Family therapy enhances communication and resolves conflicts within family systems, while individual therapy concentrates on personal emotional growth and self-awareness. Discover which approach best suits your needs by exploring this article.
Table of Comparison
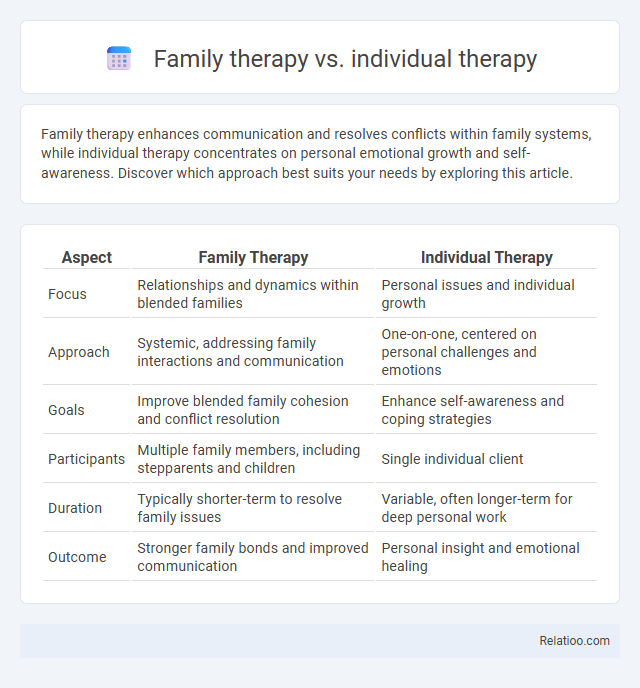
| Aspect | Family Therapy | Individual Therapy |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Relationships and dynamics within blended families | Personal issues and individual growth |
| Approach | Systemic, addressing family interactions and communication | One-on-one, centered on personal challenges and emotions |
| Goals | Improve blended family cohesion and conflict resolution | Enhance self-awareness and coping strategies |
| Participants | Multiple family members, including stepparents and children | Single individual client |
| Duration | Typically shorter-term to resolve family issues | Variable, often longer-term for deep personal work |
| Outcome | Stronger family bonds and improved communication | Personal insight and emotional healing |
Understanding Family Therapy
Family therapy addresses the dynamics and communication patterns within the family unit to resolve conflicts and improve relationships, making it a crucial approach for treating Adjustment Disorder when family interactions contribute to stress. Unlike individual therapy, which centers on personal emotions and cognitive processes, family therapy involves multiple members to foster mutual support and collective problem-solving. Research shows that engaging families in therapy enhances coping strategies and promotes a healthier environment for individuals struggling with Adjustment Disorder.
Overview of Individual Therapy
Individual therapy provides a personalized approach to treating adjustment disorder by focusing on the patient's unique emotional and psychological challenges. This therapy modality utilizes techniques such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) to help individuals develop coping strategies and address maladaptive thought patterns. Compared to family therapy, which involves multiple family members and addresses systemic issues, individual therapy offers targeted support for personal growth and symptom management in adjustment disorder.
Key Goals of Family Therapy
Family therapy primarily aims to improve communication, resolve conflicts, and strengthen relationships within the family unit, fostering a supportive environment for all members. In contrast to individual therapy, which focuses on personal growth and coping strategies, family therapy addresses collective dynamics that may contribute to adjustment disorders. Your participation in family therapy helps create systemic changes that promote emotional healing and adaptive functioning for the entire family.
Core Objectives of Individual Therapy
Individual therapy primarily aims to help you develop personalized coping strategies and address specific emotional or psychological challenges related to adjustment disorder. Unlike family therapy, which focuses on improving relational dynamics, individual therapy centers on enhancing self-awareness, emotional regulation, and resilience in the face of life changes. The core objectives include identifying maladaptive thought patterns, promoting behavioral change, and supporting mental health recovery through tailored therapeutic techniques.
Common Techniques in Family Therapy
Family therapy often employs techniques such as structural mapping, communication training, and role-playing to address relational dynamics that contribute to adjustment disorder symptoms. Unlike individual therapy, which centers on your personal cognitive and emotional processing, family therapy strives to enhance collective problem-solving and emotional support within the family unit. These common techniques promote healthier interactions and foster resilience, making them particularly effective for managing adjustment disorders rooted in family stressors.
Approaches Used in Individual Therapy
Individual therapy for adjustment disorder employs cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) to help patients identify and modify negative thought patterns and maladaptive behaviors linked to their stressors. Techniques such as problem-solving skills training and emotion regulation strategies are central to fostering resilience and coping mechanisms. Personalized goal-setting within individual therapy ensures tailored interventions that address the unique psychosocial challenges of adjustment disorder.
Benefits of Family Therapy
Family therapy enhances communication and resolves conflicts by involving all family members, creating a supportive environment for individuals with adjustment disorder. It strengthens family bonds and promotes collective problem-solving, which often leads to more sustainable improvements than individual therapy alone. This approach helps address systemic issues contributing to emotional stress, providing a holistic path to recovery.
Advantages of Individual Therapy
Individual therapy offers tailored treatment that directly addresses personal emotional challenges related to adjustment disorder, enabling focused exploration of thoughts and feelings. It provides a confidential environment fostering self-awareness, which can accelerate coping skills development and emotional regulation. Unlike family therapy, individual therapy allows for personalized pacing and targeted interventions designed to meet the unique needs of the individual.
Choosing Between Family and Individual Therapy
Choosing between family therapy and individual therapy for treating adjustment disorder depends on Your specific circumstances and support system. Family therapy addresses relational dynamics and improves communication within the household, which can be crucial if the adjustment issues stem from family-related stressors. Individual therapy, on the other hand, focuses on Your personal coping strategies, emotional processing, and self-awareness, providing tailored support for managing symptoms of adjustment disorder effectively.
Factors Influencing the Right Therapy Choice
Choosing between family therapy, individual therapy, or treatment for adjustment disorder depends on key factors such as the nature of the psychological issue, family dynamics, and individual coping mechanisms. Family therapy is optimal when interpersonal relationships and communication patterns contribute to psychological distress, while individual therapy targets personal emotional challenges and cognitive restructuring. Adjustment disorder treatment emphasizes coping strategies tailored to specific life stressors, with the choice guided by symptom severity, support systems, and the context of the stress-inducing event.
Infographic: Family therapy vs Individual therapy
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com