Parental attachment shapes early emotional security, influencing how individuals form and maintain romantic attachments later in life. Explore the dynamic interplay between parental and romantic attachment patterns to understand their impact on adult relationships in this article.
Table of Comparison
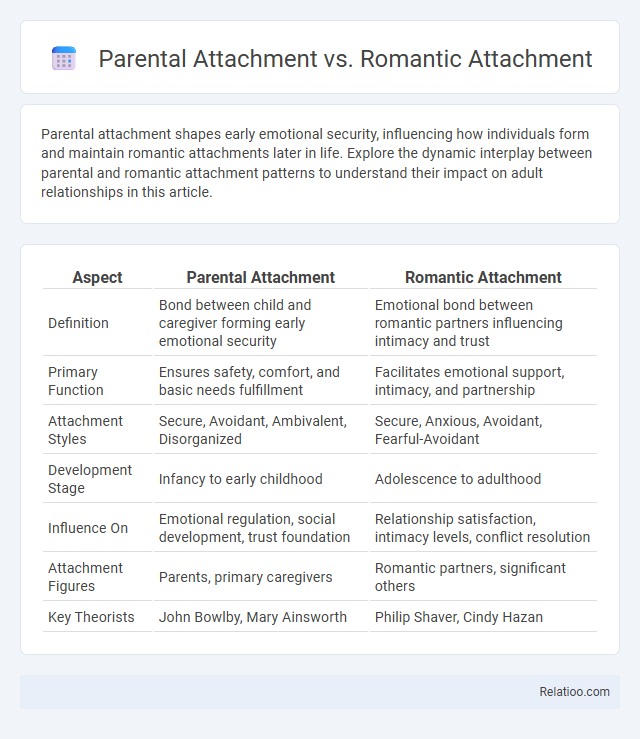
| Aspect | Parental Attachment | Romantic Attachment |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Bond between child and caregiver forming early emotional security | Emotional bond between romantic partners influencing intimacy and trust |
| Primary Function | Ensures safety, comfort, and basic needs fulfillment | Facilitates emotional support, intimacy, and partnership |
| Attachment Styles | Secure, Avoidant, Ambivalent, Disorganized | Secure, Anxious, Avoidant, Fearful-Avoidant |
| Development Stage | Infancy to early childhood | Adolescence to adulthood |
| Influence On | Emotional regulation, social development, trust foundation | Relationship satisfaction, intimacy levels, conflict resolution |
| Attachment Figures | Parents, primary caregivers | Romantic partners, significant others |
| Key Theorists | John Bowlby, Mary Ainsworth | Philip Shaver, Cindy Hazan |
Introduction to Attachment Theories
Attachment theories explore the emotional bonds formed between individuals, emphasizing the distinct roles of parental attachment, romantic attachment, and attachment figures in psychological development. Parental attachment primarily shapes early childhood security and influences later relational patterns, while romantic attachment adapts these early experiences into intimate partnerships. Understanding your attachment figure's role provides insight into how foundational bonds affect your emotional well-being and interpersonal dynamics across the lifespan.
Defining Parental Attachment
Parental attachment refers to the emotional bond formed between a child and their primary caregiver, typically a parent, which provides a foundation for security and trust. This early attachment is crucial in shaping your ability to form healthy relationships and influences patterns seen in romantic attachments later in life. Unlike romantic attachment, which involves mutual intimacy and passion between partners, parental attachment centers on caregiving, protection, and consistency from an attachment figure.
Characteristics of Romantic Attachment
Romantic attachment is characterized by intense emotional bonds, exclusivity, and a desire for physical and psychological closeness with a partner, often influenced by early parental attachment patterns. Unlike parental attachment, which centers on caregiving and security, romantic attachment involves mutual dependency, passion, and intimacy, shaping relationship satisfaction and stability. Attachment figures in romantic contexts function as sources of comfort and support, playing a crucial role in managing stress and fostering emotional regulation within adult relationships.
Key Differences Between Parental and Romantic Attachment
Parental attachment primarily involves a child's bond with caregivers, characterized by security and dependency essential for developmental stability, while romantic attachment forms between adult partners, emphasizing intimacy, passion, and emotional reciprocity. Unlike parental attachment, which provides a foundation for safety and protection, romantic attachment focuses on mutual support, companionship, and shared life experiences. Attachment figures in parental roles foster long-term emotional regulation, whereas romantic attachment figures contribute to identity formation and adult relational satisfaction.
Psychological Foundations of Attachment Styles
Parental attachment forms the foundational bond in early childhood, significantly shaping your psychological development and subsequent attachment styles. Romantic attachment emerges later, influenced by these early parental bonds, and determines patterns of intimacy, trust, and emotional regulation in adult relationships. Attachment figures, including parents and romantic partners, provide critical emotional security that underpins the internal working models guiding your expectations and behaviors in close relationships.
Impact of Parental Attachment on Adult Relationships
Parental attachment forms the foundation for adult romantic relationships by shaping an individual's attachment style, influencing emotional regulation, trust, and intimacy. Secure parental attachment often leads to healthier adult relationships characterized by effective communication and emotional support, while insecure parental attachment can result in challenges such as anxiety, avoidance, or fear of abandonment in romantic partnerships. Attachment figures beyond parents, such as caregivers and early relational experiences, also contribute but parental bonds remain the primary influence on adult attachment patterns.
How Romantic Attachment Shapes Emotional Well-being
Romantic attachment significantly influences emotional well-being by providing a secure base for emotional expression and intimacy, similar to the role of parental attachment but with greater emphasis on adult relational dynamics. Unlike parental attachment, which primarily shapes foundational security and trust, romantic attachment directly impacts self-esteem, stress regulation, and emotional resilience in adulthood. Attachment figures in romantic contexts act as key sources of support, fostering positive coping mechanisms and enhancing overall psychological health.
The Role of Attachment in Relationship Satisfaction
Attachment security with primary caregivers during early life significantly influences romantic attachment patterns and relationship satisfaction in adulthood. Secure parental attachment fosters emotional regulation and trust, leading to healthier romantic bonds and greater relationship fulfillment. Attachment figures beyond parents, including close friends and mentors, also contribute to the development of attachment models that impact interpersonal relationship satisfaction.
Navigating Attachment Issues in Therapy
Navigating attachment issues in therapy requires distinguishing between parental attachment, romantic attachment, and attachment figures to address unique emotional patterns effectively. Parental attachment forms the early blueprint for security and trust, while romantic attachment influences adult relationship dynamics and intimacy challenges. Identifying how attachment figures shape clients' relational expectations enables therapists to tailor interventions that promote healing and secure attachment development.
Conclusion: Integrating Attachment Insights for Healthy Connections
Understanding parental attachment provides a foundation for recognizing patterns in romantic attachment and identifying your primary attachment figures. Secure bonds with caregivers typically lead to healthier romantic relationships characterized by trust and emotional intimacy. Integrating insights from these attachment types empowers you to foster stronger, more resilient connections across all relationship domains.
Infographic: Parental Attachment vs Romantic Attachment
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com