Maternal caregivers typically provide nurturing and emotional support, fostering secure attachment, while paternal caregivers often emphasize play and exploration, promoting independence in children. Discover the unique roles and impacts of maternal and paternal caregiving in this article.
Table of Comparison
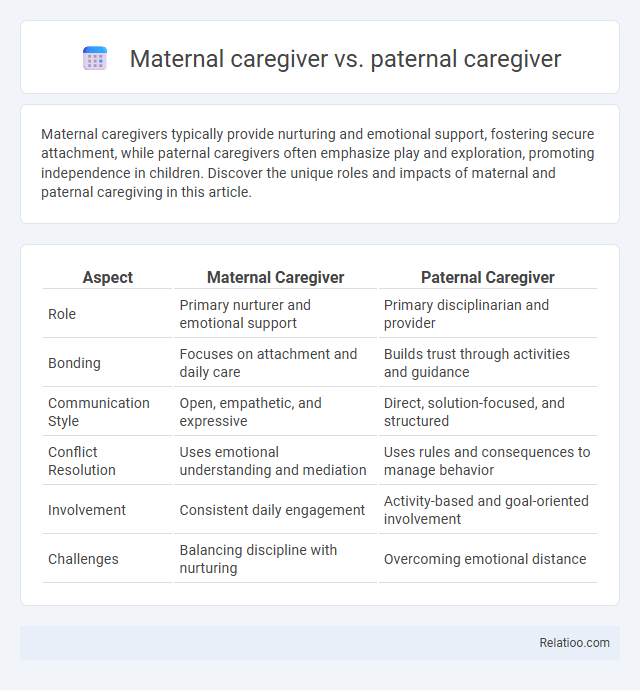
| Aspect | Maternal Caregiver | Paternal Caregiver |
|---|---|---|
| Role | Primary nurturer and emotional support | Primary disciplinarian and provider |
| Bonding | Focuses on attachment and daily care | Builds trust through activities and guidance |
| Communication Style | Open, empathetic, and expressive | Direct, solution-focused, and structured |
| Conflict Resolution | Uses emotional understanding and mediation | Uses rules and consequences to manage behavior |
| Involvement | Consistent daily engagement | Activity-based and goal-oriented involvement |
| Challenges | Balancing discipline with nurturing | Overcoming emotional distance |
Understanding Maternal and Paternal Caregiving Roles
Understanding maternal and paternal caregiving roles involves recognizing that maternal caregivers often provide nurturing, emotional support, and physical care, while paternal caregivers typically emphasize play, discipline, and protection. The primary caregiver, regardless of gender, is the person who takes the main responsibility for daily childcare tasks, influencing your child's emotional and cognitive development. Research shows that balanced involvement from both maternal and paternal caregivers enhances a child's social skills and overall well-being.
Historical Perspectives on Parental Caregiving
Historical perspectives on parental caregiving reveal that maternal caregivers traditionally assumed the primary role in nurturing and daily child-rearing, rooted deeply in cultural and biological expectations. Paternal caregivers were often associated with providing financial support and external protection, with less emphasis on direct caregiving tasks compared to maternal roles. Understanding these evolving roles helps clarify how your family's caregiving dynamics might be shaped by long-standing societal norms and shifts toward more shared responsibilities.
Biological Influences in Maternal and Paternal Care
Maternal caregivers typically exhibit stronger biological influences such as higher oxytocin levels that enhance bonding and nurturing behaviors, while paternal caregivers often show increased testosterone fluctuations influencing engagement and protective instincts. Your child's development benefits from understanding these distinct hormonal and genetic factors shaping maternal and paternal caregiving roles. Primary caregivers, regardless of gender, combine these biological elements with environmental and emotional support to effectively meet developmental needs.
Emotional Bonding: Mothers vs Fathers
Mothers often establish emotional bonding through nurturing behaviors and consistent physical closeness, which fosters a secure attachment in infants. Fathers typically engage in playful, stimulating interactions that promote emotional development and resilience. Your child's emotional well-being benefits from the complementary bonding styles of both maternal and paternal caregivers, each contributing uniquely to healthy attachment formation.
Division of Caregiving Responsibilities
Division of caregiving responsibilities often varies between maternal, paternal, and primary caregivers, reflecting societal roles and individual family dynamics. Maternal caregivers typically engage more in daily physical care and emotional support, while paternal caregivers increasingly contribute to nurturing and play activities. Primary caregivers assume the central role in managing children's schedules, health needs, and educational support, regardless of gender, emphasizing the critical function of consistent and responsive caregiving in child development.
Impact of Cultural Norms on Parenting Styles
Cultural norms significantly shape the roles and expectations of maternal, paternal, and primary caregivers, influencing parenting styles across societies. Maternal caregivers often embody nurturing roles aligned with traditional caregiving norms, while paternal caregivers may emphasize discipline and provision, reflecting culturally driven gender roles. Understanding these cultural influences helps you navigate and adapt parenting approaches to foster balanced child development within diverse family structures.
Child Development Outcomes: Maternal vs Paternal Influence
Maternal caregivers often provide more nurturing and emotional support, which is linked to enhanced language development and secure attachment in children. Paternal caregivers tend to encourage exploration and risk-taking, fostering cognitive skills and social competence. Primary caregivers, regardless of gender, significantly shape child development outcomes through consistent responsiveness, with the quality of interaction playing a critical role in emotional and behavioral regulation.
Challenges Faced by Maternal and Paternal Caregivers
Maternal caregivers often face challenges related to balancing emotional nurturing with societal expectations of motherhood, while paternal caregivers may struggle with limited social support and stereotypical views of masculinity affecting their caregiving roles. Both maternal and paternal caregivers encounter stress from managing work-life balance, but paternal caregivers frequently deal with reduced access to parental leave and flexible work arrangements. Primary caregivers, regardless of gender, face heightened responsibilities including emotional, physical, and financial strain that impact overall well-being and family dynamics.
Evolving Perceptions of Fatherhood and Motherhood
Evolving perceptions of fatherhood emphasize increased emotional involvement and nurturing roles beyond traditional breadwinning, while motherhood continues to be closely associated with caregiving and emotional support. Research shows that paternal caregivers are increasingly recognized as primary caregivers, challenging historical gender norms and promoting shared parenting responsibilities. Studies on primary caregivers highlight the importance of both maternal and paternal engagement in child development, with shifting societal attitudes fostering greater equality and flexibility in caregiving roles.
Supporting Balanced Parental Involvement
Supporting balanced parental involvement requires recognizing the unique roles of maternal caregivers, paternal caregivers, and primary caregivers in a child's development. Maternal caregivers often provide nurturing and emotional support, while paternal caregivers contribute through play and guidance, both crucial for holistic growth. Your collaborative efforts as primary caregivers ensure a well-rounded environment that fosters emotional security and cognitive development.
Infographic: Maternal caregiver vs Paternal caregiver
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com