Custody | Shared legal and/or physical custody between both parents | Both parents retain legal rights and responsibilities | Child divides time between both parents' homes | Both parents collaborate on major decisions | Promotes co-parenting, supports integration in blended family |
| Full Custody | One parent has exclusive legal and physical custody | One parent holds all legal rights; other may have visitation | Child primarily resides with the custodial parent | Custodial parent makes major decisions independently | May reduce involvement of non-custodial parent and complicate blended family dynamics |
Understanding Joint Custody
Joint custody allows both parents to share legal and physical responsibility for their child, promoting active involvement in decision-making and day-to-day care. Full custody grants one parent exclusive rights to make decisions and physical care, often resulting in limited visitation for the non-custodial parent. Understanding joint custody helps you recognize its benefits in fostering cooperation and supporting the child's emotional well-being by maintaining strong relationships with both parents.
Defining Full Custody
Full custody grants one parent exclusive legal and physical decision-making authority over the child's upbringing, education, and healthcare, ensuring complete control without requiring input from the other parent. Joint custody involves shared responsibilities and decision-making, allowing both parents to participate actively in major life choices for the child. Understanding the distinctions helps You determine which custody arrangement best supports the child's well-being and your parental rights.
Key Legal Differences
Joint custody involves both parents sharing legal and physical responsibility for the child, ensuring Your child benefits from consistent involvement by both. Full custody awards one parent the exclusive right to make key decisions and physical care, typically granted when the other parent is deemed unfit or unavailable. Legal differences hinge on decision-making power, parenting time, and the ability to modify arrangements based on the child's best interests and parental fitness assessments.
Parental Rights and Responsibilities
Joint custody grants both parents shared decision-making authority and responsibilities regarding the child's upbringing, including education, health, and welfare. Full custody awards one parent exclusive parental rights and responsibilities, giving them sole control over major decisions and daily care, while the other parent may have visitation rights. Parental rights under joint custody promote cooperation, whereas full custody centralizes legal and physical custody to one parent, impacting child support and visitation arrangements.
Impact on Child Well-being
Joint custody promotes consistent involvement of both parents, fostering emotional stability and stronger parent-child relationships, which enhances the child's overall well-being. Full custody, while providing a single primary caregiver, can offer stability but may limit the child's access to the other parent's presence and support. Research indicates that children generally benefit from frequent and meaningful contact with both parents, highlighting the importance of custody arrangements that support cooperative co-parenting.
Factors Courts Consider
Courts consider several factors when determining joint custody versus full custody, including the child's best interests, stability, and the ability of each parent to provide a safe environment. Judicial decisions weigh the mental and physical health of the parents, the child's relationship with each parent, and each parent's willingness to facilitate a positive relationship with the other parent. Courts also evaluate the child's age, preferences, and any history of abuse or neglect before awarding full custody or agreeing to joint custody arrangements.
Pros and Cons of Joint Custody
Joint custody allows both parents to share decision-making and physical time with their child, promoting balanced involvement and emotional stability. Your child benefits from consistent access to both parents, reducing feelings of abandonment and fostering cooperation. However, joint custody requires effective communication and cooperation between parents, and conflicts may negatively impact the child's well-being if not managed properly.
Pros and Cons of Full Custody
Full custody grants one parent exclusive legal and physical responsibility for a child, offering stability and clear decision-making authority, which can be beneficial in cases involving abuse or neglect. However, this arrangement may limit the non-custodial parent's involvement, potentially impacting the child's relationship with both parents. The sole custodial parent often faces increased emotional and financial responsibilities, which can pose significant challenges.
Navigating Custody Arrangements
Navigating custody arrangements requires understanding the distinctions between joint custody, full custody, and sole custody, each affecting parental rights and responsibilities differently. Joint custody allows both parents to share legal and physical decision-making, promoting ongoing involvement in the child's life, while full custody grants one parent exclusive rights and physical custody, often limiting the other parent's access. Choosing the optimal custody arrangement involves assessing the child's best interests, parental cooperation, and legal frameworks to ensure stability and support in co-parenting dynamics.
Making the Best Decision for Your Child
Choosing between joint custody and full custody requires careful consideration of your child's emotional and developmental needs. Joint custody allows both parents to actively participate in decision-making and daily care, fostering stability and balanced upbringing. Full custody grants one parent primary responsibility, which may be necessary in cases of safety concerns or parental unavailability, emphasizing the importance of prioritizing your child's best interests.
Infographic: Joint custody vs full custody
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com