Full siblings share both parents and typically have higher genetic similarity compared to half-siblings, who share only one parent. Discover more about the differences in genetics, emotional bonds, and family dynamics in this article.
Table of Comparison
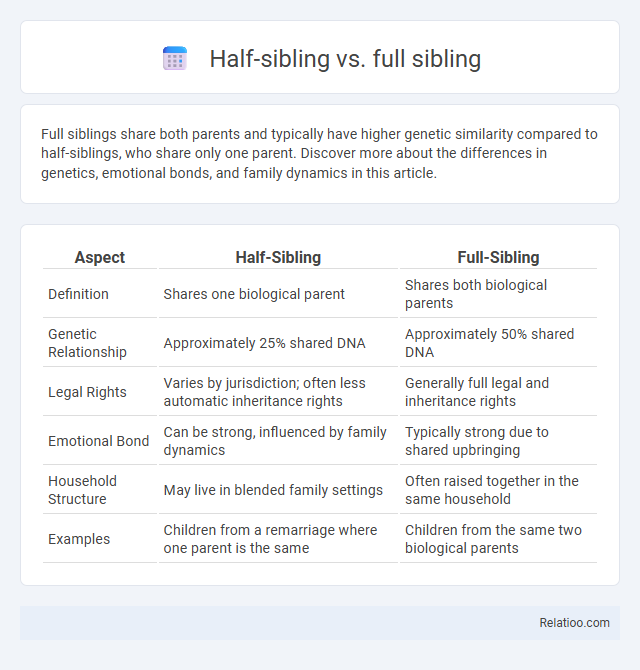
| Aspect | Half-Sibling | Full-Sibling |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Shares one biological parent | Shares both biological parents |
| Genetic Relationship | Approximately 25% shared DNA | Approximately 50% shared DNA |
| Legal Rights | Varies by jurisdiction; often less automatic inheritance rights | Generally full legal and inheritance rights |
| Emotional Bond | Can be strong, influenced by family dynamics | Typically strong due to shared upbringing |
| Household Structure | May live in blended family settings | Often raised together in the same household |
| Examples | Children from a remarriage where one parent is the same | Children from the same two biological parents |
Understanding Sibling Relationships
Full siblings share both biological parents, resulting in the highest genetic relatedness with approximately 50% shared DNA. Half-siblings share only one parent, typically sharing about 25% of their DNA, which affects inheritance patterns and familial bonds. Understanding these differences helps you navigate family dynamics and clarify legal or emotional aspects related to sibling relationships.
Defining Half-Siblings and Full Siblings
Full siblings share both biological parents, resulting in an average of 50% shared DNA, while half-siblings share only one biological parent, leading to about 25% shared DNA. Your genetic relationship with full siblings is stronger due to the complete parental overlap, impacting inherited traits and family bonding. Understanding the distinction between half-siblings and full siblings is crucial for legal, medical, and genealogical contexts.
Genetic Differences: Half-Sibling vs Full Sibling
Half-siblings share approximately 25% of their DNA because they have only one common parent, while full siblings share about 50%, inheriting genes from both parents. Understanding these genetic differences helps you determine inheritance patterns, disease risks, and biological relationships more accurately. This distinction is crucial for genetic testing, family medical history assessments, and ancestry analysis.
Legal and Inheritance Implications
Full siblings share both parents and typically have equal legal rights and inheritance claims under most jurisdictions, while half-siblings share only one parent and may have varying rights depending on specific state or country laws. Your legal rights to inherit property or assets can differ significantly if you are a half-sibling, as some inheritance laws favor full siblings or require explicit inclusion in wills. Understanding the distinctions between full sibling and half-sibling relationships is crucial for estate planning and resolving inheritance disputes effectively.
Emotional Dynamics in Sibling Bonds
Emotional dynamics in sibling bonds vary significantly between half-siblings and full siblings due to genetic relatedness and shared upbringing. Full siblings often experience deeper emotional connections and stronger loyalty stemming from shared family environments and greater genetic overlap, typically around 50%. Half-siblings, sharing approximately 25% of their genes, may navigate more complex feelings of identity and belonging, influenced by differences in parental relationships and family structures.
Social Perceptions and Family Structures
Social perceptions of half-siblings often differ from those of full siblings, with many viewing full siblings as having stronger emotional bonds due to shared genetic and familial experiences. Family structures including half-siblings are increasingly common in blended families, leading to evolving social norms that recognize diverse sibling relationships. Your understanding of these dynamics can enhance empathy and support within modern family environments.
Impact on Identity and Family Belonging
Full siblings share both biological parents, resulting in a stronger genetic connection that often reinforces a clear sense of identity and family belonging. Half-siblings share only one biological parent, which can create complexities in identity formation and feelings of inclusion within the family unit. Understanding the nuances of these relationships is crucial for addressing emotional bonds and fostering a cohesive family environment.
Sibling Rivalry and Relationship Challenges
Full siblings share both parents, often resulting in stronger genetic bonds but can still face intense sibling rivalry due to comparisons and competition for parental attention. Half-siblings share only one parent, which may lead to more complex relationship dynamics and challenges in forming close bonds due to differences in upbringing and family structure. You can navigate sibling rivalry effectively by fostering open communication and understanding each sibling's unique experiences and feelings.
Navigating Blended Families
Navigating blended families involves understanding the distinctions between half-siblings and full siblings, where full siblings share both biological parents while half-siblings share only one. You may encounter unique emotional dynamics and legal considerations related to inheritance, custody, and family roles based on these relationships. Recognizing these differences helps foster healthy communication, build strong bonds, and create a supportive environment in blended family settings.
Building Strong Connections Between Half-Siblings and Full Siblings
Building strong connections between half-siblings and full siblings involves understanding the unique dynamics of each relationship. Full siblings often share both biological parents, leading to deeper genetic bonds, while half-siblings share only one parent, requiring intentional efforts to foster emotional closeness. Your commitment to open communication, shared experiences, and mutual respect plays a crucial role in bridging differences and strengthening sibling relationships.
Infographic: Half-sibling vs Full sibling
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com